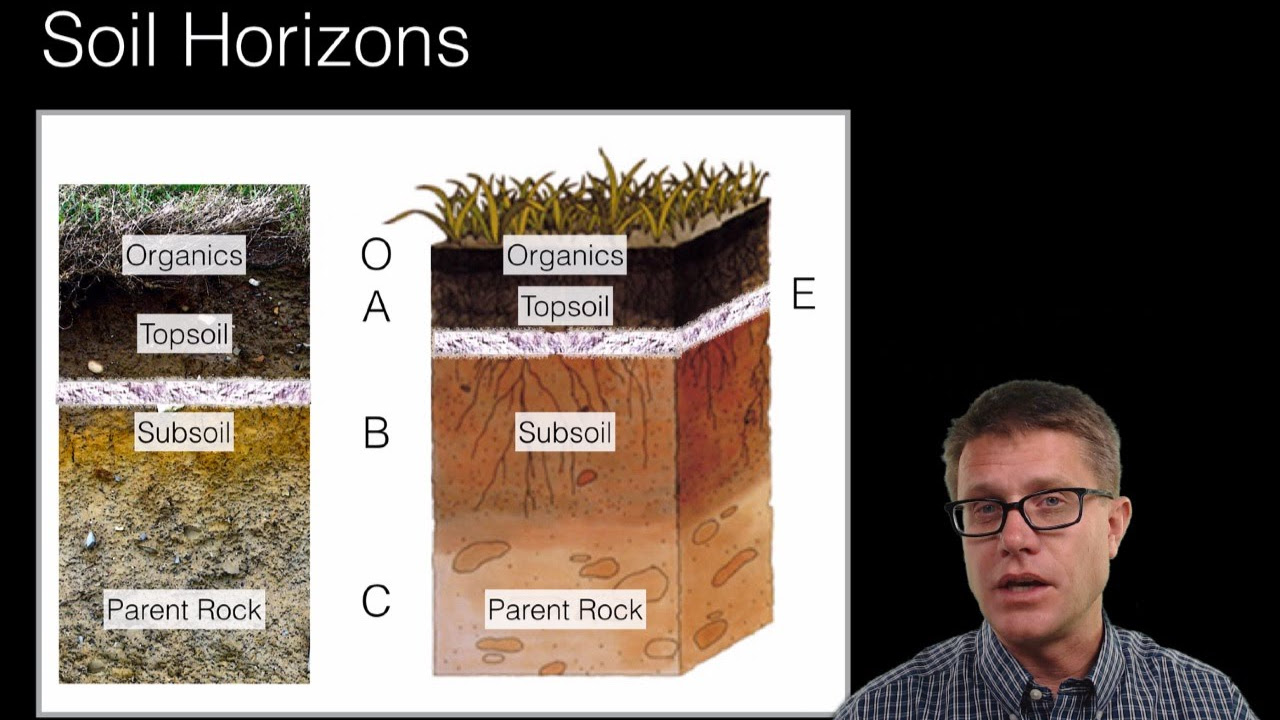
Soil Texture - Environmental Science
Summary
TLDRThis script explains the composition of soil, highlighting its mixture of organic matter, water, oxygen, and inorganic rock materials. It emphasizes soil texture's role in determining porosity, water holding capacity, and permeability, which are crucial for water movement through soil. The video demonstrates how to identify soil texture through a simple experiment using a graduated cylinder, plastic wrap, and a rubber band. The experiment separates soil into layers of sand, silt, and clay, allowing for the determination of their volume proportions. The ideal soil for most crops, known as loam, is described, containing roughly equal parts of clay, silt, and sand.
Takeaways
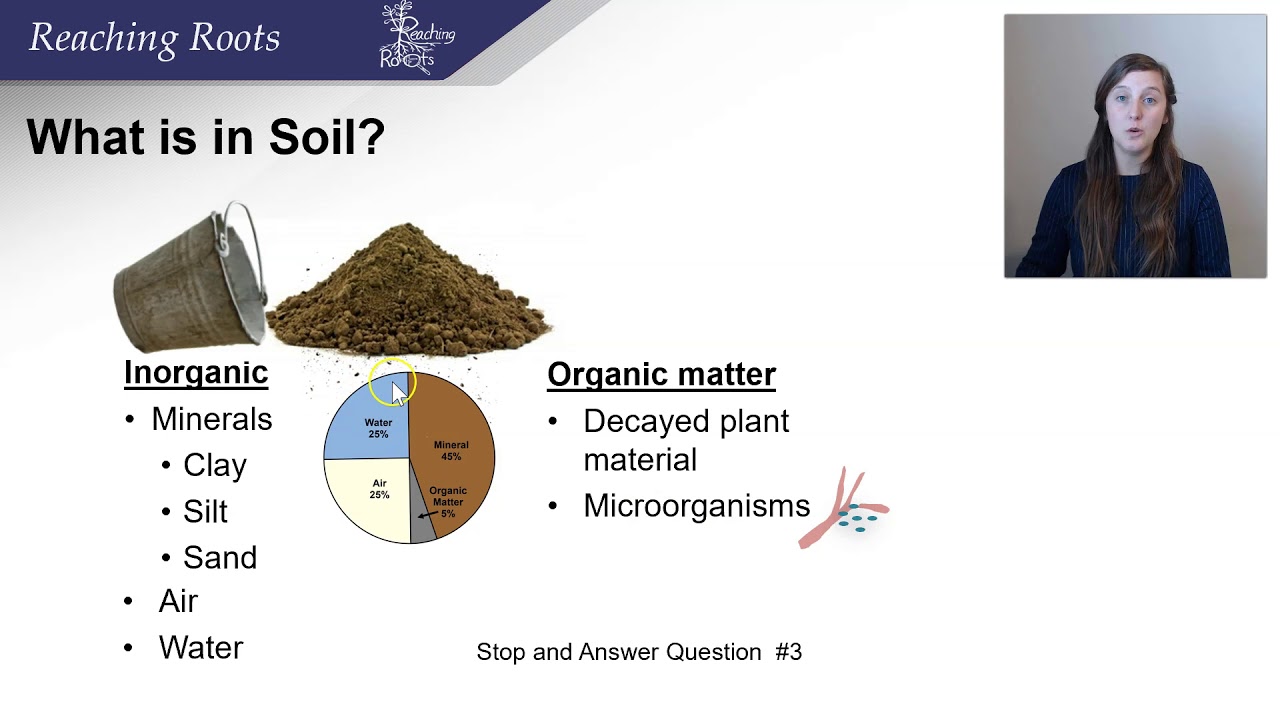
- 🌱 Soil is a complex mixture comprising organic matter, water, oxygen, and inorganic rock materials.
- 📏 Soil texture is a critical characteristic, reflecting the proportions of sand, silt, and clay within the soil.
- 💧 Soil texture significantly influences the soil's porosity and water-holding capacity.
- 💧 Permeability, or the rate at which water moves through soil, is also determined by soil texture.
- 🏖️ Sand-rich soils exhibit high permeability, allowing water to flow through them easily.
- 🏚️ Clay-rich soils have low permeability, resulting in poor water flow.
- 🌾 Loam is the most suitable soil type for growing most crops, containing a balanced mix of clay, silt, and sand.
- 🔍 A simple experiment using a graduated cylinder, plastic wrap, and a rubber band can determine soil texture.
- 🧪 The experiment involves mixing soil with water, shaking, and observing the settling of soil particles based on size.
- 📊 The volume proportions of sand, silt, and clay can be measured using the graduated cylinder's markings.
- 📋 The example soil sample described is a loam, with 25% clay, 35% silt, and 40% sand.
Q & A
What is soil composed of?
-Soil is composed of organic matter, water, oxygen, and inorganic rock materials.
What is soil texture and how does it affect soil properties?
-Soil texture is the measure of the volume proportions of rock materials like sand and clay in the soil. It affects the porosity, water holding capacity, and permeability of the soil.
