SAP FICO Full Tutorial in Hindi | SAP FICO for Beginners | SAP INTRODUCTION
Summary
TLDRIn this informative video, the host explains the importance of learning SAP (Systems, Applications, and Products in Data Processing) for securing a job in multinational companies. SAP is a comprehensive accounting software used to manage various business processes like finance, cost control, sales, HR, and more. The video focuses on the FICO module (Finance and Controlling), detailing its sub-modules and integration with other SAP modules. The host emphasizes that gaining proficiency in SAP is key for career growth in large organizations, with the potential to work as an end-user or consultant, especially for those with strong communication and accounting skills.
Takeaways
- 😀 SAP stands for System Applications and Products, a critical software used by multinational companies for various business processes, especially accounting.
- 😀 Learning SAP is essential for securing a job in multinational companies, as it is widely used for financial management and other business functions.
- 😀 SAP is more complex than other accounting tools like Tally or Busy, and it integrates various business modules into one system.
- 😀 The FI (Financial Accounting) module helps with recording transactions, preparing financial statements, and ensuring compliance with external and internal users.
- 😀 The CO (Controlling) module helps manage costs, evaluate efficiency, and optimize business processes.
- 😀 SAP includes modules for Material Management (MM), Sales and Distribution (SD), Human Resources (HR), Quality Management (QM), and Customer/Supplier Relationship Management (CRM, SRM).
- 😀 The General Ledger (GL) summarizes data from all other sub-modules, aiding in the preparation of financial reports like Profit & Loss and Balance Sheet.
- 😀 There are two main roles in SAP: End-User, who handles day-to-day transactions, and Consultant, who configures the system based on business needs.
- 😀 Becoming an SAP consultant requires experience and expertise in system configuration, while End-Users focus on using the software for daily tasks.
- 😀 To succeed in multinational companies, in addition to learning SAP, strong communication skills, accounting knowledge, and an excellent academic background are essential.
- 😀 Advanced Excel skills are an added advantage for those working with SAP, especially in multinational companies.
Q & A
What is SAP and why is it important for multinational companies?
-SAP (Systems, Applications, and Products in Data Processing) is an accounting and business management software used by multinational companies to integrate various business functions such as finance, procurement, and customer relationship management. It helps in streamlining complex business processes, making it essential for MNCs.
What is the key difference between SAP and other accounting software like Tally or Busy?
-SAP is more complex and comprehensive than software like Tally or Busy. While Tally or Busy typically focus on basic accounting tasks, SAP integrates multiple business processes across departments such as finance, HR, sales, and material management, making it suitable for large multinational organizations.
Can you explain the role of SAP’s FI (Financial Accounting) module?
-The FI module in SAP handles financial transactions and external reporting. It helps record accounting entries, prepare financial statements, and provide data for audits. The module ensures that financial data is managed effectively for both internal and external stakeholders.
What is the function of the CO (Controlling) module in SAP?
-The CO module is focused on cost management and controlling within an organization. It helps manage cost centers, allocate costs, and evaluate revenue and expenses, ultimately helping businesses optimize their resources and efficiency.
How does SAP’s Material Management (MM) module assist businesses?
-The MM module in SAP helps businesses manage procurement, vendor relationships, and inventory. It supports processes like ordering materials, evaluating vendors, and ensuring proper material flow within the supply chain.
What does the SD (Sales and Distribution) module cover in SAP?
-The SD module in SAP covers the entire sales and distribution process, including order management, pricing, delivery terms, and billing. It ensures that sales processes are efficiently handled from order creation to final delivery.
Why is the HR (Human Resources) module essential in SAP?
-The HR module in SAP is essential for managing employee data, payroll, time management, and other personnel-related functions. It automates various HR processes, improving efficiency and accuracy in managing human resources.
What are the sub-modules in SAP’s FI module and what do they handle?
-The FI module includes several sub-modules: Accounts Payable (AP) which manages vendor transactions, Accounts Receivable (AR) for customer billing and payments, Asset Management for asset procurement and depreciation, and Banking for handling bank transactions and reconciliations.
What does the General Ledger (GL) module do in SAP?
-The GL module in SAP serves as the central repository for all financial transactions recorded in other modules like Accounts Payable, Accounts Receivable, and Asset Management. It summarizes the financial data, enabling the creation of financial reports like balance sheets and profit & loss statements.
What career roles can someone pursue after learning SAP?
-After learning SAP, individuals can pursue roles as end users, consultants, or even SAP system administrators. As an end user, they would manage daily transactions, while as a consultant, they would configure the SAP system to meet business requirements. With experience, one can progress to higher roles in SAP implementation and support.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频

