Kinetic Energy and Potential Energy
Summary
TLDRThis educational video delves into the concepts of kinetic and potential energy. It explains kinetic energy as the energy of motion, formulating it as \( \frac{1}{2}mv^2 \) where 'm' is mass and 'v' is velocity, resulting in joules. The video illustrates how kinetic energy changes with mass and velocity, doubling with mass and quadrupling with velocity. It then explores potential energy, particularly gravitational potential energy, defined as \( mgh \) with 'g' being gravitational acceleration. An example calculates the potential energy of a 10 kg ball 50 meters above the ground, concluding with 4900 joules. The video also touches on elastic potential energy and the spring constant, offering a foundational understanding of these physics topics.
Takeaways
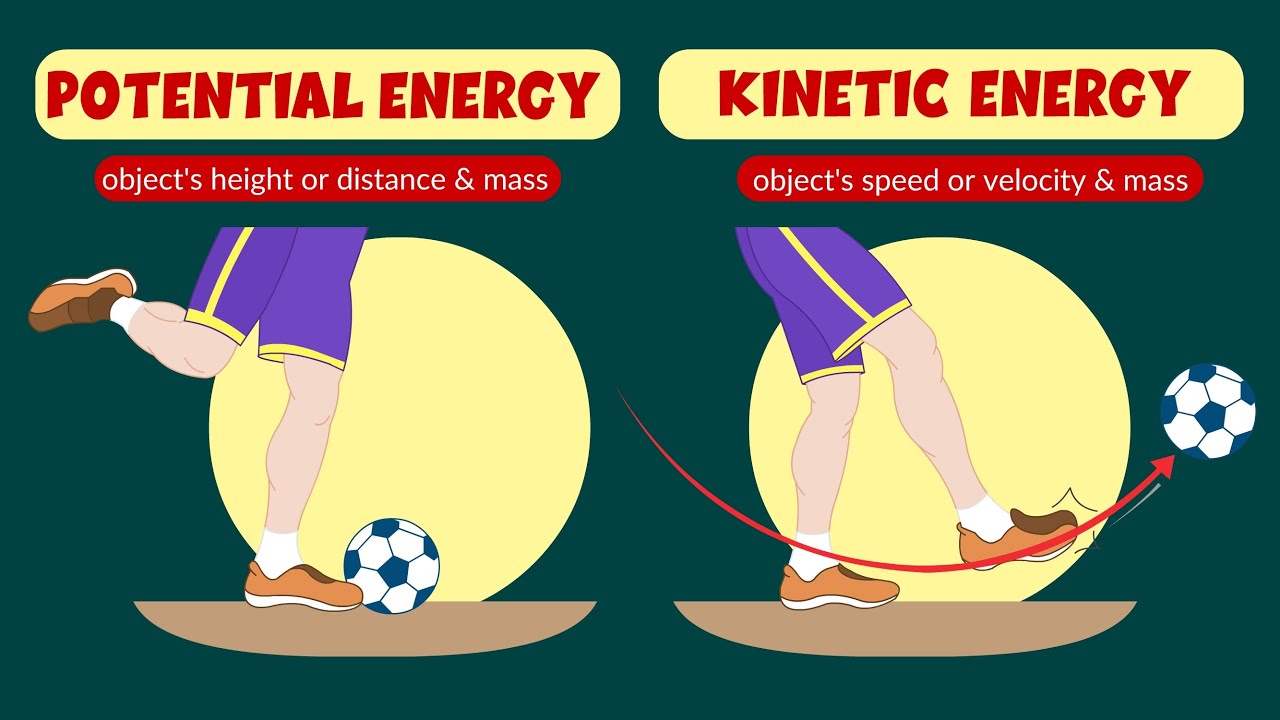
- 🏃 Kinetic energy is the energy of motion, and it's present in any object that has mass and is moving.
- 🔢 The formula for kinetic energy is \( KE = \frac{1}{2} m v^2 \), where \( m \) is mass in kilograms and \( v \) is velocity in meters per second.
- 📈 Doubling the mass of an object doubles its kinetic energy, and doubling the speed quadruples it.
- 📉 Potential energy is stored energy due to an object's position, such as height above the ground.
- 📚 The formula for gravitational potential energy is \( mgh \), where \( g \) is the acceleration due to gravity (9.8 m/s²).
- 🔄 As an object falls, its gravitational potential energy decreases while its kinetic energy increases, illustrating energy conservation.
- 🎾 A 10 kg ball 50 meters above the ground has 4900 joules of potential energy, calculated using \( mgh \).
- 📉 At the point just before hitting the ground, all potential energy is converted into kinetic energy, which can be calculated using the kinetic energy formula.
- 🌟 The speed of the ball just before impact can be found using the kinetic energy formula and solving for velocity.
- 🔗 There are various forms of potential energy, including elastic potential energy, which is stored when a spring is compressed or stretched.
Q & A
What is kinetic energy?
-Kinetic energy is the energy of an object in motion. It depends on the mass and the speed of the object, and is calculated using the formula KE = 0.5 * m * v^2, where m is the mass in kilograms and v is the speed in meters per second.
How does the kinetic energy change if the mass of an object is doubled?
-If the mass of an object is doubled, the kinetic energy will also double, assuming the speed remains constant.
What happens to the kinetic energy if the speed of an object is doubled?
-If the speed of an object is doubled, the kinetic energy will quadruple, assuming the mass remains constant.
How does the kinetic energy change when both the mass and speed of an object are increased?
-If the mass is increased by a factor of 3 and the speed is quadrupled, the kinetic energy will increase by a factor of 48, calculated as 3 * (4^2).
