Paramecium Cell Structure and Function || Protist Cell Structure @biologyexams4u
Summary
TLDRParamecium, a single-celled ciliated protozoan, thrives in freshwater and brackish environments. It features a slipper-shaped body covered with thousands of cilia for locomotion and feeding on bacteria. The cell has a protective pellicle and houses two types of nuclei: a large metabolic macronucleus and a small reproductive micronucleus. Paramecia digest food through a series of specialized structures, including the systostome, oral groove, and gullet, forming food vacuoles. They also maintain osmoregulation via contractile vacuoles, expelling waste through the cytoproct.
Takeaways
- 🐢 Paramecium is a single-celled ciliated protozoan with a slipper-shaped body.
- 🌊 It lives in freshwater and brackish environments.
- 🍽️ As a heterotroph, Paramecium feeds on other organisms for energy.
- 🏃♂️ Cilia on its surface aid in locomotion and capturing food particles.
- 🛡️ The pellicle is a flexible outer covering that provides protection and support.
- 🧬 Paramecium has two types of nuclei: a large polyploid macronucleus and a small diploid micronucleus.
- 🔄 Macronucleus controls metabolic activities, while micronucleus is involved in reproduction and genetic diversity.
- 🍽️ Systostome is the 'mouth' through which food enters the Paramecium.
- 🔄 Food vacuoles and contractile vacuoles are two types of vacuoles in Paramecium, serving digestion and osmoregulation respectively.
- 🚽 Cytoproct is the waste expulsion opening in the pellicle.
Q & A
What is a paramecium?
-A paramecium is a unicellular ciliated protozoan characterized by its slipper-shaped body and thousands of cilia covering its surface.
What type of organism is a paramecium?
-Paramecium is a heterotroph, meaning it must feed on other organisms for energy.
Where can paramecium be found?
-Paramecium can be found in freshwater and brackish water environments.
What is the function of cilia on a paramecium?
-Cilia cover the cell surface for locomotion, beating rhythmically to propel the cell through water and bring food particles into the mouth.
What is the pellicle and what is its role?
-The pellicle is a flexible outer covering made up of protein that provides protection and support for the cell.
What are the two types of nuclei found in paramecium and their functions?
-Paramecium has a macronucleus that controls metabolic activities and a micronucleus that contains germline genetic material for reproduction.
What is the role of the micronucleus during conjugation?
-The micronucleus is responsible for the exchange of genetic material during conjugation, a sexual process that helps maintain genetic diversity in the population.
How does food enter a paramecium?
-Food enters a paramecium through a mouth-like opening called the systostome.
What is the function of the oral groove in a paramecium?
-The oral groove serves to guide food particles, primarily bacteria, into the gullet.
What happens to food particles within the gullet of a paramecium?
-Within the gullet, food particles are transformed into food vacuoles.
What are the two types of vacuoles in paramecium and their functions?
-Paramecia have food vacuoles for digestion and absorption of nutrients, and contractile vacuoles for osmoregulation and excretion.
How does a paramecium expel waste products?
-Waste products are expelled through the cytoproct, an opening in the pellicle.
Outlines

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنMindmap

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنKeywords

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنHighlights

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنTranscripts

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنتصفح المزيد من مقاطع الفيديو ذات الصلة

Klasifikasi Protozoa - Protista Mirip Hewan | Dunia Biologi

Berkenalan dengan Hutan Mangrove, Pelindung Kawasan Pesisir
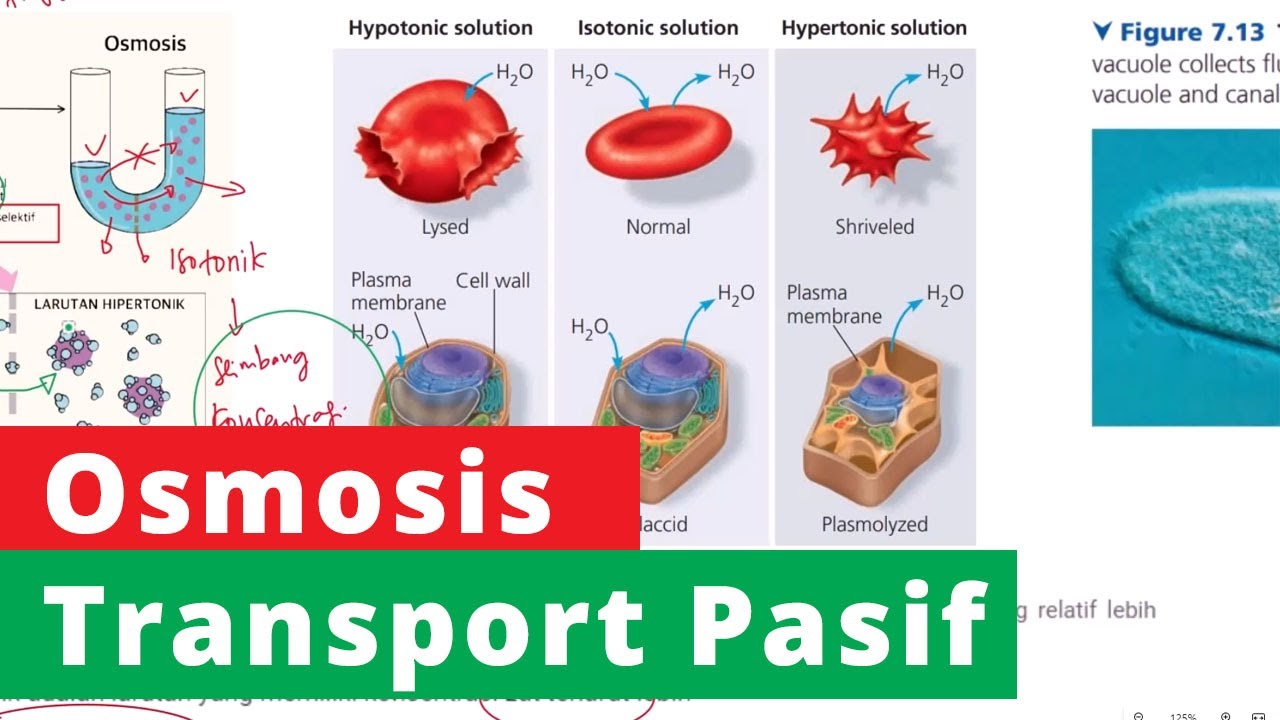
Proses Terjadinya Osmosis - Transport Pasif

Class 11th – Protozoans – Ciliata | Biological Classification | Tutorials Point

OSMORREGULAÇÃO DOS PROTOZOÁRIOS

Unicellular and Multicellular Cells
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