What Is SAP | SAP Training | SAP Explained In 4 Minutes | Learn SAP | The Knowledge Academy

SAP01 UNIT 1 INTRODUCTION
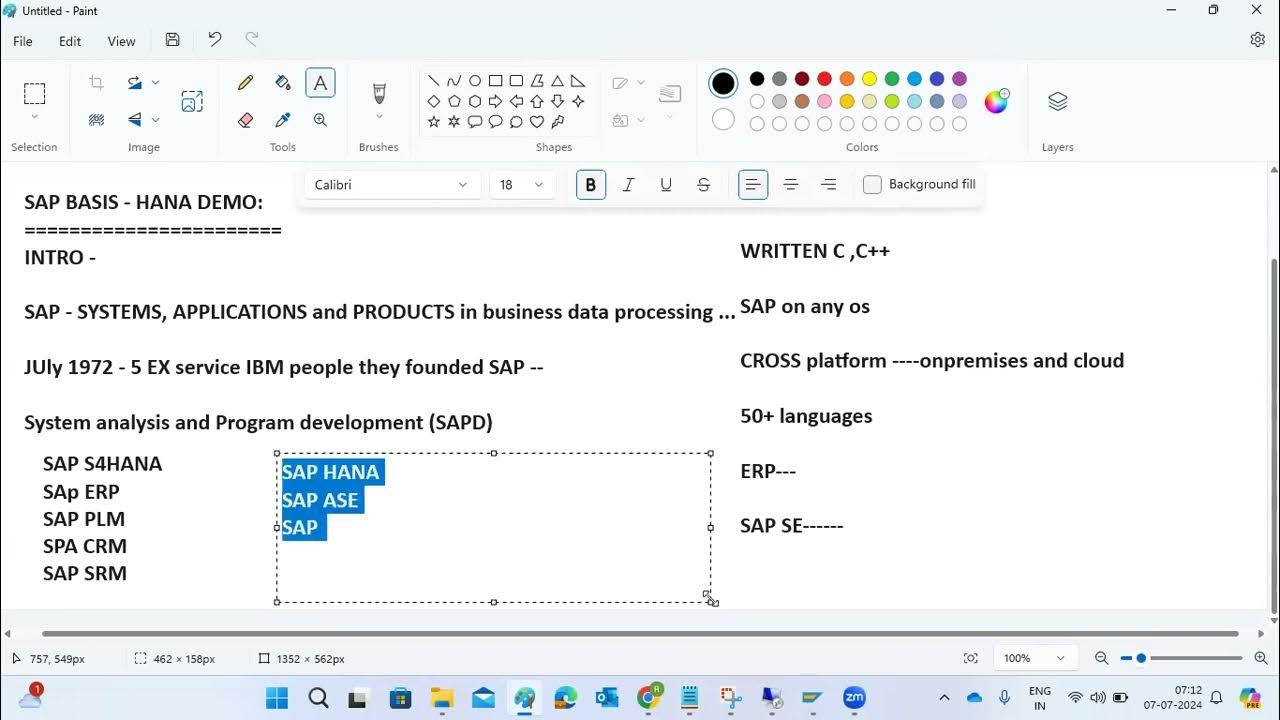
SAP BASIS & HANA - DEMO

SAP S4HANA BASIS- DEMO

Tosca Automation Jobs in 2025 | Is It Worth Learning?
What Is Version Control? | Git Version Control | Version Control In Software Engineering|Simplilearn
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