How does soil permeability influence water movement through soil?
-Soil permeability determines the rate at which water moves through the soil. Sand-rich soil has high permeability, allowing water to flow through easily, while clay-rich soil has low permeability, restricting water flow.
What type of soil is best for growing most crops?
-Soils that are best for growing most crops are called loams.
What are the approximate volume proportions of clay, silt, and sand in a loam soil?
-In a loam soil, the volume proportions are roughly 20 to 40 to 40 for clay, silt, and sand, respectively.
How can soil texture be experimentally determined?
-Soil texture can be determined by a simple experiment using a graduated cylinder, plastic wrap, and a rubber band. The soil sample is mixed with water, shaken, and then allowed to settle overnight to observe the layering of different soil particles.
What happens when a soil sample is mixed with water and shaken in a graduated cylinder?
-When a soil sample is mixed with water and shaken, the soil grains settle based on their size, with larger sand grains settling first, followed by silt, and then clay.
How can the volume proportions of sand, silt, and clay in a soil sample be measured?
-The volume proportions of sand, silt, and clay can be measured using the marks on the graduated cylinder after the soil grains have settled.
What does the soil sample described in the script indicate in terms of texture?
-The soil sample described in the script indicates that it is a loam, with 25% clay, 35% silt, and 40% sand.
Why is it important to know the soil texture for agricultural purposes?
-Knowing the soil texture is important for agricultural purposes because it helps in understanding the soil's ability to retain water and nutrients, which are crucial for plant growth.
Outlines

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنMindmap

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنKeywords

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنHighlights

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنTranscripts

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآن5.0 / 5 (0 votes)