Examples of Transmission Line | Parameters of Transmission Line | Microwave Engineering
Summary
TLDRIn this video, the presenter tackles two interesting problems related to transmission line parameters in microwave engineering. The first problem focuses on calculating the characteristic impedance, propagation constant, attenuation constant, and phase constant of a transmission line using given resistive, inductive, conductive, and capacitive components. The second problem addresses the calculation of VSWR, reflection coefficient, and load impedance for a lossless transmission line. Detailed step-by-step explanations are provided, including the use of complex numbers, polar functions, and relationships between key parameters, aiming to enhance viewers' understanding of these concepts.
Takeaways
- 😀 Understanding the parameters of a transmission line (R, L, G, C) is crucial for solving problems related to electrical engineering.
- 📏 The characteristic impedance (Z) can be calculated using the formula: Z = sqrt((R + jωL) / (G + jωC)).
- 🔄 Frequency plays a significant role in the calculations, with an operating frequency of 1 MHz in the first problem.
- 📊 Utilizing a calculator's polar function helps in determining the magnitude and angle phase of complex numbers.
- 🌊 The propagation constant (γ) consists of the attenuation constant (α) and the phase constant (β), represented as γ = α + jβ.
- 💡 In lossless transmission lines, the characteristic impedance (Z0) affects VSWR (Voltage Standing Wave Ratio) calculations.
- ⚡ VSWR is calculated by dividing the maximum voltage (Vmax) by the minimum voltage (Vmin), showcasing the effectiveness of power transfer.
- 🔗 The reflection coefficient (ρ) relates to VSWR and can be derived using the formula: ρ = (VSWR - 1) / (VSWR + 1).
- 🧮 Load impedance (ZL) can be determined using the reflection coefficient, with the equation: ρ = (ZL - Z0) / (ZL + Z0).
- ⚖ The condition of whether ZL is greater or less than Z0 influences the calculation of VSWR and the approach used to find ZL.
Q & A
What is the main topic of the video?
-The video focuses on solving two problems related to transmission line parameters, specifically in the context of microwave engineering.
What parameters are provided for the first transmission line problem?
-The parameters given include a resistance (R) of 5 ohms, inductance (L) of 1 mH, conductance (G) of 0.1 mS, capacitance (C) of 1 µF, and an operating frequency of 1 MHz.
How is the characteristic impedance calculated?
-The characteristic impedance (Z) is calculated using the formula Z = √((R + jωL) / (G + jωC)), where ω is the angular frequency (ω = 2πf).
What is the significance of using polar functions in calculations?
-Using polar functions allows for easier handling of complex numbers, enabling the calculation of magnitude and phase angles for the transmission line parameters.
What are the components of the propagation constant?
-The propagation constant consists of the attenuation constant (α) and the phase constant (β), which can be expressed as a complex number γ = α + jβ.
What is the formula for calculating the reflection coefficient?
-The reflection coefficient (ρ) can be calculated using the formula ρ = (ZL - Z0) / (ZL + Z0), where ZL is the load impedance and Z0 is the characteristic impedance.
What is the VSWR and how is it calculated?
-The Voltage Standing Wave Ratio (VSWR) is calculated as VSWR = Vmax / Vmin, where Vmax is the maximum voltage and Vmin is the minimum voltage along the transmission line.
What are the two methods mentioned for calculating load impedance?
-The two methods for calculating load impedance involve using the reflection coefficient formula and utilizing the relationship with VSWR based on the load and characteristic impedances.
What condition must be met when using the ZL > Z0 relationship in calculations?
-The condition ZL > Z0 must be satisfied for the calculation methods discussed to be valid, ensuring that the VSWR is correctly defined as ZL/Z0.
What was the final load impedance calculated in the second problem?
-The final load impedance (ZL) calculated in the second problem is approximately 125 ohms.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频

Microwave engineering interview questions & answers | MW engineer interview questions & answers

ECE3300 Lecture 8-6 quarter wave transformer

Microwave Transmission Lines | Two Parallel Wire Tx Line | Coaxial Tx Line | Microstrip Tx Line
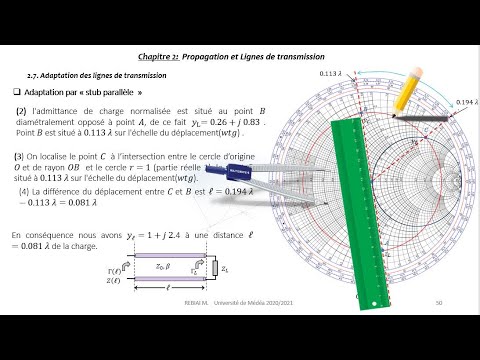
Ligne de transmission 3

Praktikum Sistem Daya Elektrik Percobaan I (Transmisi Pendek)

Transmission Media (Wireless)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
