The Gram Stain (Gram-Positive vs Gram-Negative) and Bacterial Structure | Microbiology 🧫
Summary
TLDRIn this video, Mitochosis explains the Gram stain technique and the structural differences between Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. He describes the significance of bacterial cell walls, membranes, and key components like peptidoglycan, lipopolysaccharides, and teichoic acid. The video delves into the Gram stain process, where Gram-positive bacteria appear purple due to their thick peptidoglycan walls, while Gram-negative bacteria turn pink after the crystal violet stain is washed away. Mitochosis also touches on how antibiotics like penicillin work and bacterial resistance mechanisms, preparing viewers for deeper dives into microbiology and pharmacology in future videos.
Takeaways
- 😀 The Gram stain is a technique used to differentiate between gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria based on their cell wall structure.
- 😀 Gram-positive bacteria have thick peptidoglycan layers in their cell walls, which retain the purple color of the crystal violet stain, while gram-negative bacteria have thinner peptidoglycan layers and do not retain the stain.
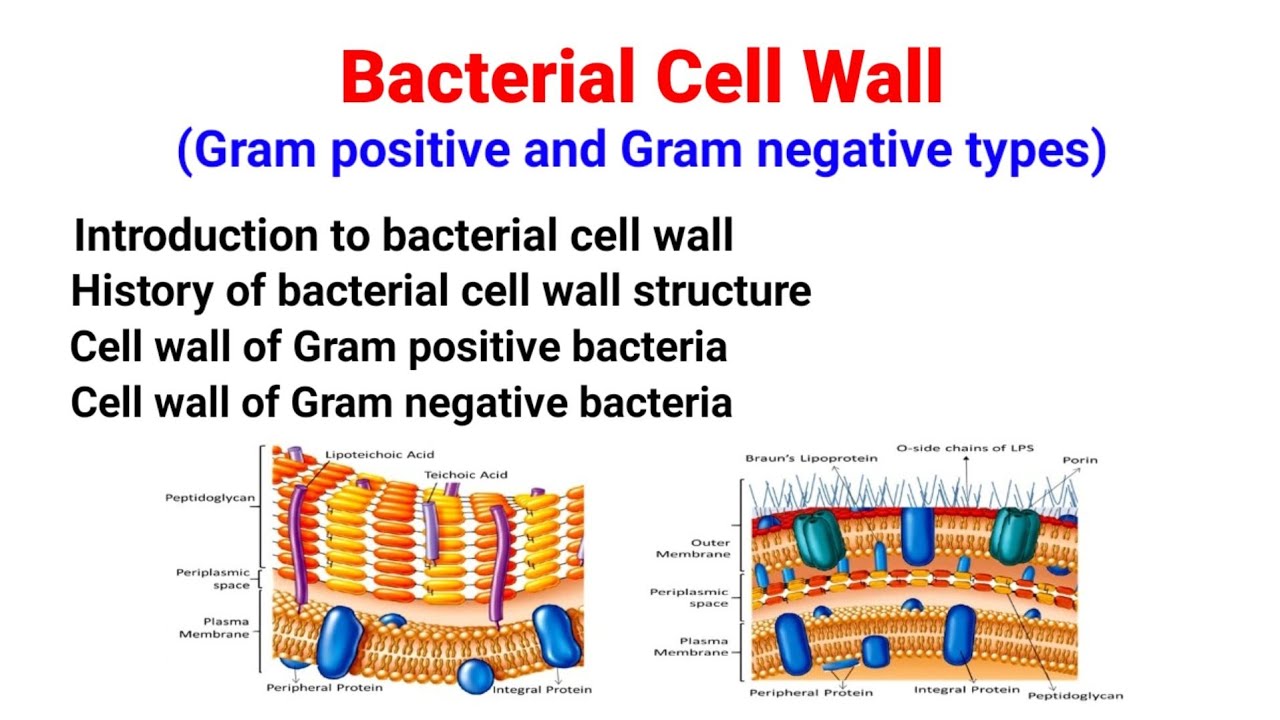
- 😀 The key difference between gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria lies in their cell structure, where gram-negative bacteria also have an outer membrane and periplasmic space.
- 😀 Gram-negative bacteria contain lipopolysaccharides (LPS) in their outer membrane, which are toxic (endotoxins) and can cause fever and inflammation in the human body.
- 😀 The outer membrane of gram-negative bacteria features protein pores (porins) for molecule transport, distinguishing it from gram-positive bacteria, which lack an outer membrane.
- 😀 Penicillin works by binding to penicillin-binding proteins in bacterial cell membranes, preventing the synthesis of peptidoglycan, ultimately destroying the bacteria.
- 😀 Bacteria like Staphylococcus have catalase enzymes that help them break down harmful hydrogen peroxide produced by the human immune system, allowing them to evade immune responses.
- 😀 The cell wall of bacteria provides rigidity and protects against osmotic damage, while human cells rely on their cell membranes for protection against osmotic stress.
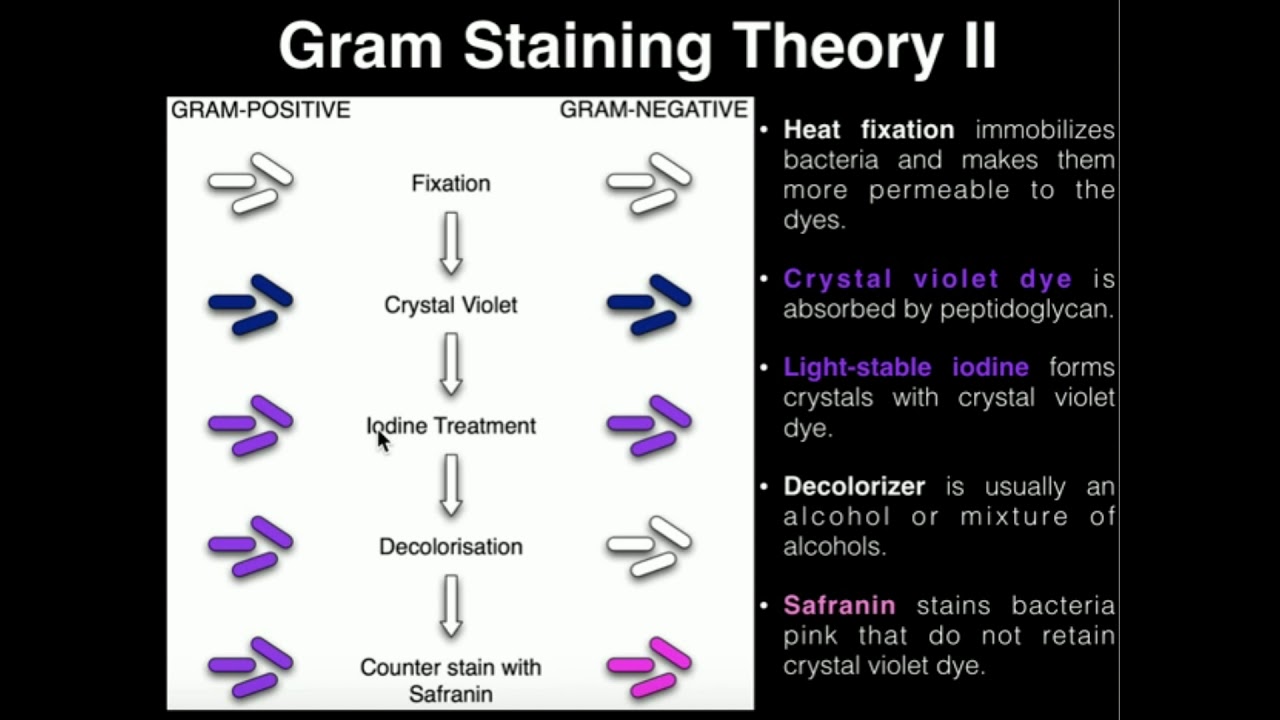
- 😀 The Gram stain involves a process of staining with crystal violet, followed by ethanol washing and counterstaining with safranin, which distinguishes gram-positive (purple) from gram-negative (pink) bacteria.
- 😀 Gram-negative bacteria can resist antibiotics like penicillin due to the presence of beta-lactamase, an enzyme that breaks down beta-lactam antibiotics and contributes to antibiotic resistance.
Q & A
What is the main purpose of the Gram stain technique?
-The Gram stain technique is used to differentiate between gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria based on the structure of their cell walls, specifically the thickness of the peptidoglycan layer.
Why do gram-positive bacteria appear purple during the Gram stain process?
