Food's BROWNING REACTION
Summary
TLDRThe video explains the two types of browning reactions that occur in food: enzymatic and non-enzymatic. Enzymatic browning happens when foods like apples are exposed to oxygen, which can be prevented by soaking in salt water. Non-enzymatic browning, such as the Maillard reaction and caramelization, occurs when sugars and proteins are heated, creating brown colors and pleasant aromas in foods like steak and pancakes. The video also demonstrates how added ingredients like sugar and eggs enhance browning in pancakes, and how caramelization forms the crispy top of crème brûlée.
Takeaways
- 🍳 Food browning typically occurs due to heat, affecting items like steak and pancakes.
- 🍏 Enzymatic browning happens when enzymes in foods, like apples, react with oxygen after the cell walls are broken.
- 🧂 To prevent enzymatic browning in apples, you can soak them in salt water, syrup, or poach them to stop enzyme activity.
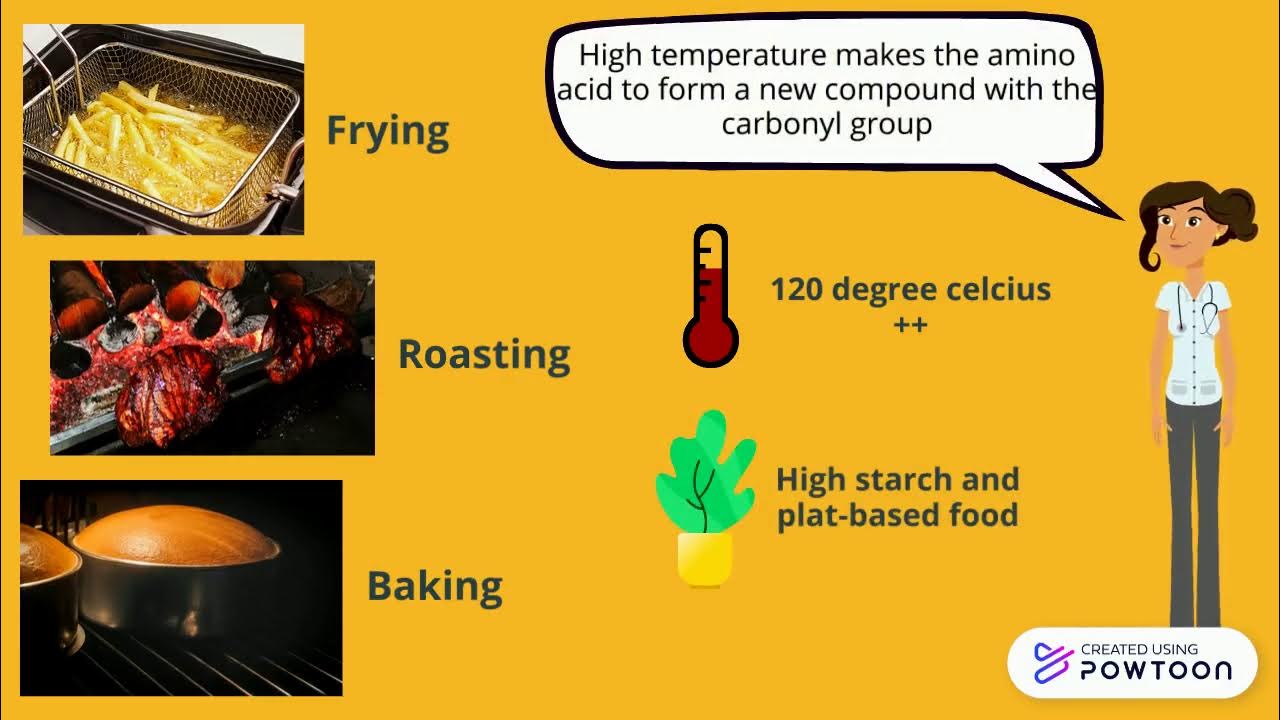
- 🥩 Non-enzymatic browning occurs mainly through two processes: the Maillard reaction and caramelization.
- 🥞 The Maillard reaction occurs when proteins and sugars in food combine under heat, leading to browning and flavor development.
- 🍫 Pancakes demonstrate the Maillard reaction differently based on the ingredients used, like added sugar or eggs, which increase browning.
- 🍮 Caramelization is another browning process where sugar is heated, decomposed, and forms new brown compounds, as seen in creme brûlée.
- 🔥 Caramelization produces new structures called oligomers, which give caramel its crispy texture and brown color.
- 👃 The Maillard reaction generates pleasant smells like caramel, roasted, and meaty aromas, enhancing the sensory experience of food.
- 🍬 Caramelization and the Maillard reaction both contribute to flavor and texture, but caramelization is primarily sugar-based, while the Maillard reaction involves both sugars and proteins.
Q & A
What are the two main types of food browning reactions mentioned in the script?
-The two main types of food browning reactions are enzymatic browning and non-enzymatic browning.
What causes enzymatic browning in foods like apples?
-Enzymatic browning occurs when the cell walls of foods like apples are broken, allowing polyphenol oxidase (PPO) enzymes and oxygen to react with monophenols in the apple cells, generating a brown substance on the surface.
How can enzymatic browning be prevented in apples?
-Enzymatic browning can be prevented by soaking the apple in salt water or syrup, which coats the surface and prevents oxygen from interacting with the enzymes. Alternatively, poaching can kill the enzymes, stopping the reaction.
What is the Maillard reaction, and how does it relate to non-enzymatic browning?
-The Maillard reaction is a type of non-enzymatic browning that occurs when sugars react with proteins under heat, producing browning and adding flavors and aromas to food like steaks and pancakes.
Why does a pancake with added sugar brown more than one without it?
-A pancake with added sugar browns more because the extra sugar dissolves and reacts more easily with the ingredients during cooking, making the Maillard reaction more intense.
What role do proteins and eggs play in the browning of pancakes?
-Proteins and eggs contribute to browning by providing amino groups that react with sugars in the Maillard reaction, intensifying the brown color and flavors.
What is caramelization, and how does it differ from the Maillard reaction?
-Caramelization is the process in which sugar breaks down when heated to around 160°C, forming a stronger structure and brown color. It differs from the Maillard reaction because it doesn't involve proteins, only sugars.
What compounds are produced during the Maillard reaction that give food its distinct smells and flavors?
-The Maillard reaction produces compounds like furans (which give a caramel-like smell), pyrazines (which add roasted aromas), and pyrroles (which provide a nutty smell).
Why does crème brûlée have a crispy brown top, and how is it formed?
-Crème brûlée has a crispy brown top due to caramelization. Sugar is sprinkled on the surface of the custard and then heated, causing the sugar to break down and reform into a crackable brown layer.
What is oligomerization in the context of caramelization?
-Oligomerization is the process in which individual sugar molecules stick together to form glucose polymers during caramelization, contributing to the creation of the brown color and caramel texture.
Outlines

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنMindmap

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنKeywords

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنHighlights

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنTranscripts

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآن5.0 / 5 (0 votes)