Steps in Cloning a Gene
Summary
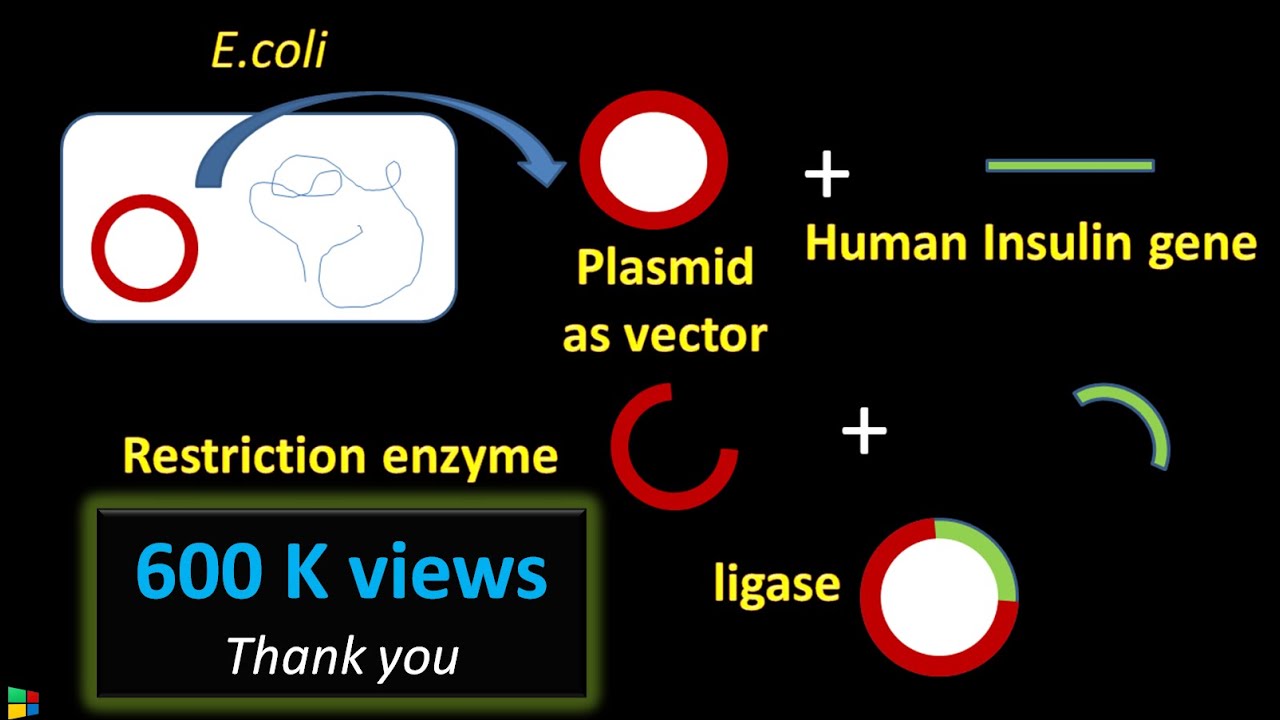
TLDRThe video script outlines the cloning process of a gene, starting with DNA isolation from an organism. It details the purification and fragmentation using restriction enzymes, which create cohesive ends. These DNA fragments are then inserted into plasmids with compatible cohesive ends, forming a DNA library. The library is introduced into bacterial host cells through transformation, allowing for the identification and isolation of the desired gene within colonies grown on agar medium.
Takeaways
- 🔬 The first step in gene cloning is isolating DNA from the organism containing the desired gene.
- 🧬 Isolated DNA is purified and fragmented using a restriction enzyme.
- ✂️ Restriction enzymes produce staggered cuts in specific DNA sequences, creating fragments with cohesive ends.
- 🔗 Each DNA fragment has single-stranded sequences at its ends that can hybridize with other DNA fragmented by the same enzyme.
- 🧪 The fragmented DNA is incorporated into plasmids, which have a single restriction site.
- ⚙️ When cleaved by the restriction enzyme, plasmids generate cohesive ends that align with the DNA fragments.
- 🔗 DNA ligase is used to form phosphodiester bonds between plasmid and DNA fragments, completing the insertion.
- 🦠 Plasmids are incorporated into bacterial host cells through transformation, each carrying different DNA segments.
- 📚 These cells collectively represent a DNA library containing segments from the original organism.
- 🔍 Desired cloned gene colonies can be identified and isolated after plating the transformed cells on agar medium.
Q & A
What is the first step in cloning a gene?
-The first step in cloning a gene is to isolate the DNA from the organism that contains the desired gene.
Why is the DNA purified after isolation?
-The DNA is purified to remove contaminants and ensure only the desired DNA is used for further steps in the cloning process.
What role do restriction enzymes play in gene cloning?
-Restriction enzymes cut the DNA at specific sequences, producing fragments with cohesive ends that can hybridize with other DNA fragments.
What are cohesive ends and why are they important?
-Cohesive ends are single-stranded sequences of nucleotides on the ends of DNA fragments. They are important because they allow the DNA fragments to hybridize with DNA fragmented by the same restriction enzyme.
How are the DNA fragments incorporated into plasmids?
-The DNA fragments are incorporated into plasmids by aligning the cohesive ends of the plasmid and DNA fragments, then using the enzyme DNA ligase to form phosphodiester bonds between them.
What type of plasmids are used in cloning?
-The type of plasmid used in cloning has a single restriction site that, when cleaved by the restriction enzyme, generates the same cohesive ends as the DNA fragments to be cloned.
What is the purpose of DNA ligase in the cloning process?
-DNA ligase is used to form phosphodiester bonds between the cohesive ends of the plasmid and the DNA fragments, sealing the fragments into the plasmid.
How are the plasmids introduced into bacterial host cells?
-The plasmids are introduced into bacterial host cells through a process called transformation, where the bacterial cells take up the plasmids.
What is a DNA library in the context of gene cloning?
-A DNA library is a collection of bacterial cells, each containing a different segment of DNA from the original organism. Taken together, these cells represent the entire DNA of the organism.
How can the desired cloned gene be identified and isolated?
-The bacterial cells are plated on an agar medium, and the colony containing the desired cloned gene can be identified and isolated for further study.
Outlines

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنMindmap

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنKeywords

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنHighlights

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنTranscripts

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنتصفح المزيد من مقاطع الفيديو ذات الصلة

CBSE Class 12 Biology || Biotechnology Principles And Processes || Full Chapter || By Shiksha House
Steps in Recombinant DNA Technology or rDNA technology | Biotechnology

DNA Rekombinan - Pembuatan Insulin

Gene Cloning | Introduction | Basic Science Series

Animation 27.1 Basic principle of recombinant DNA technology

DNA cloning and recombinant DNA | Biomolecules | MCAT | Khan Academy
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
