Cell Biology: Active Transport
Summary
TLDRThis video delves into active transport, a cellular process where particles move from low to high concentration, requiring energy. It contrasts with passive transport, illustrating the need for energy to move particles against the concentration gradient. Key mechanisms of active transport include endocytosis, where cells ingest substances, exocytosis for cellular ejection of materials, and protein pumps like the sodium-potassium pump. The video emphasizes the vital role of active transport in cellular functions, particularly in heart muscle cells.
Takeaways
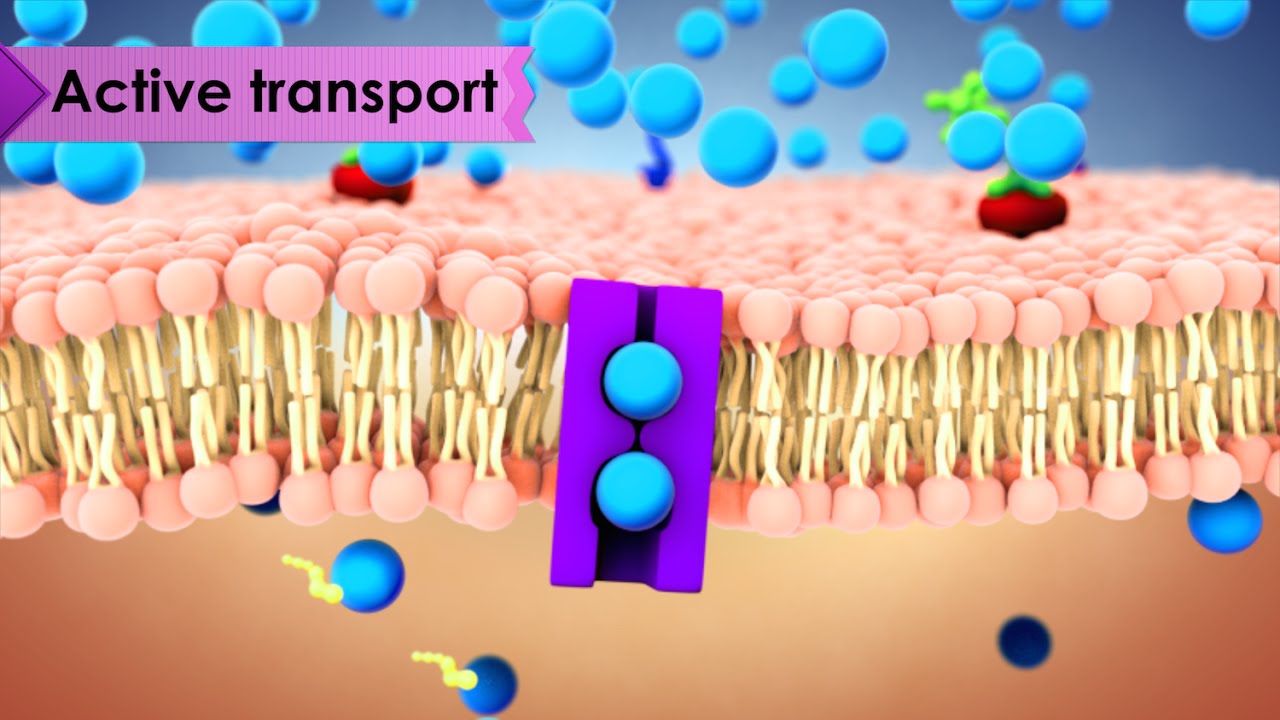
- 🚀 Active transport involves moving particles from an area of low concentration to high concentration, which is against the concentration gradient.
- ⚡ Active transport requires energy, unlike passive transport which does not.
- 💡 The energy needed for active transport is often in the form of ATP molecules.
- 🔁 Active transport is essential for cellular functions, including processes in heart muscle cells.
- 🌀 Endocytosis is a type of active transport where cells ingest large particles or fluids by engulfing them with their cell membrane.
- 🍽️ Phagocytosis and pinocytosis are two types of endocytosis, with the former involving the intake of nutrients and the latter involving the intake of fluids.
- 🔄 Exocytosis is the opposite of endocytosis, used for cells to expel large molecules or wastes by fusing vesicles with the cell membrane.
- 🚪 The terms 'endocytosis' and 'exocytosis' can be remembered by their relation to 'enter' and 'exit' respectively.
- 🔋 Protein pumps are used in active transport to move small molecules or ions against the concentration gradient, such as the sodium-potassium pump.
- 🔄 The sodium-potassium pump is an example of a protein pump that uses ATP to move sodium ions out of the cell and potassium ions in.
Q & A
What is active transport?
-Active transport is the process where particles move from an area of low concentration to high concentration, which is against the concentration gradient. It requires energy to move substances against their natural tendency to diffuse from areas of high concentration to low concentration.
How does active transport differ from passive transport?
-Active transport moves substances against the concentration gradient, requiring energy, whereas passive transport allows substances to move along the concentration gradient without the need for energy.
Why is energy necessary for active transport?
-Energy is necessary for active transport because it involves moving substances from areas of low concentration to high concentration, which is against their natural diffusion tendency and requires an input of energy to overcome this.
What role does active transport play in cellular functions?
-Active transport is crucial for cellular functions as it allows cells to maintain proper concentrations of substances inside and outside the cell, which is essential for the cell to function properly. For instance, heart muscle cells use active transport to move molecules or ions against their concentration gradient.
What are the main types of active transport mechanisms mentioned in the script?
-The main types of active transport mechanisms mentioned are endocytosis, exocytosis, and protein pumps.
Can you describe the process of endocytosis?
-Endocytosis is a type of active transport where cells ingest large particles or fluids by creating pockets in the cell membrane. These pockets then pinch off into the cytoplasm, bringing the substance inside the cell.
What is phagocytosis and how does it relate to endocytosis?
-Phagocytosis is a type of endocytosis where cells take in solid particles, often nutrients, by engulfing them with the cell membrane and forming a vesicle around the particle.
How does pinocytosis differ from phagocytosis?
-Pinocytosis is a type of endocytosis where cells take in fluids by creating small pockets in the cell membrane, which then pinch off to bring the fluid into the cell. It differs from phagocytosis in that it involves the intake of liquids rather than solid particles.
What is exocytosis and how does it function?
-Exocytosis is the process where cells expel large molecules or wastes by fusing membrane-bound vesicles containing these substances with the cell membrane, effectively pushing them out of the cell.
How is the term 'exocytosis' related to the concept of 'exit'?
-The term 'exocytosis' shares the first two letters with 'exit', which is a mnemonic to remember that it is a process for substances to leave the cell.
What is a protein pump, and how does it function in active transport?
-A protein pump is a specialized protein that uses energy, often in the form of ATP, to move small molecules or ions against the concentration gradient into or out of the cell. An example is the sodium-potassium pump, which moves sodium ions out and potassium ions into the cell.
Why do protein pumps require energy for active transport?
-Protein pumps require energy because they facilitate the movement of molecules or ions from an area of low concentration to high concentration, which is against their natural diffusion direction and thus requires an external energy source.
Outlines

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنMindmap

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنKeywords

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنHighlights

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنTranscripts

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآن5.0 / 5 (0 votes)