Gerak Parabola - Fisika Kelas 10 (Quipper Video)
Summary
TLDRThe video script introduces the concept of parabolic motion in physics, focusing on projectile motion. It explains that parabolic motion is a combination of uniform linear motion (ULM) and uniformly accelerated linear motion (UACM). The script discusses the importance of understanding the definitions and formulas related to ULM and UACM, particularly the equations for vertical projectile motion. It also covers how to analyze projectile motion by breaking it down into horizontal and vertical components, using trigonometric functions to determine initial velocity projections. The video aims to help viewers understand and solve problems involving parabolic motion.
Takeaways
- 📚 The script introduces the concept of parabolic motion in physics, focusing on its definition and analysis.
- 🔍 Parabolic motion is described as the path of an object moving in a trajectory shaped like a parabola, resulting from the combination of two types of motion: uniform linear motion (ULM) and uniformly accelerated linear motion (UACM).
- 📐 The script explains that ULM involves an object moving at a constant velocity, while UACM involves an object moving with a constant acceleration, typically due to gravity.
- 🎯 Key formulas for ULM include the relationship between velocity, time, and displacement, often summarized as 'velocity times time equals distance'.
- 📈 For UACM, the script emphasizes three important equations: the displacement-time formula, the velocity-time formula, and the relationship between displacement, initial velocity, and acceleration.
- 🚀 The concept of projectile motion, a specific type of parabolic motion, is introduced, where an object is given an initial velocity at an angle to the horizontal.
- 📏 The script discusses how to break down the initial velocity into its horizontal (v0x) and vertical (v0y) components using trigonometric functions.
- 📉 The vertical component of projectile motion is analyzed using the UACM equations, taking into account the effect of gravity, which is represented as a negative acceleration.
- 🛤️ The horizontal component of projectile motion is considered to be in ULM, meaning the horizontal velocity remains constant throughout the motion.
- 📏 The script also covers how to calculate the maximum horizontal distance (x) an object can travel in parabolic motion using the ULM formula.
- 🔢 Finally, the script touches on how to determine the velocity of an object at any arbitrary point in its parabolic trajectory by combining the horizontal and vertical velocities.
Q & A
What is the definition of parabolic motion according to the script?
-Parabolic motion is the movement of an object that follows a parabolic trajectory, resulting from the combination of uniform linear motion (GLB) and uniformly accelerated motion (GLBB).
What are GLB and GLBB as described in the script?
-GLB (Gerak Lurus Beraturan) is uniform linear motion, where an object moves with zero acceleration and constant velocity. GLBB (Gerak Lurus Berubah Beraturan) is uniformly accelerated motion, where an object moves with constant acceleration, causing its velocity to change over time.
How is the initial velocity v_0 projected onto the x and y axes in parabolic motion?
-The initial velocity v_0 is projected onto the x-axis as v_0x = v_0 cos(α) and onto the y-axis as v_0y = v_0 sin(α), where α is the angle of elevation.
What role does gravity play in parabolic motion?
-Gravity acts as the acceleration that influences the vertical component of the motion (along the y-axis), causing the velocity in the y direction v_y to decrease over time as the object rises and increase as it falls.
What is the formula for the velocity at any point in parabolic motion?
-The velocity at any point in parabolic motion can be calculated using the formula V = sqrt(v_x^2 + v_y^2), where v_x and v_y are the components of velocity along the x and y axes, respectively.
How does the script explain the concept of 'range' or horizontal distance in parabolic motion?
-The range or horizontal distance S_x is calculated using the formula S_x = v_0x × t, where v_0x is the horizontal component of the initial velocity, and t is the time of flight.
What are the key differences between GLB and GLBB highlighted in the script?
-GLB involves motion with constant velocity and no acceleration, whereas GLBB involves motion with constant acceleration, causing the velocity to change over time.
How does the script relate parabolic motion to real-life examples?
-The script mentions that parabolic motion is commonly observed in scenarios like the motion of a projectile or a ball, where the object follows a curved path due to the combination of horizontal motion and the effect of gravity.
What is the significance of the angle of elevation in parabolic motion?
-The angle of elevation α determines the initial projection of the velocity components along the x and y axes. It influences the shape of the parabolic trajectory and the range of the motion.
What is the importance of the time of flight in analyzing parabolic motion?
-The time of flight is crucial for determining the overall duration of the motion and calculating the range. It is influenced by the initial velocity and the angle of elevation.
Outlines

