Economic Alliances P2
Summary
TLDRThis video script delves into the dynamics of economic alliances, focusing on BRICS and ASEAN, exploring their goals, achievements, and challenges. It discusses BRICS' impact on global economic growth and political cooperation, ASEAN's pursuit of regional stability and economic integration, and introduces the MINT countries as emerging economies with significant potential. The script highlights the importance of these alliances in shaping the global economic landscape and the geopolitical influence of non-Western powers.
Takeaways
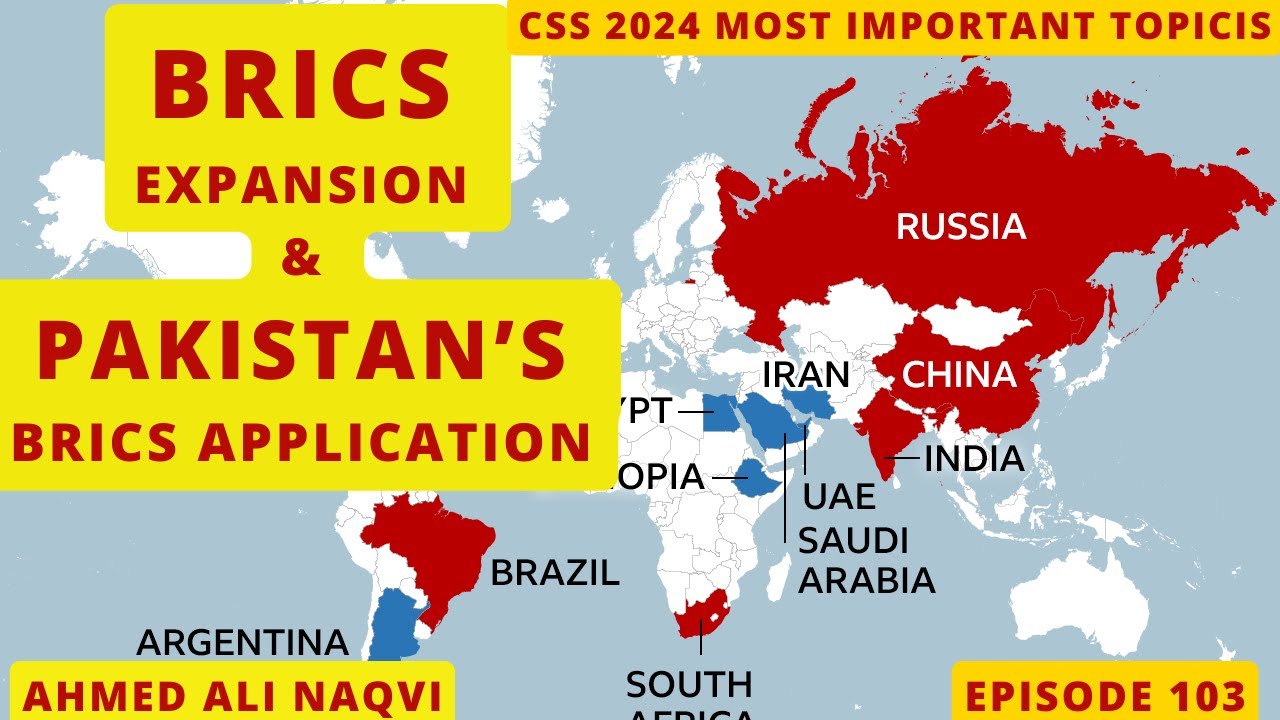
- 🌐 The BRICS alliance (Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa) aims to promote economic growth, political cooperation, and a collective voice to challenge Western powers.
- 📚 The concept of BRICS was first introduced in 2001, highlighting the economic potential of Brazil, Russia, India, and China, with South Africa joining later in 2010.
- 💼 The BRICS countries have established the New Development Bank (NDB) and a Contingent Reserve Arrangement (CRA) to provide financial support and alternatives to Western-dominated financial institutions.
- 🔄 BRICS seeks to reduce reliance on the US dollar by promoting trade in national currencies and has expanded to include Argentina, Egypt, Ethiopia, Iran, Saudi Arabia, and UAE in 2023.
- 🌍 ASEAN (Association of Southeast Asian Nations) was established in 1967 to promote economic growth, social progress, and regional stability among its 10 member states.
- 🛍️ ASEAN has pursued free trade agreements and the establishment of a single market and production base to enhance economic integration and reduce trade barriers.
- 🏗️ Infrastructure development is a priority for ASEAN to improve connectivity and reduce logistical challenges, promoting economic activities within the region.
- 🤝 ASEAN faces challenges such as sovereignty issues, differing political systems, and varying levels of development, which can affect consensus and cooperation.
- 🌟 The MINT countries (Mexico, Indonesia, Nigeria, and Turkey) are considered as emerging economies with significant potential for growth, based on demographic, geographic, and economic factors.
- 🌱 The concept of MINT highlights the diversification of global economic influence and the importance of emerging markets in international economic discussions.
- 🔑 MINT showcases market opportunities for businesses and investors, emphasizing the collective strength and potential of these four nations in the global economy.
Q & A
What are the main goals of BRICS alliance?
-The main goals of the BRICS alliance are to promote economic growth, political cooperation, and to develop a collective voice on the global stage capable of challenging Western powers.
Which countries are part of the BRICS alliance?
-The BRICS alliance is composed of Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa.
When was the concept of BRICS first introduced?
-The concept of BRICS was first introduced in 2001 in a paper that highlighted the significant economic growth potential of Brazil, Russia, India, and China.
What was the significance of the 2009 BRICS Summit held in Russia?
