Eliminasi urine 1
Summary
TLDRThis video delves into the essential process of urine elimination in the human body, highlighting its role in removing metabolic waste through urination. It explains how the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra work together to ensure proper urine production and excretion. Factors such as diet, lifestyle, psychological stress, and medical conditions like diabetes can influence urination patterns. The video also covers common urinary disorders, including retention, incontinence, and enuresis. The content is designed to offer a comprehensive yet accessible understanding of urinary physiology and its impact on health.
Takeaways
- 😀 Urine elimination is a vital process for humans to remove metabolic waste from the body.
- 😀 A decrease in fluid intake or blood volume can reduce urine output, which is also impacted by kidney diseases.
- 😀 If urine elimination is impaired, conditions like urine retention, incontinence, and enuresis may arise.
- 😀 Urine elimination is part of a broader bodily process involving organs like the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra.
- 😀 The kidneys play a crucial role in excreting metabolic waste and regulating fluid and electrolyte balance.
- 😀 The bladder functions as a reservoir for urine produced continuously by the kidneys.
- 😀 The urethra is responsible for expelling urine from the bladder.
- 😀 Urine elimination involves complex physiological processes like bladder contraction and nerve reflexes.
- 😀 Urine output should be approximately 1 cc per kilogram per hour, with normal urine characteristics including clear, pale yellow color and a slightly aromatic scent.
- 😀 Factors such as diet, hydration, lifestyle, and stress can affect urine elimination patterns and frequency.
- 😀 Common urine elimination disorders include retention, incontinence, and enuresis, which require attention for proper treatment.
Q & A
What is urine elimination and why is it important?
-Urine elimination is the process of removing metabolic waste from the body through urine. It is important because it helps the body get rid of excess waste, maintain fluid balance, and regulate electrolytes, ensuring the body's proper functioning.
Which organs are involved in urine elimination?
-The organs involved in urine elimination include the kidneys (which filter blood and produce urine), the ureters (which transport urine to the bladder), the bladder (which stores urine), and the urethra (which expels urine from the body).
How does the process of urination occur in the body?
-Urination begins when the bladder fills with urine, causing it to stretch. This triggers nerve reflexes that signal the brain. The bladder contracts, the sphincter muscles relax, and urine is expelled through the urethra.
What factors affect urine production?
-Several factors affect urine production, including diet (such as protein and sodium intake), lifestyle habits (like delayed urination), medical conditions (such as diabetes), and psychological stress.
What are the normal characteristics of urine?
-Normal urine is typically clear, pale yellow to amber in color, has an aromatic but not foul odor, and a specific gravity between 1.016 and 1.025. The pH is slightly acidic (4.5–7.5), and it does not contain protein or blood.
How does diet influence urine production?
-Diet influences urine production by affecting the volume and composition of urine. For example, high-protein and sodium diets can alter urine output, and beverages like coffee can increase urine production.
What is the role of the kidneys in urine elimination?
-The kidneys filter blood, remove waste, and regulate the balance of fluids, electrolytes, and pH. They are responsible for producing urine as a byproduct of this filtration process.
What are common disorders related to urine elimination?
-Common disorders include urinary retention (inability to empty the bladder), urinary incontinence (difficulty holding urine), and enuresis (bedwetting). These conditions may arise from anatomical blockages, nerve damage, or infections.
What is urinary retention and how does it affect the body?
-Urinary retention is the inability to completely empty the bladder. It can lead to discomfort, urinary tract infections, and kidney damage if not treated.
How do psychological stress and lifestyle factors affect urination?
-Psychological stress can increase the frequency of urination due to heightened sensitivity to the urge. Lifestyle factors, such as having limited access to clean toilets or ignoring the urge to urinate, can also impact the frequency and effectiveness of urination.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频

Urinary System, Part 2: Crash Course Anatomy & Physiology #39

GINJAL DAN PEMBENTUKAN URINE | SISTEM EKSRESI MANUSIA

Biology Learning - Learn About Excretory System

Sistem Ekskresi | IPA SMP
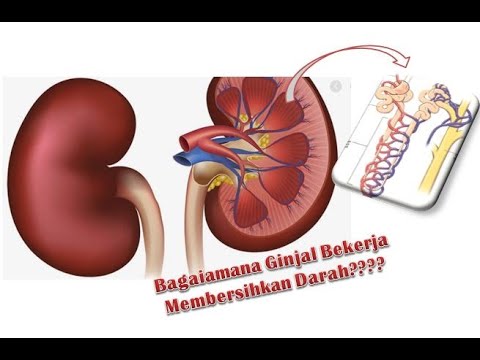
Bagaimana cara kerja ginjal dalam menyaring darah???

SISTEM EKSKRESI - Proses Pembentukan Urine ✔️ Kelas XI semester II
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