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنMindmap

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنKeywords

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنHighlights

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنTranscripts

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنتصفح المزيد من مقاطع الفيديو ذات الصلة
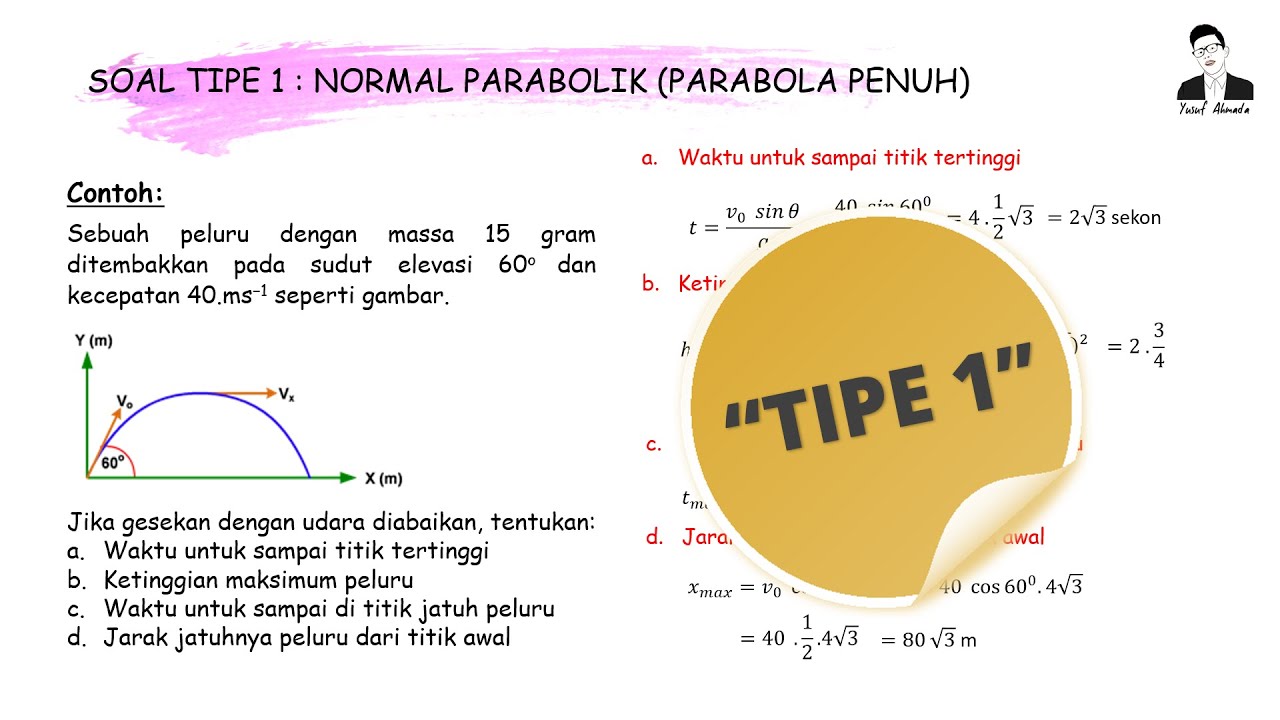
