Peter Attia's 80% Zone 2, 20% VO2 Max Training Protocol (and the optimal VO2 max interval length)
Summary
TLDRThe transcript discusses the concept of metabolic flexibility, the ability to switch between glucose and fatty acids for energy. It emphasizes the importance of zone 2 training for enhancing this flexibility and mitochondrial capacity. High-intensity interval training (HIIT) is also highlighted for its role in mitochondrial biogenesis. The speaker, drawing from experience with cyclists, explains the 80/20 training model, with 80% of cardio time spent in zone 2 and 20% in high-intensity workouts, to achieve optimal metabolic flexibility. The discussion also touches on the training methods of elite endurance athletes and the balance between intensity and efficiency in exercise routines.
Takeaways
- 🔄 Metabolic flexibility is the ability to switch between using glucose and fatty acids as fuel, which is crucial for endurance training.
- 🚴♂️ Zone 2 training is emphasized for enhancing metabolic flexibility, with the recommendation of 80% of cardio training time spent in this zone.
- 🏃♂️ High-intensity interval training (HIIT) is also beneficial for mitochondrial biogenesis, but should be limited to 20% of cardio training volume.
- 🌍 The most metabolically flexible individuals are high-level endurance athletes, such as cross-country skiers, distance runners, and cyclists.
- 🏆 World-class cyclists can produce 4-4.3 watts per kilogram of power sustainably, demonstrating exceptional metabolic flexibility.
- ⚖️ The training approach should be a balance between Zone 2 efficiency and high-intensity training to achieve a broad and high cardiorespiratory engine.
- 🏋️♀️ The 80/20 rule (80% Zone 2, 20% V2 Max) is derived from empirical observations of what works best for achieving high performance.
- ⏱️ V2 Max training involves longer intervals (3-8 minutes) at a slightly lower intensity than traditional HIIT, with a focus on efficiency.
- 📊 Personalized training plans should consider the individual's available time and willingness to exercise, balancing strength, stability, and cardio.
- ✅ Finding the 'sweet spot' in training intensity is an individualized process that requires practice and adjustment based on personal feedback.
Q & A
What is metabolic flexibility and why is it important?
-Metabolic flexibility refers to the body's ability to switch between using glucose and fatty acids for energy. It is crucial for optimizing health and athletic performance, as it allows the body to efficiently utilize different fuel sources under varying conditions.
What is Zone 2 training and how does it contribute to metabolic flexibility?
-Zone 2 training is a type of cardiovascular exercise performed at a moderate intensity, typically around 60-70% of maximum heart rate. It is believed to enhance metabolic flexibility by promoting the use of fatty acids as an energy source and expanding the capacity of mitochondria.
Why do endurance athletes like cross-country skiers and distance runners exhibit high levels of metabolic flexibility?
-Endurance athletes such as cross-country skiers and distance runners have high levels of metabolic flexibility due to their extensive training, which involves a significant amount of Zone 2 training. This training enhances their ability to utilize both glucose and fatty acids effectively for energy.
How does high-intensity interval training (HIIT) affect mitochondrial biogenesis and metabolic flexibility?
-High-intensity interval training (HIIT) is a potent stimulator of mitochondrial biogenesis, leading to an increase in the number of mitochondria. While it may not directly enhance metabolic flexibility as Zone 2 training does, it plays a role in overall fitness by improving the body's ability to handle high-intensity efforts.
What is the recommended ratio of Zone 2 to high-intensity training for optimal metabolic flexibility?
-The recommended ratio for optimal metabolic flexibility is approximately 80% Zone 2 training to 20% high-intensity training. This balance is based on empirical observations and the training regimens of high-level endurance athletes.
What is the significance of the 'pyramid' training model mentioned in the script?
-The 'pyramid' training model signifies a balanced approach to training where the base represents Zone 2 efficiency, the peak represents V2 Max, and the total area represents the cardiorespiratory engine. The goal is to have a broad base and a high peak, indicating a strong aerobic base and high performance capacity.
How does the concept of V2 Max training differ from traditional HIIT?
-V2 Max training focuses on slightly longer intervals (3 to 8 minutes) with a 1:1 rest-to-work ratio, which is different from traditional HIIT that often involves shorter, more intense bursts. V2 Max training is designed to improve the body's ability to sustain high levels of effort over longer periods.
Why is it important to have an aerobic base before engaging in high-intensity training?
-An aerobic base is essential for high-intensity training because it provides the necessary foundation for the body to handle the increased demands. Without a solid aerobic base, the body may not be efficient in utilizing energy sources, which can limit performance and increase the risk of injury.
How can an individual determine their optimal training intensity for V2 Max?
-An individual can determine their optimal training intensity for V2 Max by monitoring their heart rate and lactate levels during exercise. The goal is to find a 'sweet spot' where they can sustain high effort without reaching excessive fatigue or lactic acid accumulation.
What is the role of power meters in training for cyclists, as mentioned in the script?
-Power meters allow cyclists to measure their wattage output, providing precise data on their performance. This data helps in tailoring training programs to improve efficiency and power output, which is crucial for enhancing metabolic flexibility and overall cycling performance.
Outlines

