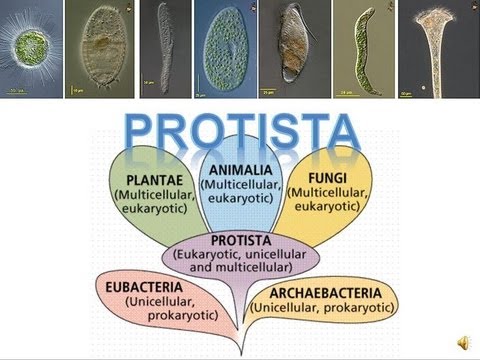
REINO PROTISTA
Summary
TLDRThis video explores the Protista kingdom, which includes protozoa and algae. Protista are eukaryotic organisms that can be autotrophic or heterotrophic. Protozoa are single-celled and can be free-living or parasitic, divided into four groups: amoeboids, ciliates, flagellates, and sporozoans. Algae, often mistaken for plants, are photosynthetic eukaryotes with diverse storage substances. They are crucial for oxygen production and form the base of aquatic food chains. While beneficial for food and climate, some protists can cause diseases like malaria and Chagas.
Takeaways
- 🌿 **Protista Kingdom**: The script introduces the Protista kingdom, a classification for microscopic organisms that do not fit neatly into the animal or plant kingdoms.
- 🔬 **Classification Evolution**: It discusses how the advancement of microscopic studies led to the creation of the Protista kingdom, separating it from traditional animal and plant classifications.
- 🐠 **Main Organisms**: Protista includes protozoa and algae, which can be either eukaryotic or organisms with cells defined by a nuclear envelope.
- 🌱 **Autotrophic and Heterotrophic**: Protists can be autotrophic, producing their own food, or heterotrophic, feeding on other organisms.
- 💧 **Habitats**: They can be found in freshwater, marine environments, and moist soil.
- 🔄 **Protozoa Groups**: Protozoa are divided into four groups: amoeboids, ciliates, flagellates, and sporozoans, each with distinct movement and feeding mechanisms.
- 🌊 **Algae Characteristics**: Algae are often confused with plants but are classified as protists, characterized by photosynthetic pigments and specific energy storage substances.
- 🍃 **Diversity of Algae**: Algae come in various types including euglenoids, dinoflagellates, diatoms, brown algae, and red algae, each with unique features and habitats.
- 🌍 **Environmental Impact**: Protists play a crucial role in photosynthesis, releasing oxygen into the atmosphere and forming the base of aquatic food chains.
- 🥗 **Human Use**: Algae are used in food preparation, providing protein, vitamins, and minerals, while some protists can cause diseases like Chagas, malaria, and amoebiasis.
- 🛡️ **Preventive Measures**: The script emphasizes the importance of basic sanitation and food safety to reduce the risk of protist-borne diseases.
Q & A
What are the main organisms of the Protista kingdom?
-The main organisms of the Protista kingdom are protozoa and algae.
What are the characteristics of organisms in the Protista kingdom?
-Protists are eukaryotic organisms with cells delimited by a nuclear envelope. They can be autotrophic, producing their own food, or heterotrophic, feeding on other organisms. They can be unicellular or multicellular.
What are the two main groups that protists can be divided into?
-Protists can be divided into two main groups: protozoa, which are eukaryotic unicellular heterotrophs, and algae, which are eukaryotic unicellular and multicellular autotrophs through photosynthesis.
What is the meaning of the term 'protozoan'?
-The term 'protozoan' means 'first animal' and was used when they were classified as animals.
How are protozoa classified into groups?
-Protozoa are classified into four groups: amoeboids, ciliates, flagellates, and sporozoans.
What are the characteristics of amoeboids?
-Amoeboides are characterized by their movement and feeding through temporary projections of the cell wall called pseudopodes.
What is the role of cilia in ciliate protozoa?
-In ciliate protozoa, cilia help in movement and food capture. Food enters through the cytostome and leaves through the cytoproct.
What is the mode of movement in flagellated protozoa?
-Flagellated protozoa move by the beating of flagella.
What is the primary difference between algae and plants?
-Although algae can be mistaken for plants, they are actually protists. They are eukaryotic with a nucleus, organelles, and a plasma membrane.
What are the main types of algae mentioned in the script?
-The main types of algae mentioned are euglenoids, dinoflagellates, diatoms, brown algae (phaeophyceae), and red algae (rhodophyta).
What is the importance of protists to the planet?
-Protists are important and fundamental for maintaining life on Earth. They are major oxygen producers through photosynthesis, essential for cloud formation and climate maintenance, and form the base of aquatic food chains.
How can protists affect human health?
-Some protists can cause serious diseases in humans, such as Chagas disease, malaria, and amoebiasis.
Outlines

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنMindmap

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنKeywords

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنHighlights

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنTranscripts

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنتصفح المزيد من مقاطع الفيديو ذات الصلة

KINGDOM PROTISTA (PART 1} : BIOLOGI KELAS 10 SMA

Protozoários - Brasil Escola

BIOLOGI IPA Kelas 10 | Kingdom Protista (Protista Mirip Hewan) | GIA Academy

Kingdom Monera Protista Fungi - Klasifikasi Makhluk Hidup - sistem klasifikasi 5 kingdom
Kingdom Protista

PROTOZOÁRIOS: características e classificação | Biologia para o Enem | Cláudia de Souza Aguiar
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
