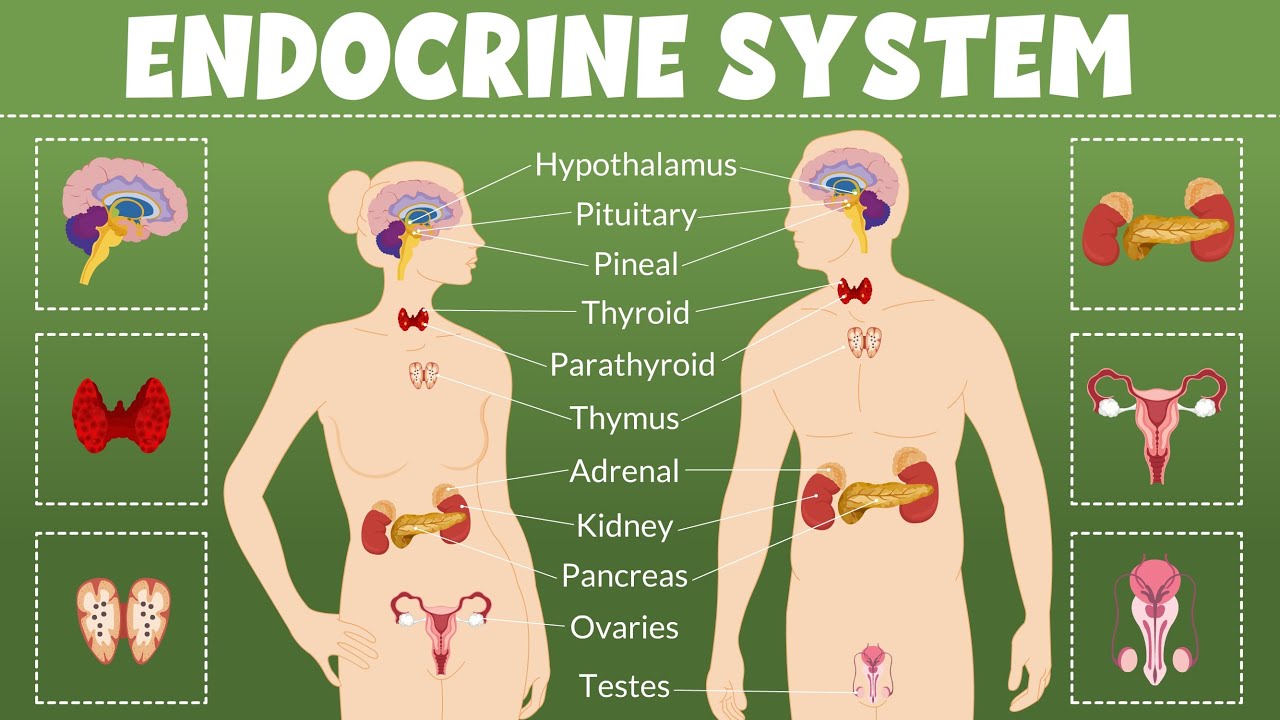
El SISTEMA ENDOCRINO explicado: cómo funciona, partes y hormonas🧠🧍
Summary
TLDRThe endocrine system is a complex network of glands responsible for producing hormones that regulate vital bodily functions, including metabolism, growth, reproduction, and mood. Key glands like the pituitary, thyroid, adrenal, and gonads play crucial roles in maintaining homeostasis. Hormones can be classified into categories such as steroids, amines, polypeptides, and glycoproteins, each with distinct functions and interactions. Disorders such as hyperthyroidism, Cushing's disease, and polycystic ovary syndrome illustrate the impact of endocrine imbalances on health. Understanding this system is essential for recognizing its influence on overall well-being.
Takeaways
- 🧠 The endocrine system produces hormones that regulate essential bodily functions, including metabolism, growth, and mood.
- 🏥 It consists of various glands that maintain homeostasis by secreting hormones directly into the bloodstream.
- 🔗 The hypothalamus connects the nervous and endocrine systems, controlling the pituitary gland's hormone release.
- ⚖️ The pituitary gland, known as the 'master gland,' regulates other endocrine glands and produces critical hormones like growth hormone and oxytocin.
- 🌙 The pineal gland produces melatonin, which regulates sleep-wake cycles and influences other hormonal functions.
- 🔄 The thyroid gland controls metabolism and regulates calcium levels through hormones like thyroxine and calcitonin.
- 💉 The pancreas plays a dual role in digestion and hormone production, specifically insulin and glucagon for blood sugar regulation.
- 👩⚕️ In women, the ovaries produce hormones that regulate the menstrual cycle and secondary sexual characteristics, while the testes in men produce testosterone.
- 🦴 Adipose tissue and other organs like the heart, kidneys, and liver also contribute to hormone production, influencing appetite and blood cell production.
- ⚠️ Disorders of the endocrine system can lead to various health issues, including growth abnormalities, adrenal insufficiency, and thyroid imbalances.
Q & A
What is the primary function of the endocrine system?
-The primary function of the endocrine system is to produce hormones that regulate various vital processes in the body, including metabolism, growth, development, reproduction, mood, and sleep.
How do hormones function in the body?
-Hormones act as chemical messengers released into the bloodstream by endocrine glands, traveling to target cells or organs that contain specific hormone receptors, allowing them to regulate various functions.
What distinguishes endocrine glands from exocrine glands?
-Endocrine glands secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream, whereas exocrine glands release substances outside the body or into the digestive tract.
What role does the hypothalamus play in the endocrine system?
-The hypothalamus connects the endocrine and nervous systems, controlling the pituitary gland by secreting releasing and inhibiting hormones that dictate hormone production by the pituitary.
What are some key hormones produced by the pituitary gland?
-Key hormones produced by the pituitary gland include growth hormone, oxytocin, antidiuretic hormone, prolactin, and luteinizing hormone.
What hormones are associated with the thyroid gland, and what do they regulate?
-The thyroid gland produces hormones such as thyroxine, triiodothyronine, and calcitonin, which regulate metabolism, growth, and calcium levels in the blood.
What is the function of insulin produced by the pancreas?
-Insulin helps regulate blood sugar levels by facilitating the uptake of glucose into cells, thus lowering blood sugar levels and promoting energy storage.
How does the adrenal gland contribute to stress response?
-The adrenal glands produce hormones like adrenaline and glucocorticoids, which play significant roles in regulating metabolism and the body's response to stress.
What are some disorders associated with the endocrine system?
-Disorders associated with the endocrine system include acromegaly, adrenal insufficiency, Cushing's disease, hyperthyroidism, hypothyroidism, and polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS).
How can hormones interact with one another?
-Hormones can interact in several ways: synergistically, where their combined effect is greater; antagonistically, where they oppose each other; or permissively, where one hormone enhances the action of another.
Outlines

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنMindmap

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنKeywords

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنHighlights

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنTranscripts

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنتصفح المزيد من مقاطع الفيديو ذات الصلة
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)