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنMindmap

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنKeywords

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنHighlights

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنTranscripts

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنتصفح المزيد من مقاطع الفيديو ذات الصلة

Fatty Acid Synthesis - Part I

Destino del esqueleto de carbonos | Catabolismo de aminoácidos - Parte 2

Biochimie | Métabolisme des lipides | Partie 01/06

Liver Function 3, Carbohydrate storage and metabolism

Proses Metabolisme Karbohidrat, Protein, dan LIPID
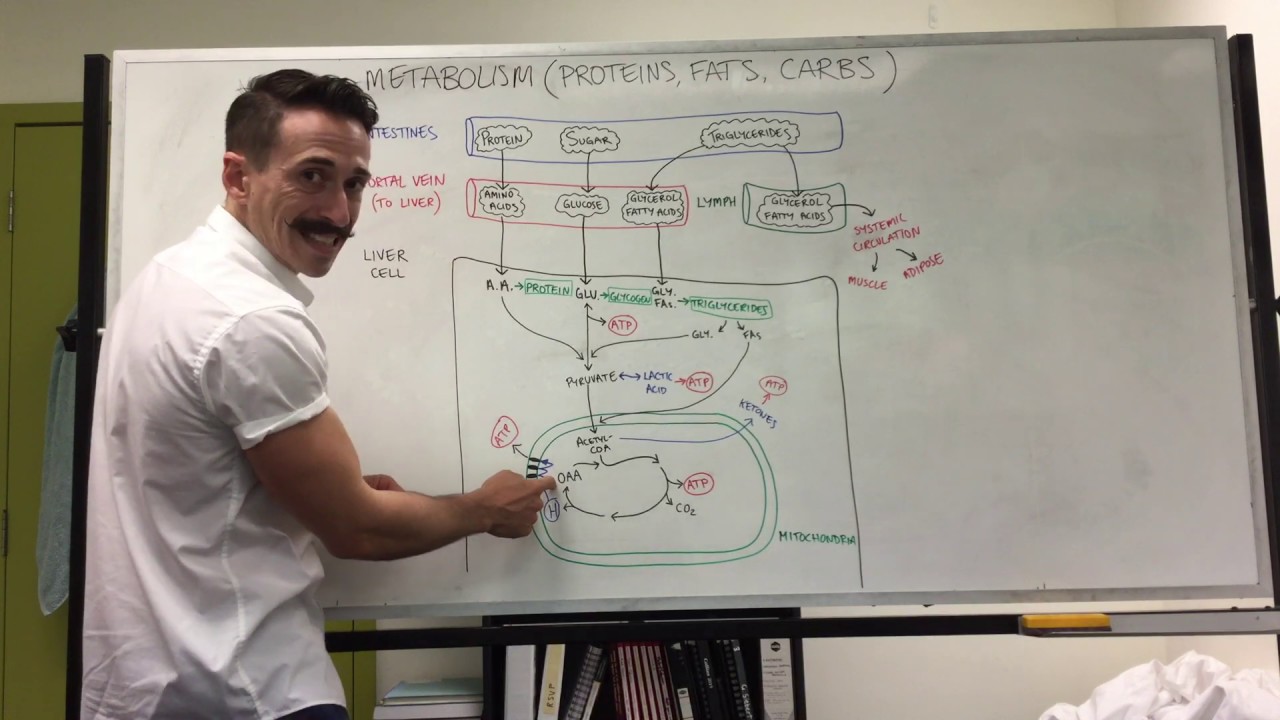
Carbohydrate, Protein, and Fat Metabolism | Metabolism
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
