GCSE Biology - Nervous System and Reflex Arc #58
Summary
TLDRThis script delves into the human nervous system, highlighting its role in communication within the body. It describes neurons, the basic units of the system, as long, thin cells with branching connections for message transmission. The video explains how neurons communicate via synapses, releasing chemicals to trigger impulses in adjacent cells. It outlines the structure of the nervous system, emphasizing the central nervous system's role in processing sensory information and directing motor neurons to effectors like muscles or glands. A key concept is the reflex arc, which facilitates rapid, automatic responses to stimuli, such as pulling a hand away from heat. The script promises more on the endocrine system in a subsequent video.
Takeaways
- 🧠 The nervous system and the endocrine system are crucial for communication within the body.
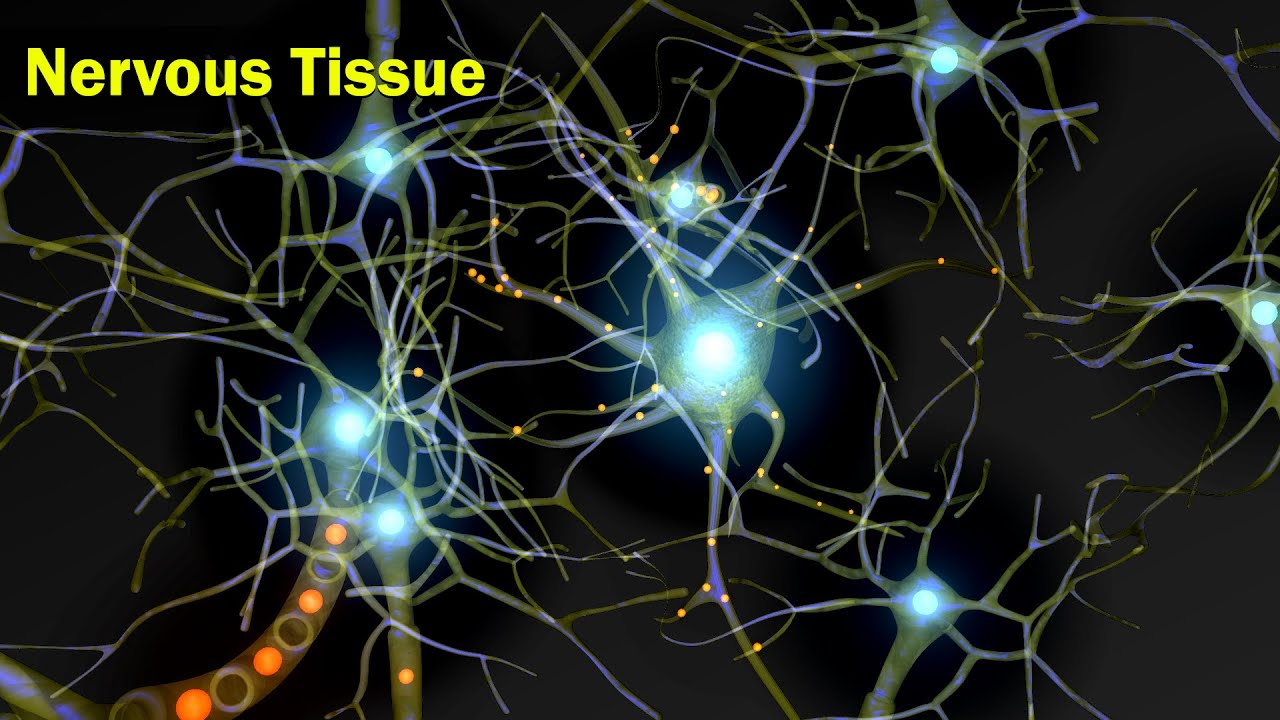
- 🌐 Neurons, also known as nerve cells, are specialized for transmitting electrical impulses and have a distinctive long, thin structure with branch connections.
- 🔗 Synapses are the junctions between neurons, facilitating communication through the release of chemicals that trigger electrical impulses in the next neuron.
- 🧬 The human body contains approximately 100 billion neurons, which when networked, form the complex nervous system.
- 🧠 The central nervous system, composed of the brain and spinal cord, is responsible for processing sensory information and issuing commands to the body.
- 👀 Sensory neurons carry information from various receptors throughout the body to the central nervous system, such as temperature changes and carbon dioxide levels.
- 🏃♂️ Motor neurons transmit signals from the central nervous system to effectors, which can be muscles or glands, instructing them to contract or release substances.
- 🔄 The nervous system works in concert with the endocrine system to maintain homeostasis and respond to environmental changes.
- 🏃 Reflex arcs are automatic, rapid responses to stimuli, such as pulling your hand away from a hot surface, and involve a specific nerve pathway.
- 🔎 The reflex arc process involves sensory neurons detecting stimuli, relay neurons processing the information in the spinal cord, and motor neurons executing the response.
Q & A
What are the two organ systems in humans that enable communication between different body parts?
-The two organ systems are the nervous system and the endocrine system.
What is the basic unit of the nervous system?
-The basic unit of the nervous system is the neuron, also known as a nerve cell.
What is the function of a neuron?
-A neuron carries electrical impulses from one point to another, acting as a biological wire to transmit signals.
How does one neuron communicate with another?
-One neuron communicates with another through a synapse, where an electrical impulse triggers the release of chemicals that cross the gap and trigger an impulse in the next neuron.
What is the central nervous system composed of?
-The central nervous system is composed of the brain and the spinal cord, where 'thinking' takes place and sensory information is processed.
What is the role of sensory neurons in the nervous system?
-Sensory neurons carry information from receptors all over the body to the central nervous system, such as changes in temperature or carbon dioxide levels in the bloodstream.
How does the central nervous system send out orders to the rest of the body?
-The central nervous system sends out orders via motor neurons to effectors, which are typically muscles or glands, instructing them to contract or release hormones.
What is a reflex arc and why is it important?
-A reflex arc is the nerve pathway underlying unconscious reflexes, such as pulling your hand away from a hot pan. It is important because it allows rapid, automatic responses to stimuli, helping to avoid injury.
Can you describe the process of a reflex arc using the example of touching a sharp object?
-When touching a sharp object, receptor cells in the skin detect the pressure, a sensory neuron carries the impulse to the spinal cord, a relay neuron passes it to a motor neuron, and the effector, like the bicep, contracts to move the hand away.
What happens at a synapse between different neurons?
-At a synapse, the electrical signal is temporarily converted to a chemical signal to be passed between different nerve cells.
Outlines

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنMindmap

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنKeywords

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنHighlights

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنTranscripts

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنتصفح المزيد من مقاطع الفيديو ذات الصلة
Nervous Tissue | Structural Organization in Animals | Anatomy | Inter 2nd year Class 11 Biology

The Nervous System In 9 Minutes

vidio kelompok 1 mata kuliah ilmu biomedik dasar

As grandes vias aferentes e eferentes: Introdução e vias aferentes - Parte 1

Sistem Saraf Pada Manusia| Sistem Koordinasi part 1 - Biologi

The Nervous System, Part 1: Crash Course Anatomy & Physiology #8
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
