Sistema endócrino - Introdução - Fisiologia veterinária - Aula 1
Summary
TLDRThis video introduces the fundamental concepts of endocrinology, focusing on the regulation of biological processes by the nervous and endocrine systems. It explains how hormones, chemical messengers produced by endocrine glands, regulate various physiological functions like metabolism, growth, and reproduction. The video covers the synthesis, transport, and action of hormones, highlighting their differences and mechanisms. It also delves into the role of the hypothalamus and pituitary gland in hormone regulation, feedback systems, and the circadian rhythms of hormone secretion. The content is designed to lay the foundation for a deeper understanding of the endocrine system.
Takeaways
- 😀 The nervous and endocrine systems regulate biological processes through chemical substances, like neurotransmitters and hormones.
- 😀 Hormones are produced by endocrine glands, enter the bloodstream, and act on target organs to produce biological effects.
- 😀 Hormones are classified based on their method of action: endocrine (distant target), paracrine (nearby cells), and autocrine (act on the secreting cell).
- 😀 Protein and polypeptide hormones are synthesized by ribosomes, processed in the endoplasmic reticulum, and secreted by exocytosis.
- 😀 Steroid hormones are synthesized from cholesterol, secreted immediately after synthesis, and include hormones like glucocorticoids and sex hormones.
- 😀 Amino acid derivatives, like thyroid hormones and adrenal medulla hormones, are also significant in hormonal regulation.
- 😀 Protein hormones are water-soluble and dissolve easily in the bloodstream, whereas steroid hormones are fat-soluble and require transport proteins.
- 😀 Steroid hormones enter cells, bind to receptors in the cytoplasm or nucleus, and influence gene expression to produce biological effects.
- 😀 Hormone secretion is regulated by feedback mechanisms, mainly negative feedback, which prevents excessive hormone secretion.
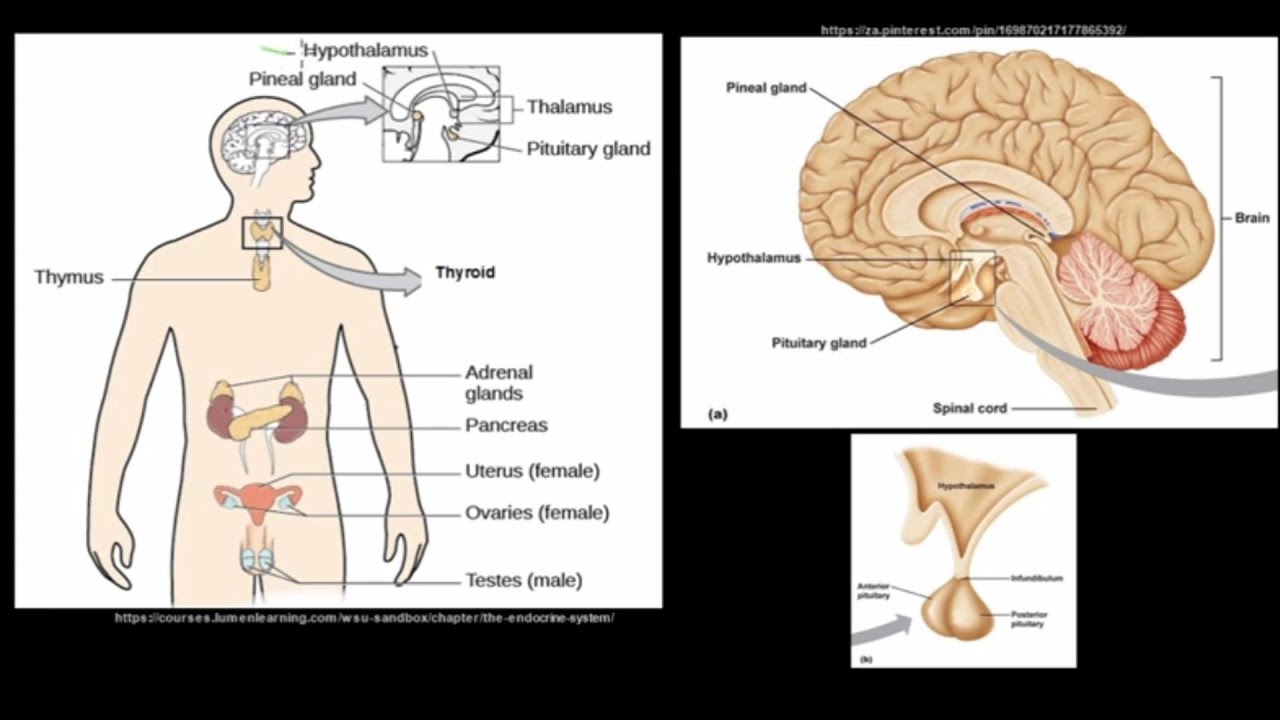
- 😀 The hypothalamus, pituitary, and adrenal glands work together in feedback loops to regulate hormones like cortisol, with the hypothalamus controlling pituitary secretion.
Q & A
What are the two main systems involved in regulating biological processes in the body?
-The two main systems involved in regulating biological processes are the nervous system and the endocrine system. The nervous system controls organic activities through neurotransmitters, while the endocrine system regulates cellular activities through hormones.
What is the role of hormones in the body?
-Hormones are chemical messengers produced by endocrine glands, released into the bloodstream, and act on target organs or tissues to promote specific biological effects. They facilitate communication between different organs or tissues.
