LECTURE NOTES: HEAT TRANSFER, CHAPTER I, PART 1
Summary
TLDRThis script delves into the fundamentals of heat transfer, exploring its mechanisms—conduction, convection, and radiation—and the laws governing them, such as Fourier's, Newton's, and Stefan-Boltzmann's. It distinguishes between thermal energy and other forms of energy, emphasizing the importance of understanding heat transfer in various applications, from household appliances to industrial processes. The script also touches on the historical evolution of our understanding of heat, from the caloric theory to the kinetic theory, and discusses energy units, types of energy, and the significance of thermodynamics in analyzing heat transfer processes.
Takeaways
- 🔍 This chapter introduces the basics of heat transfer, its mechanisms, and its significance in various applications.
- 🌡️ Heat transfer occurs due to temperature differences and ceases when thermal equilibrium is reached between mediums.
- 🔗 Thermodynamics is related to the amount of heat transferred during a process, but it does not indicate the time it takes for the process to occur.
- 🏡 Heat transfer is crucial in everyday life, including in the human body's regulation of heat and in the design of household appliances.
- 🛠️ The rate of heat transfer is a key concern in engineering, influencing the design of systems like refrigerators, heaters, and even buildings for energy efficiency.
- ⚖️ The laws of thermodynamics underpin the study of heat transfer, with the first law relating to energy conservation and the second law to the direction of heat flow.
- 🌡️ The gradient of temperature or the difference in temperature per unit length is a significant factor influencing the rate of heat transfer.
- 🌡️ Various mechanisms of heat transfer are discussed, including conduction, convection, and radiation, each with its own laws and principles.
- 🔬 The concept of energy balance and the different forms of energy, such as thermal and mechanical, are explored in relation to heat transfer.
- ⏱️ The study of heat transfer is not only theoretical but also practical, with applications in designing systems that either minimize or maximize heat transfer for specific purposes.
- 🌐 The script also touches on the historical understanding of heat, from the caloric theory to the modern kinetic theory, which describes heat as a form of energy related to the random motion of molecules.
Q & A
What is the main focus of the chapter discussed in the transcript?
-The main focus of the chapter is to introduce the basic concepts of heat transfer, its mechanisms, and its applications in various practical scenarios.
What are the three primary mechanisms of heat transfer mentioned in the script?
-The three primary mechanisms of heat transfer mentioned are conduction, convection, and radiation.
According to the script, what is the relationship between thermodynamics and heat transfer?
-Thermodynamics is related to the amount of heat transferred when a system undergoes a process, but it does not indicate the duration of the process. Heat transfer, on the other hand, is concerned with the rate of heat transfer and is a non-equilibrium phenomenon.
What is the significance of the first law of thermodynamics in the context of heat transfer?
-The first law of thermodynamics states that the rate of energy transfer into a system is equal to the rate of increase of the system's energy, which is fundamental to understanding heat transfer processes.
How does the concept of temperature difference drive heat transfer, as explained in the transcript?
-Heat transfer occurs due to a temperature difference, with heat always moving from a medium with a higher temperature to one with a lower temperature. The greater the temperature gradient, the higher the rate of heat transfer.
What are some practical applications of heat transfer mentioned in the script?
-Practical applications of heat transfer include home appliances like electric stoves, heating systems, air conditioners, refrigerators, and even computers and TVs, all of which are designed based on heat transfer principles.
Why is it important to study the rate of heat transfer according to the script?
-Studying the rate of heat transfer is important because it helps in determining the time required to heat or cool a system to a desired state, which is crucial for design and efficiency in various applications.
What is the difference between sensible heat and latent heat as discussed in the transcript?
-Sensible heat is the energy associated with the kinetic energy of molecules and is directly related to temperature. Latent heat is the energy required for a phase change, such as from liquid to gas, without a change in temperature.
How is the concept of specific heat capacity relevant to the script's discussion on heat transfer?
-Specific heat capacity is relevant as it represents the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of a substance by one degree Celsius per unit mass, which is essential for calculating heat transfer in materials.
What role does the understanding of heat transfer play in the design of energy-efficient buildings, as mentioned in the script?
-Understanding heat transfer plays a crucial role in designing energy-efficient buildings by minimizing heat loss in cold seasons and maximizing heat absorption in warm seasons, thus optimizing energy use.
How does the historical perspective on heat, as discussed in the script, differ from the modern understanding?
-Historically, heat was considered a substance called caloric, which was thought to be transferable between objects. Modern understanding, however, views heat as a form of energy associated with the random motion of atoms and molecules, as per the kinetic theory of heat.
Outlines

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنMindmap

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنKeywords

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنHighlights

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنTranscripts

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنتصفح المزيد من مقاطع الفيديو ذات الصلة

9. Fenomena Transport - Termodinamika - Fisika N20

ILMU BIOMEDIK DASAR (TERMOFISIKA DAN PEMELIHARAAN ALAT KEPERAWATAN)
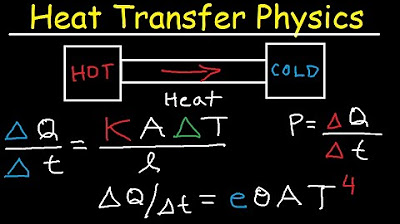
Thermal Conductivity, Stefan Boltzmann Law, Heat Transfer, Conduction, Convecton, Radiation, Physics

Pendahuluan - Perpindahan Kalor dan Massa

Heat Transfer - Conduction, Convection, and Radiation

Propagação de calor - CONDUÇÃO, CONVECÇÃO E IRRADIAÇÃO
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
