1 1 1 Definition and essential characteristics of Cloud Computing
Summary
TLDRCloud computing offers on-demand computing resources via the internet on a pay-for-use basis. NIST defines it with five key characteristics: on-demand self-service, broad network access, resource pooling, rapid elasticity, and measured service. It includes three deployment models—Public, Private, and Hybrid—and three service models: IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS. This technology revolutionizes how we consume compute services, enhancing cost-efficiency and organizational agility.
Takeaways
- 🌐 **Cloud Computing Defined**: Cloud computing is defined by NIST as a model for on-demand network access to a shared pool of configurable computing resources.
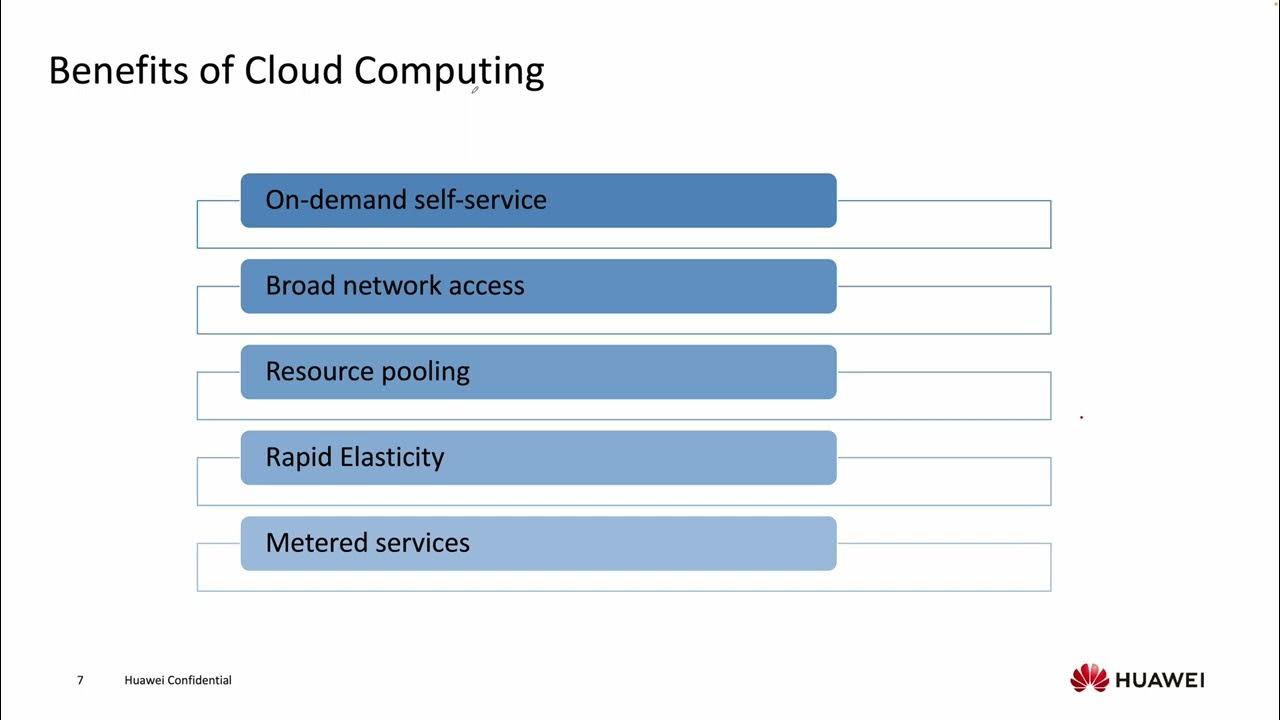
- 💡 **Five Essential Characteristics**: Cloud computing includes on-demand self-service, broad network access, resource pooling, rapid elasticity, and measured service.
- 🔑 **On-Demand Self-Service**: Users can access cloud resources without human interaction with each service provider.
- 📡 **Broad Network Access**: Resources are accessible via various devices like mobiles, tablets, laptops, and workstations.
- 💼 **Resource Pooling**: Providers pool resources to serve multiple consumers, offering cost-efficiency.
- 🔄 **Rapid Elasticity**: Resources can be provisioned or released elastically based on demand.
- 📏 **Measured Service**: Users pay for what they use, with resource usage monitored and reported transparently.
- 🌟 **Technology as a Service**: Cloud computing allows for the use of technology services on-demand, scaling up or down as needed.
- 🌍 **Deployment Models**: There are three cloud deployment models: Public, Private, and Hybrid.
- 🌉 **Public Cloud**: Services are provided over the internet on shared hardware owned by the cloud provider.
- 🏢 **Private Cloud**: Infrastructure is provisioned exclusively for one organization, either on-premises or by a service provider.
- 🔧 **Hybrid Cloud**: A seamless mix of public and private clouds.
- 🛠️ **Service Models**: Cloud services are categorized into IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS based on the layers of the computing stack.
- 💻 **IaaS**: Provides access to physical computing resources without the need to manage them.
- 🛤️ **PaaS**: Offers a platform including hardware and software tools needed for developing and deploying applications.
- 📚 **SaaS**: Software is centrally hosted, licensed on a subscription basis, and delivered as 'on-demand software'.
Q & A
What is cloud computing?
-Cloud computing is a model that enables on-demand network access to a shared pool of configurable computing resources over the internet on a pay-for-use basis.
How does the US National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) define cloud computing?
-NIST defines cloud computing as a model for enabling convenient, on-demand network access to a shared pool of configurable computing resources that can be rapidly provisioned and released with minimal management effort or service provider interaction.
What are the five essential characteristics of cloud computing?
-The five essential characteristics of cloud computing are on-demand self-service, broad network access, resource pooling, rapid elasticity, and measured service.
What does 'on-demand self-service' in cloud computing mean?
-On-demand self-service means accessing cloud resources such as processing power, storage, and network using a simple interface without requiring human interaction with each service provider.
How is 'broad network access' characterized in cloud computing?
-Broad network access refers to the ability to access cloud computing resources via the network through standard mechanisms and platforms such as mobile phones, tablets, laptops, and workstations.
What is the significance of 'resource pooling' in cloud computing?
-Resource pooling gives cloud providers economies of scale, which they pass on to their customers, making cloud cost-efficient. It involves using a multi-tenant model where computing resources are pooled to serve multiple consumers dynamically.
What does 'rapid elasticity' imply in the context of cloud computing?
-Rapid elasticity implies the ability to access more resources when needed and scale back when not, as resources are elastically provisioned and released.
What is 'measured service' in cloud computing?
-Measured service means that users only pay for what they use or reserve, with resource usage monitored, measured, and reported transparently based on utilization.
How does cloud computing change the way compute services are consumed?
-Cloud computing changes the way compute services are consumed by making them more cost-efficient and enabling organizations to be more agile in responding to changes in their markets.
What are the three types of cloud deployment models?
-The three types of cloud deployment models are Public, Private, and Hybrid.
What is the difference between Public and Private cloud deployment models?
-Public cloud involves leveraging cloud services over the open internet on hardware shared by other companies, while Private cloud means the infrastructure is provisioned for exclusive use by a single organization, either on-premises or managed by a service provider.
Can you explain the three service models in cloud computing?
-The three service models are Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS). IaaS provides access to physical computing resources, PaaS provides access to the platform including development tools, and SaaS is a software licensing and delivery model where applications are centrally hosted and licensed on a subscription basis.
Outlines

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنMindmap

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنKeywords

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنHighlights

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنTranscripts

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآن5.0 / 5 (0 votes)