Production Possibilities Curve- Macro Topic 1.2 (Micro Topic 1.3)
Summary
TLDRIn this educational video, Jacob Clifford introduces viewers to the concept of the production possibilities curve through an interactive drawing game. Participants draw squares and triangles within a time limit, illustrating scarcity and the trade-offs between goods. The video explains the curve's significance in economics, including efficiency, opportunity cost, and the law of increasing opportunity cost. It also touches on how improved resources or technology can shift the curve, leading to economic growth. The video concludes with a call to action for viewers to practice these concepts and offers a free resource for further learning.
Takeaways
- 😀 The video introduces an economics game where participants draw shapes within a time limit, illustrating the concept of scarcity and efficiency.
- ✏️ Participants are challenged to draw squares with their non-dominant hand, emphasizing the impact of resource allocation on production.
- 📊 The production possibilities curve (PPC) is introduced as a tool to visualize the trade-offs between two goods, showing the limits of production due to scarcity.
- 🔄 The concept of opportunity cost is explained through the game, highlighting the idea that choosing one option means giving up another.
- 📉 The video demonstrates the law of increasing opportunity cost, using the analogy of picking cherries versus playing video games to show how opportunity costs can change.
- 📈 The script explains how the PPC can shift outward due to increased productivity, better resources, or technological advancements, representing economic growth.
- 🛠️ The video uses a 'double pencil' as a memory device to symbolize productivity and economic growth, reinforcing the idea that improvements in these areas can expand the PPC.
- 💡 The importance of understanding and calculating opportunity cost is stressed, as it is a fundamental skill in economics for making informed decisions.
- 📚 The video promotes an educational resource called the 'ultimate review packet' for further study and practice of economic concepts, including the PPC.
- 🎓 The script concludes with a call to action for viewers to like, subscribe, and participate in a pop quiz to test their understanding of the video's content.
Q & A
What is the main activity Jacob asks viewers to participate in at the beginning of the video?
-Jacob asks viewers to draw as many squares as they can in ten seconds using their non-dominant hand.
What is the purpose of the drawing activity in the video?
-The purpose of the drawing activity is to illustrate the concept of production possibilities and opportunity cost in economics.
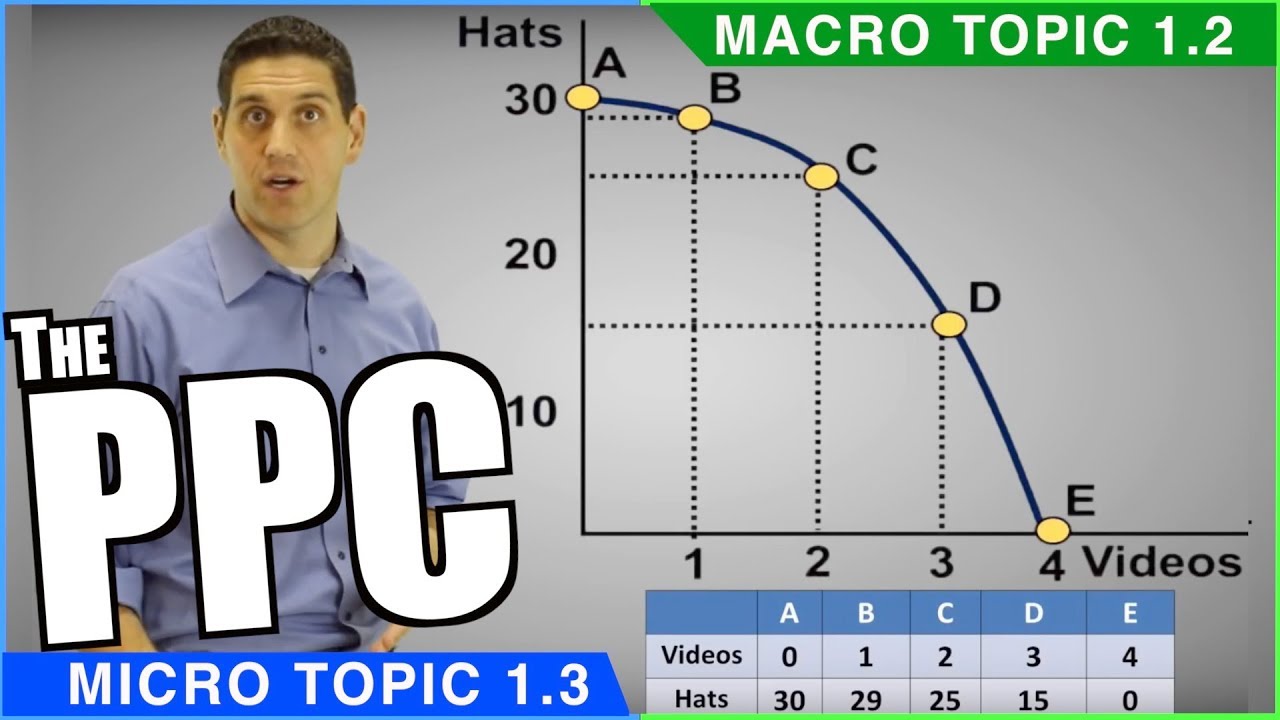
What does the production possibilities curve (PPC) represent?
-The production possibilities curve represents the different combinations of goods that can be produced with available resources, given a certain level of technology and full employment of resources.
Why can't Jacob produce 15 squares and 10 triangles simultaneously according to the PPC?
-Jacob cannot produce 15 squares and 10 triangles simultaneously because such a combination is outside the PPC, indicating it is unattainable with the current resources and technology.
What does a point inside the PPC signify?
-A point inside the PPC signifies inefficiency, as it represents a scenario where resources are not being fully utilized.
What is the concept of opportunity cost explained in the video?
-Opportunity cost is the value of the next best alternative that is foregone when making a decision. In the video, it is demonstrated by the number of squares Jacob has to give up to produce additional triangles.
How does the law of increasing opportunity cost apply to the example of picking cherries?
-The law of increasing opportunity cost applies to picking cherries as the easier cherries are picked first, and as one moves to higher branches, the opportunity cost of picking each additional basket of cherries increases.
What does a bowed-out shape of the PPC indicate?
-A bowed-out shape of the PPC indicates that the opportunity cost is not constant; it increases as one moves from producing one good to producing more of another.
What does a shift in the PPC represent?
-A shift in the PPC represents an increase in productivity, which could be due to more resources, better resources, or improved technology, allowing for the production of more output.
How can the PPC be applied to the overall economy?
-The PPC can be applied to the overall economy by showing combinations inside the curve as representing unemployment, points on the curve as full employment, and points outside the curve as potential growth areas.
What resource does Jacob offer to help viewers practice and review economic concepts?
-Jacob offers 'The Ultimate Review Packet' which includes study guides, exclusive videos, and worksheets to help practice and review macro and microeconomics.
Outlines

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنMindmap

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنKeywords

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنHighlights

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنTranscripts

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنتصفح المزيد من مقاطع الفيديو ذات الصلة
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)