Campo Elétrico | ELETROSTÁTICA
Summary
TLDRThis educational video explains the concept of electric fields and electric force. The speaker clarifies that the electric field is a property of a region, unaffected by the charge placed there. By multiplying the charge by the electric field, one can calculate the electric force on that charge. The speaker uses the analogy of gravitational force to help viewers understand the relationship between electric fields and forces. Additionally, electric field lines are briefly discussed, and the video emphasizes how charges experience different forces depending on their size. The speaker encourages interaction and follows for further learning.
Takeaways
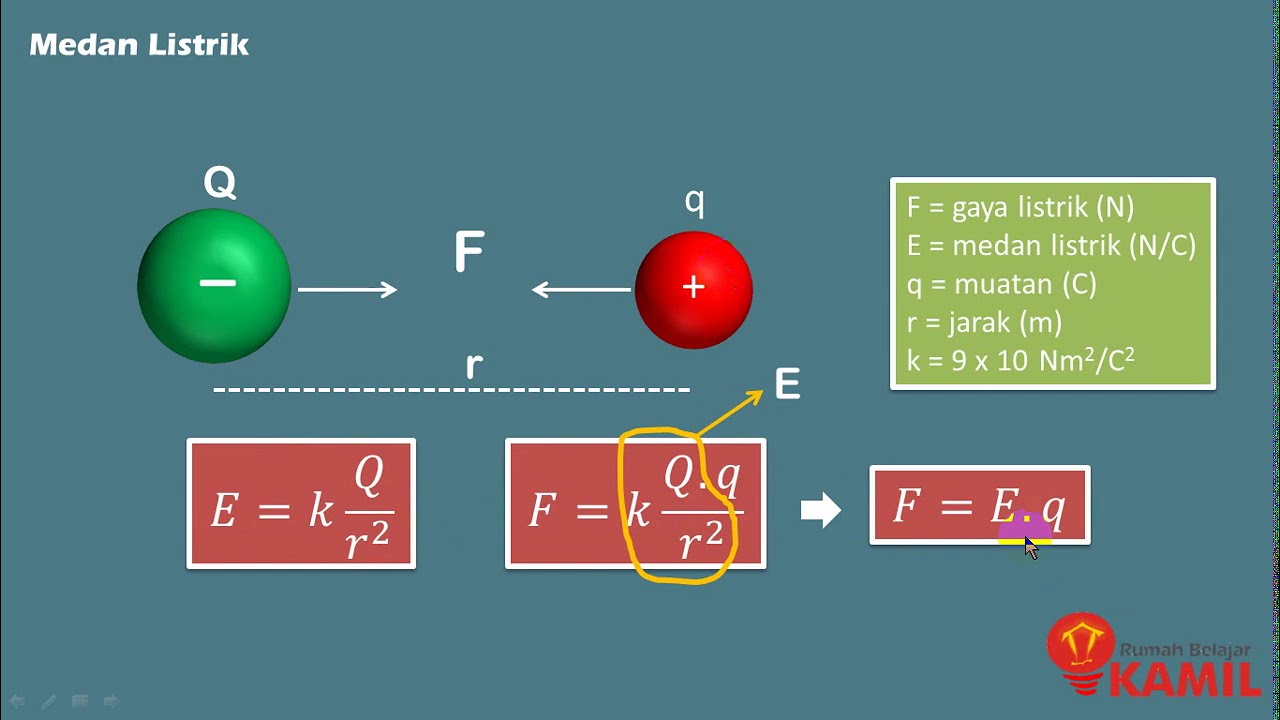
- 😀 The electric force on a charge is calculated by multiplying the charge's value by the electric field at that location.
- 😀 The electric field at a particular point remains constant, regardless of the presence of charges in that location.
- 😀 The force on a charge depends on the magnitude of the charge and the electric field at that point.
- 😀 A 1 C charge experiences 100,000 N of force in a specific electric field, while a 2 C charge experiences 200,000 N, and so on.
- 😀 The electric field in a region is not affected by the test charge but only by the source charge creating the field.
- 😀 The concept of electric force is analogous to the force of gravity: weight is determined by mass and gravitational field, while electric force is determined by charge and electric field.
- 😀 The electric field is a property of the region, like gravity, and does not change based on what is placed there.
- 😀 The electric force equation (F = qE) is similar to the equation for weight (F = mg), where electric field and gravity replace each other.
- 😀 The electric field at a point is the same regardless of the charge placed there, but the force felt by the charge changes with its magnitude.
- 😀 Understanding electric fields and forces is essential for analyzing the behavior of charges in different locations.
- 😀 The video encourages interaction through liking, sharing, commenting, and subscribing for more educational content on related topics.
Q & A
What is the main concept explained in the video?
-The video explains the concept of electric fields, how they are represented, and how to calculate the force experienced by a charge placed in an electric field. The speaker draws an analogy to gravitational force to help clarify the relationship between electric fields, charge, and force.
How is the electric force calculated in the video?
-The electric force is calculated by multiplying the magnitude of the charge by the electric field at the location where the charge is placed. This can be expressed as F = q * E, where F is the force, q is the charge, and E is the electric field.
What analogy does the speaker use to explain the electric field?
-The speaker uses the analogy of gravity on Earth. Just as the gravitational field remains constant at a location (around 10 m/s²), the electric field at a given point remains constant, regardless of the charge placed there. The force on an object depends on its mass (for gravity) or charge (for electric fields), but the field itself is independent of the objects placed within it.
What happens to the electric force if the charge is increased?
-If the charge is increased, the electric force experienced by the charge also increases. This is because the force is directly proportional to the magnitude of the charge, as expressed by F = q * E.
What is the relationship between electric force and electric field as described in the video?
-The electric force is directly proportional to the electric field. The stronger the electric field at a location, the greater the force on a charge placed in that field. The field strength (E) remains constant for a given point, and the force changes as the magnitude of the charge (q) changes.
How does the speaker clarify the role of the test charge in an electric field?
-The speaker clarifies that the test charge (or probe charge) does not affect the electric field; rather, it experiences the force determined by the field. The field itself is a property of the location and is independent of the presence of any test charge.
What is the formula that represents electric force and how is it similar to the formula for weight?
-The formula for electric force is F = q * E, which is similar to the formula for weight, W = m * g, where m is mass and g is the acceleration due to gravity. In both formulas, the force is the product of a property of the object (charge or mass) and a constant (electric field or gravitational field).
What happens to the electric field when a charge is added or removed in the location?
-The electric field at a given location remains unchanged regardless of the charge placed there. What changes is the electric force experienced by the charge, which depends on the magnitude of the charge placed in the field.
What is the difference between the electric field and the force it produces?
-The electric field is a property of space around a charged object and does not change with the presence of other charges. In contrast, the electric force is the result of the interaction between the electric field and the charge placed within it. The force changes as the charge changes, but the field itself is constant at a point.
Why is it important to understand the distinction between electric field and electric force?
-Understanding the distinction is crucial for correctly interpreting how charges interact in an electric field. The electric field is a property of space created by charged objects, while the electric force depends on both the field and the charge placed in that field. This distinction helps in calculating the forces on charges and understanding the behavior of electric fields.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)