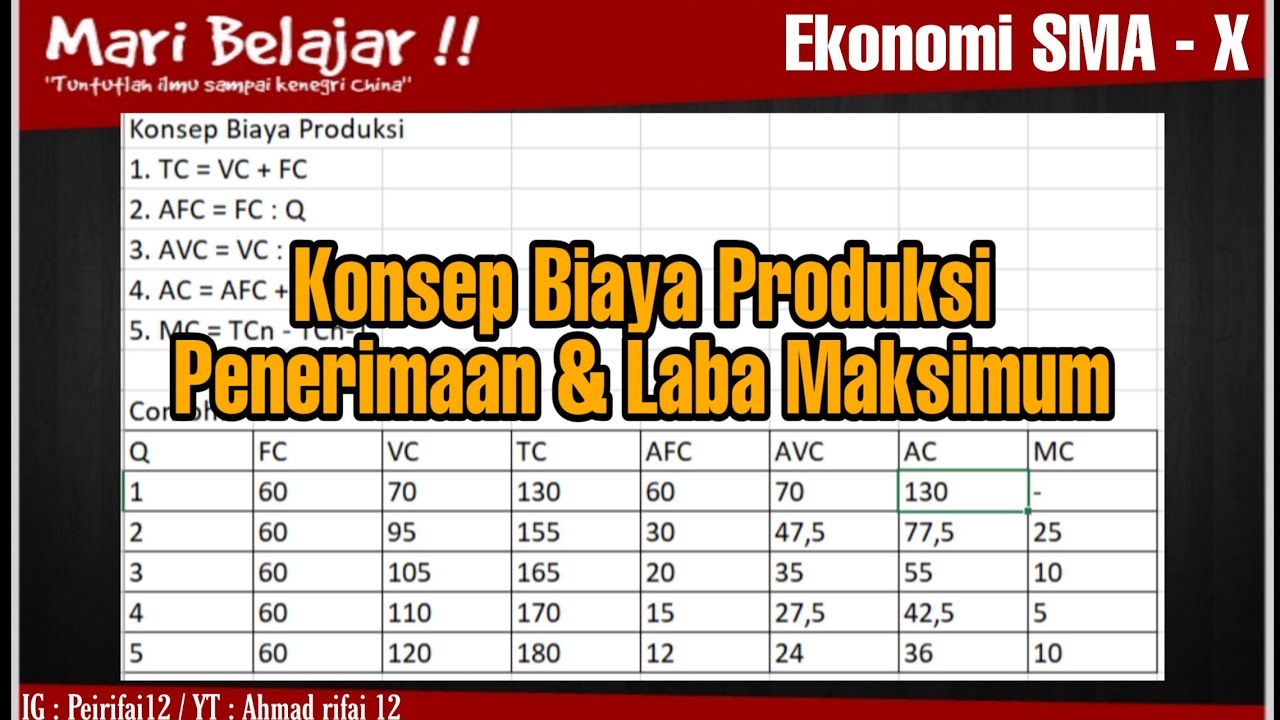
Biaya Produksi | Biaya Tetap | Biaya Variabel | Biaya Total | Biaya Rata-rata | Biaya Marginal
Summary
TLDRThis educational video script delves into cost analysis for product prototyping, focusing on key cost concepts for production. It explains fixed costs (FC), which remain constant regardless of production volume, and variable costs (VC), which fluctuate with output. The script outlines formulas to calculate average fixed cost (AFC), average variable cost (AVC), and total cost (TC). It also introduces average cost (AC) and marginal cost (MC), illustrating how costs change with production levels. The video aims to educate entrepreneurs on cost management for better financial planning and decision-making.
Takeaways
- 📈 Understanding Production Costs: The script emphasizes the importance of analyzing production costs for entrepreneurs to determine the profitability of a business and to manage daily expenses.
- 🔢 Fixed Costs (FC): These are costs that do not change with the level of production, such as rent, salaries, and interest payments.
- 📊 Total Fixed Cost (TFC): Represents the total amount of fixed costs that must be paid regardless of the quantity of goods produced.
- 💹 Average Fixed Cost (AFC): Calculated by dividing the Total Fixed Cost by the quantity of goods produced, showing the fixed cost per unit.
- 📉 Variable Costs (VC): These costs vary with the quantity of goods produced, such as raw materials and utilities.
- 🔼 Total Variable Cost (TVC): The total expenses for variable costs incurred in producing a certain quantity of goods.
- 📊 Average Variable Cost (AVC): The cost per unit of goods produced, calculated by dividing the Total Variable Cost by the quantity of goods.
- 💼 Total Cost (TC): The sum of both Fixed and Variable Costs, which is essential for calculating the overall expenses of production.
- 📉 Average Cost (AC): Represents the cost per unit of goods produced, which is the sum of Average Fixed Cost and Average Variable Cost.
- 📈 Marginal Cost (MC): The change in total cost that arises when the production level is increased or decreased by one unit, initially decreasing and then increasing as production rises.
Q & A
What is the main topic discussed in the video script?
-The main topic discussed in the video script is the analysis of production costs, specifically focusing on the concepts of fixed and variable costs in the context of business operations.
Why is it important for entrepreneurs to understand production costs?
-Understanding production costs is important for entrepreneurs to determine the profit or loss of a business and to manage the daily expenses associated with producing goods or services.
What are the two main categories of fixed costs mentioned in the script?
