Conceitos básicos de genética - Biologia - Ensino Médio
Summary
TLDRIn this lecture, Professor Andrei explains key genetic concepts, beginning with chromosomes as condensed DNA and the distinction between autosomal and sex chromosomes. He delves into genes, highlighting their role in protein production through transcription and translation. The lecture also covers dominant and recessive genes, genotype and phenotype, and the influence of the environment on phenotype. Additionally, terms like homologous chromosomes, homozygous, and heterozygous are clarified. The professor emphasizes that understanding these fundamentals is essential for grasping how genetics shape traits in organisms.
Takeaways
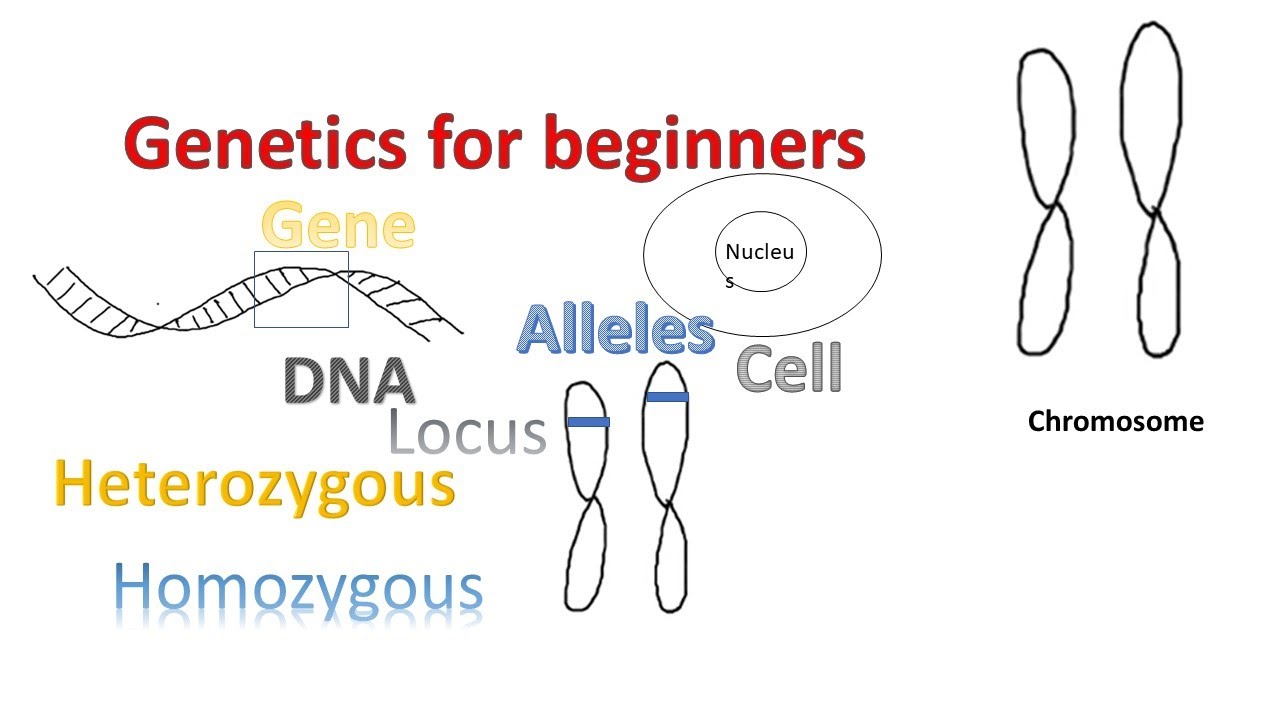
- 😀 A chromosome is a condensed form of DNA, containing a sequence of genes.
- 😀 Genes are fragments of DNA that carry information to produce proteins.
- 😀 Autosomal chromosomes carry structural information about the body and are not related to sex determination.
- 😀 Sex chromosomes are responsible for determining the biological sex of an individual.
- 😀 Homologous chromosomes are identical in size, shape, and gene sequence, and they pair with each other during reproduction.
- 😀 Alleles are different versions of the same gene, found on homologous chromosomes in the same location.
- 😀 Genotype refers to the genetic makeup of an organism, while phenotype refers to the physical expression of genetic traits.
- 😀 A dominant gene only requires one copy to express its trait, whereas a recessive gene requires two copies to be expressed.
- 😀 Dominant genes are represented by uppercase letters, while recessive genes are represented by lowercase letters.
- 😀 Homozygous individuals have two identical alleles (either both dominant or both recessive), while heterozygous individuals have one dominant and one recessive allele.
- 😀 The environment can influence the phenotype, meaning that external factors can affect how genetic traits are expressed.
Q & A
What is a chromosome in the context of genetics?
-A chromosome is a condensed form of DNA. It is created when DNA is tightly packed into a structure, making it easier for the cell to manage during processes like cell division.
What is the relationship between chromosomes and genes?
-Chromosomes are made up of genes. A chromosome is essentially a long, linear sequence of genes, which are the segments of DNA that contain the information necessary for building proteins.
What is the purpose of a gene in genetics?
-A gene is a fragment of DNA that carries the information needed to produce a protein. It is like a recipe for creating a specific protein that the body needs.
What are autosomal chromosomes?
-Autosomal chromosomes are chromosomes that are not related to sex determination. They carry information about the structure and functioning of the body and are identical in both males and females.
What is the difference between autosomal and sex chromosomes?
-Autosomal chromosomes contain genetic information that is unrelated to the sex of an individual. Sex chromosomes, on the other hand, determine the genetic traits related to sex, like whether an individual will be male or female.
What are homologous chromosomes?
-Homologous chromosomes are pairs of chromosomes that are identical in size, shape, and genetic sequence. Each homologous chromosome carries the same genes in the same positions, one inherited from the mother and one from the father.
What is the difference between genotype and phenotype?
-Genotype refers to the genetic makeup of an individual, or the specific genes they carry. Phenotype is the physical manifestation or trait that results from the genotype, such as eye color or hair type.
What is a dominant gene?
-A dominant gene is one that expresses its trait in the phenotype even when only one copy of the gene is present. If a dominant allele is present in a genotype, the associated characteristic will prevail.
What is a recessive gene?
-A recessive gene only expresses its trait in the phenotype if both copies of the gene are recessive. For example, a person must inherit two recessive alleles for a recessive trait (e.g., blue eyes) to appear.
What is the significance of homozygosity and heterozygosity in genetics?
-Homozygosity refers to having two identical alleles for a gene, either both dominant or both recessive. Heterozygosity refers to having two different alleles for a gene, one dominant and one recessive. These genetic combinations influence whether a dominant or recessive trait will be expressed.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级5.0 / 5 (0 votes)