-Gram-positive bacteria have a thick peptidoglycan layer in their cell wall, which retains the crystal violet stain, making them appear purple after the procedure.
What is the role of the outer membrane in gram-negative bacteria?
-The outer membrane in gram-negative bacteria serves as an additional protective layer, containing lipopolysaccharides (LPS) and porins that control the passage of molecules into and out of the cell.
What makes gram-negative bacteria more resistant to antibiotics like penicillin?
-Gram-negative bacteria are more resistant to antibiotics because they possess an outer membrane that acts as a barrier, and they may produce enzymes like beta-lactamase, which can neutralize antibiotics.
What is the difference between peptidoglycan in gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria?
-Peptidoglycan in gram-positive bacteria is thick and multilayered, whereas in gram-negative bacteria it is thinner and found in the periplasmic space between the inner and outer membranes.
What is lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and how does it contribute to the virulence of gram-negative bacteria?
-Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) is a component of the outer membrane in gram-negative bacteria. It acts as an endotoxin, triggering immune responses such as fever and inflammation, and can contribute to the severity of infections.
How does the Gram stain process differentiate between gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria?
-The Gram stain uses crystal violet to initially stain all bacteria purple, followed by ethanol treatment. In gram-negative bacteria, the ethanol washes out the stain due to their thinner cell wall, while in gram-positive bacteria, the thick wall retains the purple stain. A counterstain is then applied, which turns gram-negative bacteria pink.
What are the functions of teichoic acid in gram-positive bacteria?
-Teichoic acid is a polymer found in the cell wall of gram-positive bacteria. It plays a role in cell wall structure, regulates ion movement, and can also be involved in bacterial adhesion and pathogenesis.
What is the significance of catalase in some gram-positive bacteria?
-Catalase is an enzyme that breaks down hydrogen peroxide, which is produced by the immune system to kill bacteria. Some gram-positive bacteria possess catalase to neutralize this harmful substance and evade immune defense mechanisms.
What is the primary function of the peptidoglycan layer in bacterial cell walls?
-The peptidoglycan layer provides structural support to the bacterial cell, helping to maintain its shape and protect it from osmotic damage.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频
Microbiology: Gram Staining

PlantEd Digital Learning Library - Gram Stain Procedure

How to prepare the perfect Gram stain - Gram staining procedure

GRAM POSITIVE VS GRAM NEGATIVE BACTERIA

Introduction To Microbiology
Bacterial Cell Wall | Gram positive & Gram negative bacteria cell wall| Structure|Salient features|
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