What is potential energy?
-Potential energy is the stored energy an object possesses due to its position relative to other objects. It can be released to do work, such as gravitational potential energy when an object falls.
What is the formula for gravitational potential energy?
-The formula for gravitational potential energy is mgh, where m is the mass in kilograms, g is the gravitational acceleration (approximately 9.8 m/s^2), and h is the height above the ground in meters.
How is the potential energy of an object related to its height above the ground?
-The potential energy of an object is directly related to its height above the ground. The higher the object, the more potential energy it has, assuming the mass is constant.
What is the relationship between potential energy and kinetic energy during the fall of an object?
-As an object falls, its potential energy decreases while its kinetic energy increases. This is due to the conversion of potential energy into kinetic energy as the object accelerates towards the ground.
How can you find the speed of an object just before it hits the ground if you know its potential energy at a certain height?
-You can find the speed of an object just before it hits the ground by using the conservation of energy principle. If you know the potential energy at a certain height, you can equate it to the kinetic energy at the ground level and solve for the speed using the kinetic energy formula KE = 0.5 * m * v^2.
What is elastic potential energy and how is it calculated?
-Elastic potential energy is the stored energy in a spring when it is stretched or compressed. It is calculated using the formula 0.5 * k * x^2, where k is the spring constant in newtons per meter and x is the displacement from the spring's equilibrium position in meters.
What does the spring constant (k) represent in the context of elastic potential energy?
-The spring constant (k) represents the stiffness of the spring. A higher spring constant indicates a stiffer spring that requires more force to stretch or compress the same distance compared to a spring with a lower spring constant.
Outlines

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنMindmap

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنKeywords

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنHighlights

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنTranscripts

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنتصفح المزيد من مقاطع الفيديو ذات الصلة

Grade 8 Science Q1 Ep6: Potential Energy and Kinetic Energy

Bill Nye The Science Guy on Energy

Bentuk- bentuk Energi Kelas 10 Kurikulum Merdeka

Work and Energy | Grade 8 Science DepEd MELC Quarter 1 Module 3 Part 2 Potential Energy
Potential and kinetic energy - Law of conservation of energy - Video for kids

Belajar IPA - Energi Kinetik, Potensial dan Mekanik Kelas 7 SMP/MTs #Energi #energikinetik
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
