Internal Organs | Human Body | Science Video Lecture
Summary
TLDRThis script delves into the critical internal organs of the human body that are essential for survival and reproduction. It highlights the brain as the central nervous system controller, the lungs as oxygen providers, the liver as a blood processor, the kidneys as waste excretors, the heart as the blood pump, the stomach as the food digester, and the intestines for nutrient absorption and waste excretion. These organs work in harmony to maintain the body's vital functions.
Takeaways
- 🧠 The brain is the control center of the nervous system, responsible for muscle control, coordination, sensory reception, speech production, memory, and emotions.
- 🫁 The lungs are essential for providing oxygen to the bloodstream and exhaling carbon dioxide.
- 💊 The liver processes blood to maintain its composition, breaks down fats, produces urea, filters harmful substances, and regulates glucose levels.
- 🫅 The kidneys maintain the body's chemical balance by excreting waste products and excess fluid as urine.
- ❤️ The heart is a muscular organ that pumps blood through the blood vessels via rhythmic contractions.
- 🍲 The stomach is a muscular, elastic sac in the abdominal cavity that digests food through the production of gastric juices.
- 🌀 The intestines, consisting of the small and large intestines, are responsible for absorbing nutrients and excreting solid waste.
- 🔬 Internal organs work in conjunction with associated structures to form body systems, which are crucial for survival and reproduction.
- 📚 Higher-level classes will delve deeper into the functions and interrelationships of these vital organs.
- 🌟 The script emphasizes the fear of easily recognizable internal organs and their associated functions, highlighting their importance in human physiology.
Q & A
What is the primary function of the brain in the human body?
-The primary function of the brain is to serve as the control center of the nervous system, which includes muscle control, coordination, sensory reception, integration, speech production, memory storage, and the elaboration of thought and emotion.
How do the lungs contribute to the respiratory process?
-The lungs provide oxygen from inhaled air to the bloodstream and exhale carbon dioxide, facilitating the respiratory process.
What is the liver's role in maintaining the body's blood composition?
-The liver processes the contents of the blood to ensure its composition remains constant. It breaks down fats, produces urea, filters harmful substances, and maintains a proper level of glucose in the blood.
What are the kidneys responsible for in terms of body chemical balance?
-The kidneys maintain the body's chemical balance by excreting waste products and excess fluid in the form of urine.
Describe the heart's function in the circulatory system.
-The heart pumps blood through the blood vessels by repeated rhythmic contractions, playing a crucial role in the circulatory system.
What is the stomach's main purpose in the digestive process?
-The stomach's main purpose is the digestion of food through the production of gastric juices, which help in breaking down, mixing, and churning food into a thin liquid.
How do the intestines contribute to digestion and waste elimination?
-The small intestine absorbs most of the digested food, while the large intestine is responsible for absorbing water and excreting solid waste material.
Why is the liver considered essential for detoxification?
-The liver is essential for detoxification because it filters harmful substances from the blood, helping to maintain the body's internal environment.
How do the kidneys help in maintaining the body's fluid balance?
-The kidneys help maintain the body's fluid balance by regulating the amount of water in the body through the production and excretion of urine.
What is the significance of the brain being located within the skull?
-The brain's location within the skull provides it with protection from physical trauma, which is crucial for its proper functioning as the control center of the nervous system.
What is the role of the diaphragm in relation to the liver and other abdominal organs?
-The diaphragm separates the thoracic cavity, which contains the heart and lungs, from the abdominal cavity, where organs like the liver are located. It plays a role in respiration and helps protect these organs.
Outlines

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنMindmap

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنKeywords

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنHighlights

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنTranscripts

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنتصفح المزيد من مقاطع الفيديو ذات الصلة

Cells, Tissues, Organs, Organ systems | Level of organisation in organisms | Easy science video

Types of Tissue Part 3: Muscle Tissue

Phylum Cnidaria | Animal kingdom | Biology | Khan Academy
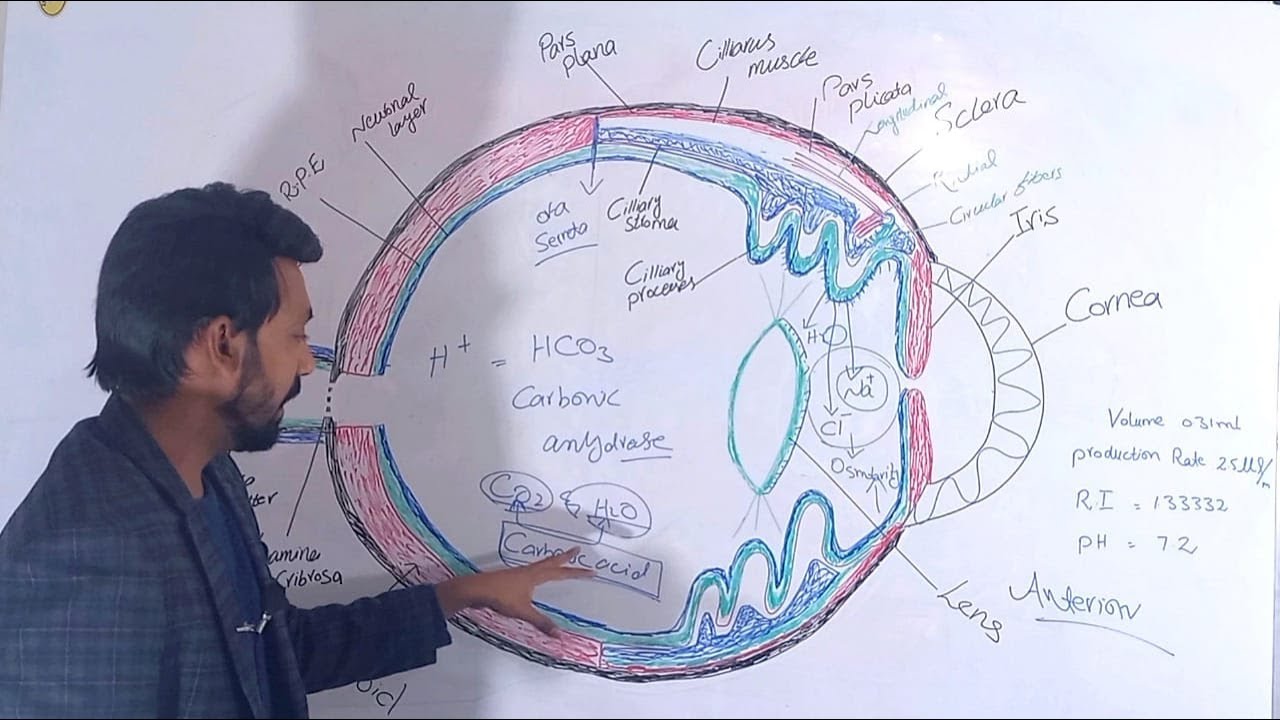
Aqueous humor production

Rangkuman Materi IPA Kelas 9 Bab 1 | Sistem Reproduksi Manusia

SISTEM REPRODUKSI PADA MANUSIA | RINGKAS
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