-The two main categories of fixed costs mentioned are Total Fixed Cost (TFC) and Average Fixed Cost (AFC).
How is Average Fixed Cost (AFC) calculated?
-Average Fixed Cost (AFC) is calculated by dividing the Total Fixed Cost (TFC) by the quantity of goods produced (Q).
What is the definition of Variable Cost (VC)?
-Variable Cost (VC) is the cost that varies with the number of goods produced, meaning it is influenced by the quantity of goods manufactured.
What are the two types of variable costs discussed in the script?
-The two types of variable costs discussed are Total Variable Cost (TVC) and Average Variable Cost (AVC).
How is Average Variable Cost (AVC) calculated?
-Average Variable Cost (AVC) is calculated by dividing the Total Variable Cost (TVC) by the quantity of goods produced (Q).
What is the relationship between Total Cost (TC) and the other cost concepts?
-Total Cost (TC) is the sum of Total Fixed Cost (TFC) and Total Variable Cost (TVC), representing all expenses incurred in producing a certain quantity of goods or services.
What is Average Cost (AC) and how does it change with production quantity?
-Average Cost (AC) is the cost per unit of goods produced by the producer. It tends to decrease as the quantity of goods produced increases, reaching a minimum point, but then increases again if production is further increased.
How is Marginal Cost (MC) defined and how does it behave with changes in production?
-Marginal Cost (MC) is the change in Total Cost (ΔTC) when production is increased or decreased by one unit. It initially decreases but then increases as the quantity of goods produced increases.
What is the relationship between Marginal Cost (MC), Average Variable Cost (AVC), and Average Fixed Cost (AFC)?
-The relationship is that Marginal Cost (MC) is influenced by both Average Variable Cost (AVC) and Average Fixed Cost (AFC), and it can be used to understand the behavior of costs as production levels change.
Outlines

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنMindmap

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنKeywords

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنHighlights

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنTranscripts

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنتصفح المزيد من مقاطع الفيديو ذات الصلة

Analisa Biaya Prototype Barang/Jasa #jussul #religi #edukasi #shorts

ANALISIS HARGA POKOK PRODUKSI DAN PEMASARAN PRODUK
Cara Menghitung Biaya Produksi, Penerimaan dan Laba Maksimum

INVENTORY COSTING AND CAPACITY ANALYSIS

Teori Produksi dan Biaya

| AKTU Digital Education| Managerial Economics |Fundamental Principles of Managerial Economics ....
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