How does the endocrine system differ from the nervous system in terms of action duration?
-The endocrine system's actions are slow and prolonged, with hormone effects lasting from minutes to days, whereas the nervous system's responses are rapid and short-lived.
What are the three types of hormone transportation?
-The three types of hormone transportation are endocrine, paracrine, and autocrine. Endocrine hormones are transported via the bloodstream, paracrine hormones act on nearby cells, and autocrine hormones affect the same cell that secreted them.
What is the primary difference between protein/polypeptide hormones and steroid hormones?
-The primary difference is that protein and polypeptide hormones are hydrophilic and transported in the plasma, whereas steroid hormones are lipophilic and require specific transport proteins to travel through the bloodstream.
How do protein and polypeptide hormones exert their effects on target cells?
-Protein and polypeptide hormones bind to receptors on the cell membrane, triggering a second messenger system (like cAMP) inside the cell, which activates a cascade of intracellular events that lead to the desired biological response.
Why don't steroid hormones need second messengers to exert their effects?
-Steroid hormones are lipophilic, allowing them to pass easily through the cell membrane. Once inside the cell, they bind to intracellular receptors, forming a complex that interacts with DNA to initiate protein synthesis and elicit biological effects.
What is the role of feedback mechanisms in hormone secretion?
-Feedback mechanisms, particularly negative feedback, regulate hormone secretion to maintain balanced levels in the body. When a hormone reaches a certain concentration, it inhibits further secretion of itself, preventing excess production.
What are some examples of hormones that follow a circadian rhythm of secretion?
-Examples of hormones that follow a circadian rhythm include cortisol, which peaks in the morning to help mobilize energy, and melatonin, which is produced at night to regulate sleep-wake cycles.
How does the hypothalamus communicate with the anterior pituitary gland?
-The hypothalamus communicates with the anterior pituitary via the hypophyseal portal system, a network of blood vessels that transports hormones released by the hypothalamus to the anterior pituitary, where they regulate the secretion of various hormones.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频

Control and Coordination Class 10 Full Chapter (Animation) | Class 10 Science Chapter 7 | CBSE
Grade 12 Life Sciences Responding to the Environment The Endocrine System

IGCSE Biology - Chapter 14 | Coordination and Response

SISTEM KOORDINASI PADA MANUSIA - KELAS XI

Chemical and Nervous Control for Plants and Animals | Group 5 of 12 - Kendall | Biology

APA ITU HOMEOSTASIS ?? - KELOMPOK 3 BIOMEDIS
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