FISIKA KELAS X || CONTOH SOAL GERAK PARABOLA TIPE 1 (Parabola Penuh)
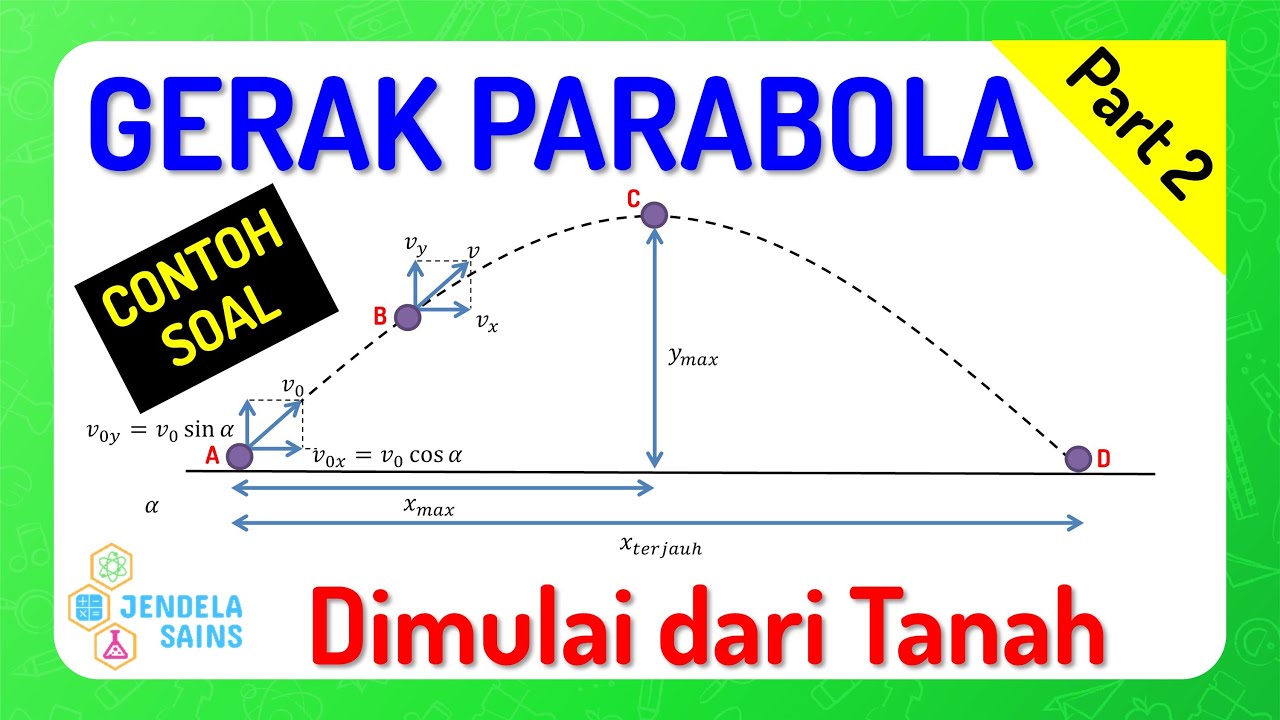
Gerak Parabola • Part 2: Contoh Soal Gerak Parabola Dimulai dari Tanah
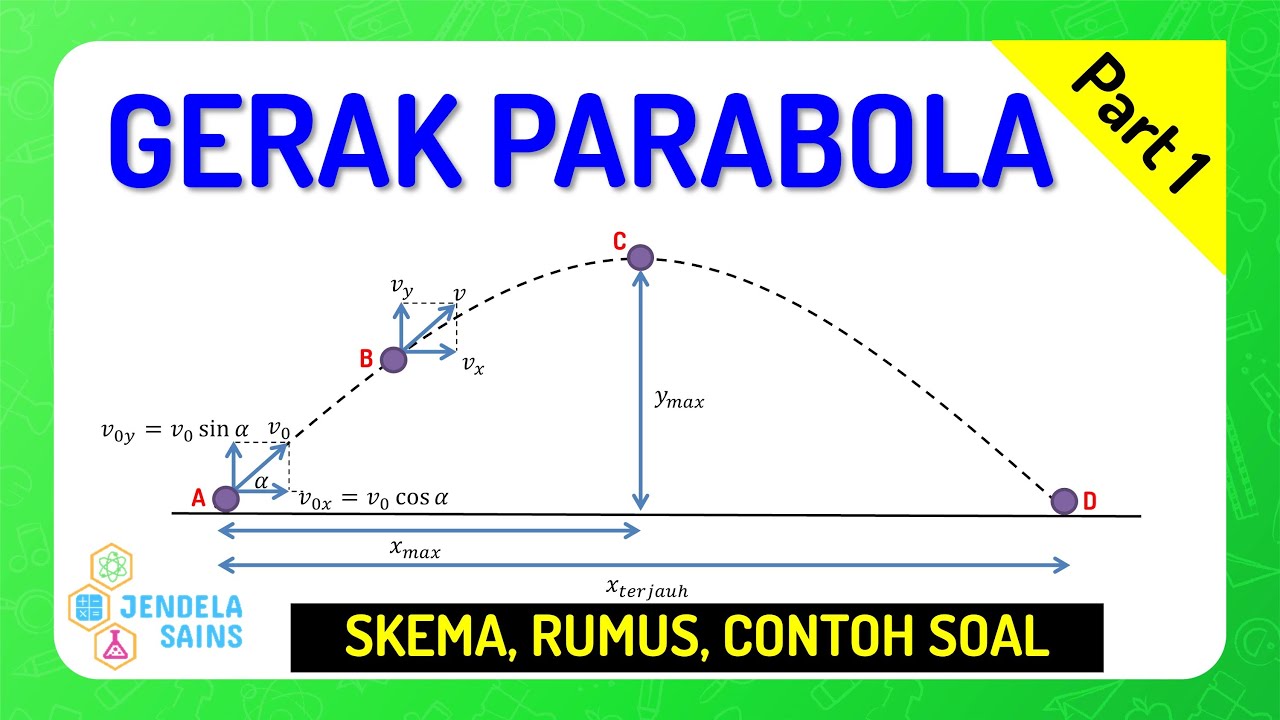
Gerak Parabola • Part 1: Konsep, Skema, dan Rumus Gerak Parabola
kinematics 6of6 projectile motion final

Der waagerechte Wurf - tolles Experiment

BAB V Gerak Parabola
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
