Unit 1 Topic 1 Packet
Summary
TLDRThis lesson provides an introduction to the structure of water and hydrogen bonding, starting with a chemistry review of matter, elements, compounds, and the periodic table. It covers atomic structure, the Bohr and Lewis dot models, and the types of chemical bonds, including covalent, ionic, and hydrogen bonds. The video emphasizes water's unique properties such as cohesion, adhesion, high specific heat, evaporative cooling, and its role as a versatile solvent. Additionally, the lesson highlights how water's structure supports life, especially in plants and marine environments.
Takeaways
- 💧 Matter includes anything that takes up space and has mass, such as liquids, solids, and gases.
- 🧪 An element cannot be broken down into another substance by chemical reactions, while a compound consists of two or more elements combined in a fixed ratio.
- ⚛️ Essential elements like carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, phosphorus, and nitrogen (CHOPIN) make up 96% of living matter, while trace elements are required in small amounts.
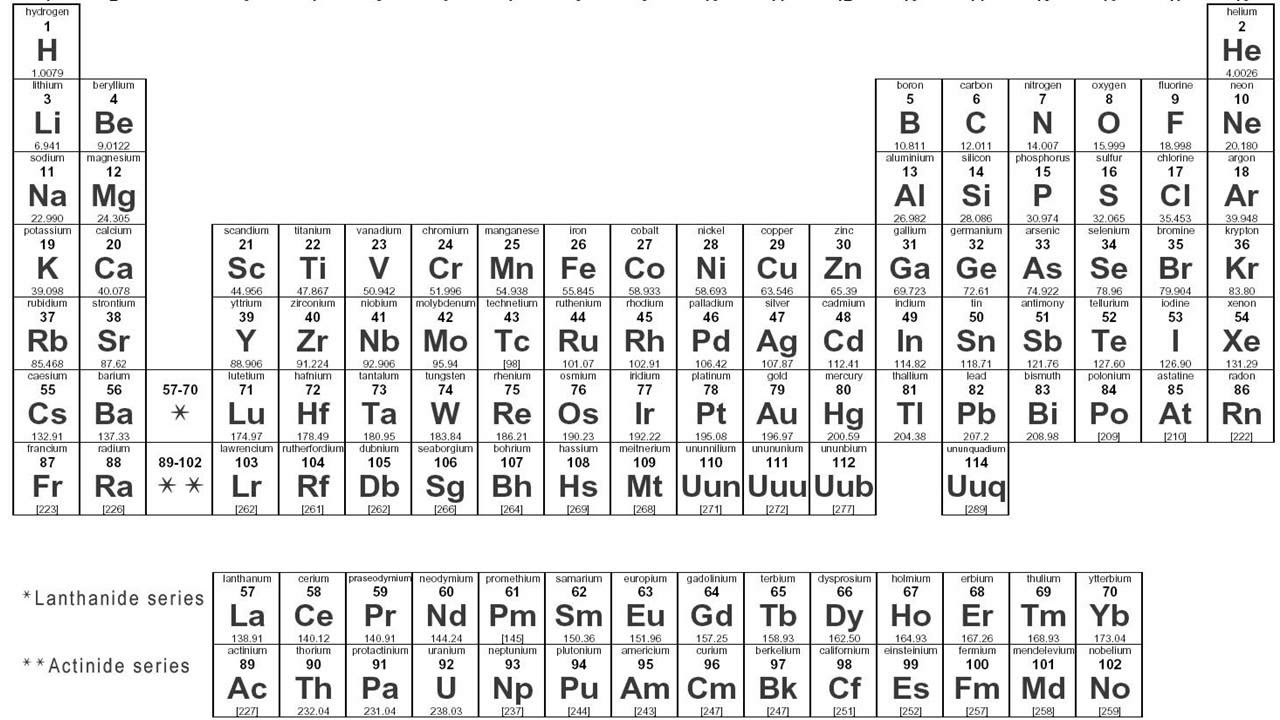
- 🔢 The periodic table is organized by groups (vertical columns) that have the same number of valence electrons and periods (horizontal rows) with the same number of electron shells.
- 🔬 The Bohr model shows electrons orbiting the nucleus in energy levels, while the Lewis dot model focuses only on valence electrons.
- 🔗 Chemical bonds form based on the octet rule, where elements gain, lose, or share electrons to complete their valence shells, leading to stability.
- 🧲 Covalent bonds involve the sharing of electrons between atoms, which can be polar (unequal sharing) or non-polar (equal sharing).
- ⚡ Ionic bonds are formed by the transfer of electrons between oppositely charged ions, typically between metals and non-metals.
- 🌊 Hydrogen bonds are intermolecular attractions, not actual bonds, occurring between polar covalent molecules like water.
- 🌡️ Water has unique properties due to hydrogen bonding, including cohesion, adhesion, capillary action, temperature control, and solvent capabilities.
Q & A
What is the difference between matter, elements, and compounds?
-Matter is anything that takes up space and has mass, such as liquids, solids, gases, or living organisms. An element is a substance that cannot be broken down into simpler substances by chemical reactions, while a compound consists of two or more elements combined in a fixed ratio, like water (H2O) or sodium chloride (NaCl).
What are essential elements, and why are they important?
-Essential elements, such as carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, phosphorus, and nitrogen (abbreviated as 'CHOPN'), make up 96% of living matter. These elements are crucial for various biological processes, like forming biomolecules (proteins, lipids, DNA).
What are trace elements, and what role do they play in organisms?
-Trace elements are required by organisms in very small quantities. Examples include iron (important for oxygen transport in blood) and iodine (needed for thyroid hormone production). Despite their small presence, they are vital for maintaining healthy biological functions.
How do you interpret the atomic number and atomic mass of an element?
