How Your Muscles Work
Summary
TLDRThis video delves into the fascinating structure and contraction mechanism of skeletal muscles. It explains how these voluntary muscles, controlled by the nervous system, consist of fascicles made up of muscle fibers. Each fiber contains myofibrils organized into sarcomeres, the basic contractile units composed of myosin and actin filaments. The contraction process involves excitation through action potentials, calcium release, binding of myosin to actin, and finally relaxation as calcium returns to the sarcoplasmic reticulum. This overview highlights the intricate steps that allow for muscle movement and function, making it an engaging topic for anyone interested in human physiology.
Takeaways
- 😀 Skeletal muscles are voluntary and controlled consciously by the nervous system.
- 😀 Muscles are made up of fascicles, which are bundles of muscle fibers surrounded by connective tissue, blood vessels, and nerves.
- 😀 Each muscle fiber contains myofibrils organized into contractile units called sarcomeres, which show the characteristic striations of skeletal muscle.
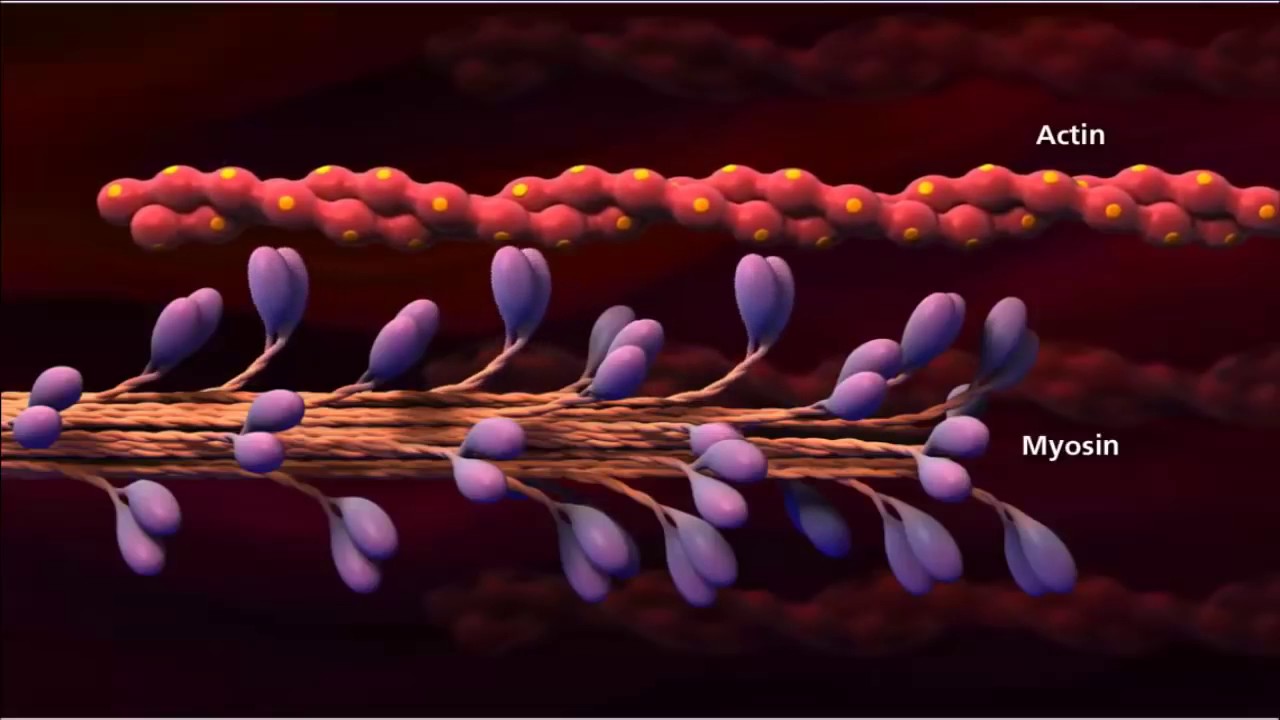
- 😀 Sarcomeres consist of thick myofilaments (myosin) and thin myofilaments (actin).
- 😀 Myosin heads form cross bridges with actin filaments, facilitated by ATP, which is an energy transport molecule.
- 😀 At rest, actin molecules are bound to tropomyosin and troponin, which inhibit contraction.
- 😀 Muscle contraction begins at the sarcolemma with T-tubules, which connect to the sarcoplasmic reticulum that stores calcium.
- 😀 The contraction process involves four main steps: excitation, coupling, contraction, and relaxation.
- 😀 During excitation, a motor nerve fires an impulse that depolarizes the sarcolemma and generates an action potential.
- 😀 Relaxation occurs when calcium ions return to the sarcoplasmic reticulum, breaking myosin-actin bonds and allowing the muscle to lengthen.
Q & A
What are skeletal muscles and how are they controlled?
-Skeletal muscles are voluntary muscles controlled consciously by the nervous system.
What are fascicles in skeletal muscles?
-Fascicles are bundles of muscle fibers surrounded by connective tissue, blood vessels, and nerves.
What constitutes a motor unit in skeletal muscles?
-A motor unit consists of one or more skeletal muscle fibers supplied by motor nerve axons.
What are myofibrils and how are they organized?
-Myofibrils are thread-like structures within a muscle fiber organized into contractile units known as sarcomeres.
What are the roles of myosin and actin in muscle contraction?
-Myosin forms thick filaments, while actin forms thin filaments; together, they enable muscle contraction through cross-bridge formation.
How does the process of excitation initiate muscle contraction?
-Excitation begins when a motor nerve fires an impulse across the neuromuscular junction, depolarizing the sarcolemma and generating an action potential.
What happens during the coupling phase of muscle contraction?
-During coupling, the action potential depolarizes the T-tubules, leading to the release of calcium ions from the sarcoplasmic reticulum into the sarcoplasm.
What is the role of tropomyosin and troponin in muscle contraction?
-Tropomyosin and troponin are contractile proteins that inhibit contraction at rest; calcium binds to troponin, causing tropomyosin to shift and expose myosin binding sites on actin.
What occurs during the contraction phase of muscle contraction?
-In the contraction phase, the myosin heads bind to actin, releasing energy that causes the myosin heads to rotate, pulling the thin filaments inward and shortening the sarcomere.
What is the process of muscle relaxation?
-Relaxation occurs when calcium ions return to the sarcoplasmic reticulum, breaking the myosin-actin bonds, causing the cross-bridges to disengage and the sarcomere to lengthen.
Outlines

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنMindmap

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنKeywords

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنHighlights

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنTranscripts

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنتصفح المزيد من مقاطع الفيديو ذات الصلة
3. Muscle contraction detail Concept Cell Biology

Mekanisme Kerja Otot | Sistem Gerak Manusia

Cellule musculaire : organisation - SVT - SANTÉ Term spé #7 - Mathrix

Sistem gerak pada manusia part 2 - Biologi kelas 11 SMA

[#1] Fisiologia do Músculo Esquelético: CONTRAÇÃO MUSCULAR | MK Fisiologia
Skeletal Muscle Tissue: Contraction, Sarcomere, Myofibril Anatomy Myology
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