-The 2009 BRICS Summit marked the beginning of coordinated efforts among Brazil, Russia, India, and China to strengthen economic cooperation and political collaboration.
How did South Africa's inclusion in BRICS impact the group?
-South Africa's inclusion in BRICS expanded the organization and added an African perspective to the group's discussions, increasing its geographical diversity.
What are the three main economic mechanisms used by BRICS to promote growth among member countries?
-The three main economic mechanisms used by BRICS include trade and economic partnerships, the New Development Bank for financing infrastructure and sustainable development projects, and promoting trade in national currencies to reduce reliance on the US dollar.
What is the New Development Bank (NDB), and what is its purpose?
-The New Development Bank, formerly known as the BRICS Development Bank, was established to finance infrastructure and sustainable development projects in member countries and other emerging economies, providing an alternative to Western-dominated financial institutions.
What is the purpose of the Contingent Reserve Arrangement (CRA) within BRICS?
-The CRA was created to provide financial support to member countries facing balance of payments problems or currency crises, aiming to create financial stability.
What are the challenges faced by BRICS in terms of economic disparities among member countries?
-Economic disparities among BRICS member countries can lead to unequal benefits from the group's initiatives and hinder effective collaboration due to varying levels of development and economic structures.
How does the concept of MINT differ from the formal alliances like BRICS and ASEAN?
-MINT is more of a concept rather than a formal political or economic alliance. It is based on the potential for future growth of Mexico, Indonesia, Nigeria, and Turkey, and does not have formal structures or specific objectives like BRICS and ASEAN.
What are the main goals of ASEAN, and how do they achieve them?
-ASEAN's main goals are to promote economic growth, social progress, and regional stability. They achieve these through mechanisms such as free trade agreements, the ASEAN Economic Community, infrastructure development, and capacity building in human capital.
What are some of the criticisms faced by ASEAN in terms of their mechanisms and effectiveness?
-ASEAN faces criticisms such as weak enforcement mechanisms, non-binding agreements, varying levels of commitment from member states, and limited dispute resolution mechanisms, which can undermine the effectiveness of their economic integration and goal achievement.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频

A GEOPOLÍTICA DO BRICS - THIAGO DE ARAGÃO

Setiap ALIANSI Di Dunia Dijelaskan Dalam 8 MENIT!

Proyeksi Menkeu Soal Serangan Tarif dari Trump Terbukti, Kini Krisis dan Stagflasi Menanti

Geografi Kelas XII (14) Regionalisasi Kawasan Dunia Berdasarkan Pertumbuhan Ekonomi | Regionalisasi
CSS 2024: BRICS EXPANSION & PAKISTAN'S BID TO JOIN BRICS I Ahmed Ali Naqvi I Episode 103

Economic Alliances Part 1
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