-The atomic number represents the number of protons in an atom, while the atomic mass is the combined total of protons and neutrons, averaged across all isotopes of the element.
What is the difference between covalent, polar covalent, and ionic bonds?
-Covalent bonds involve the sharing of electrons between two non-metals. Polar covalent bonds are a type of covalent bond where electrons are shared unequally, leading to partial charges (e.g., in water). Ionic bonds occur when one atom transfers electrons to another, typically between a metal and non-metal, resulting in oppositely charged ions (e.g., sodium chloride).
What is the octet rule, and how does it relate to chemical bonding?
-The octet rule states that atoms tend to gain, lose, or share electrons to complete their valence shell with eight electrons, resembling the stable configuration of noble gases. This rule drives the formation of chemical bonds between atoms.
What are hydrogen bonds, and how do they differ from other types of bonds?
-Hydrogen bonds are weak attractions between a partially positive hydrogen atom in one polar covalent molecule and an electronegative atom (like oxygen or nitrogen) in another polar covalent molecule. Unlike covalent and ionic bonds, hydrogen bonds are intermolecular attractions, not true bonds.
Why is water considered a polar molecule, and how does this contribute to hydrogen bonding?
-Water is polar because of the unequal sharing of electrons between oxygen and hydrogen atoms, with oxygen having a partial negative charge and hydrogen having a partial positive charge. This polarity allows water molecules to form hydrogen bonds with each other, contributing to water's unique properties.
What are cohesion and adhesion, and how do they contribute to water's movement in plants?
-Cohesion refers to water molecules sticking to each other due to hydrogen bonding, while adhesion refers to water molecules sticking to other surfaces, like plant cell walls. Together, these properties facilitate capillary action, allowing water to move against gravity in plants from roots to leaves.
How do hydrogen bonds contribute to water's high specific heat and evaporative cooling?
-Hydrogen bonds in water require heat to be absorbed to break and release heat when they form, stabilizing water's temperature (high specific heat). During evaporative cooling, water molecules with the highest kinetic energy leave as gas, cooling the surface they evaporate from, like during sweating or transpiration in plants.
Outlines

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنMindmap

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنKeywords

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنHighlights

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنTranscripts

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنتصفح المزيد من مقاطع الفيديو ذات الصلة

Unsur, Senyawa, dan Campuran Kelas 8 | IPA Bab 5 Kurikulum Merdeka - Lengkap

UNSUR SENYAWA DAN CAMPURAN | KLASIFIKASI MATERI

Materi dan klasifikasinya, Kimia kelas 10 kurikulum merdeka
Fundamentals of chemistry

Das Kugelwolkenmodell und die Valenzelektronen

Kurikulum Merdeka Rangkuman Materi IPA Kelas 8 Bab 5 Unsur Senyawa dan Campuran
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
