Animation 27.1 Basic principle of recombinant DNA technology
Summary
TLDRRecombinant DNA technology is a method where a DNA fragment from one organism is inserted into the DNA of another organism to introduce new traits. This process involves four steps: obtaining the gene of interest, using plasmids as vectors, cutting the DNA and plasmid with restriction enzymes, and joining them with DNA ligase. The recombinant plasmid is then introduced into a host cell for various applications, such as producing proteins like human insulin or creating genetically modified organisms with new characteristics.
Takeaways
- 🧬 **Recombinant DNA Technology**: It's a method to insert a DNA fragment from one organism into another's DNA.
- 🔍 **Purpose**: To introduce new characteristics into an organism by adding new genes.
- 🧐 **Major Steps**: The process involves four main steps for gene transfer and expression.
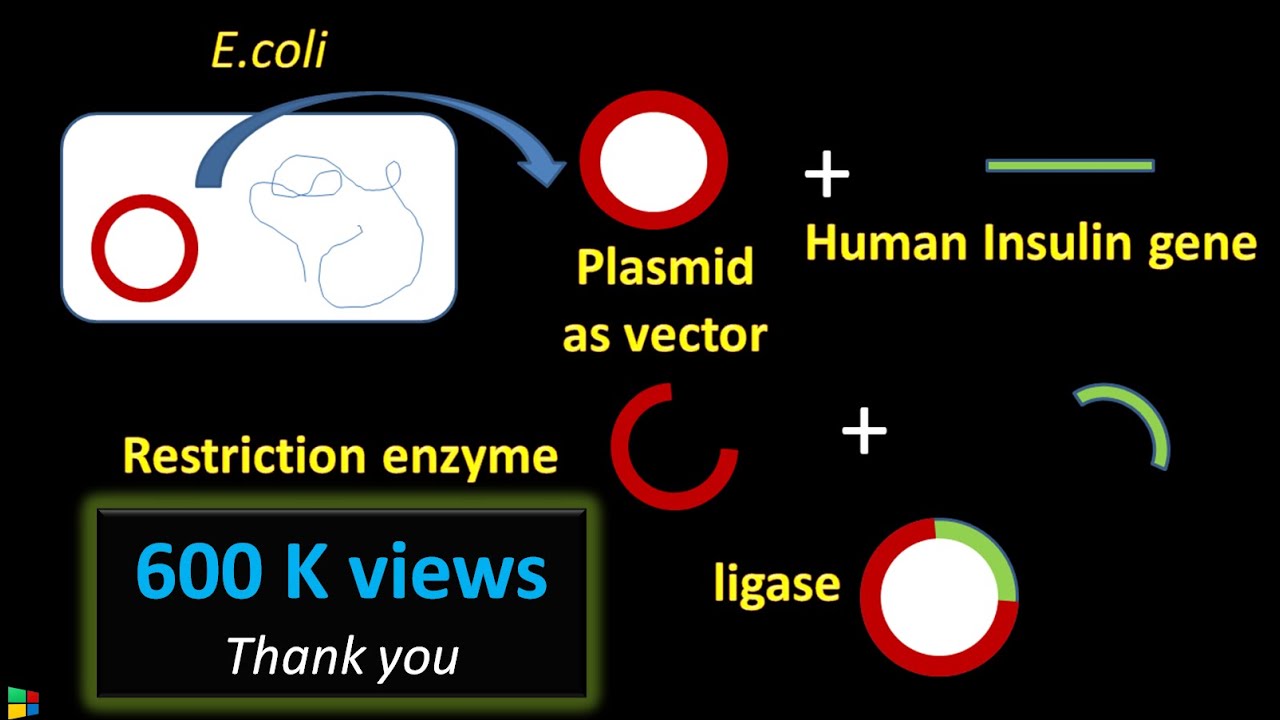
- 🧬 **Obtaining DNA Fragment**: The first step is to get a DNA fragment with the desired gene from a donor cell.
- 🌐 **Plasmid Role**: A plasmid, obtained from bacteria, is used as a vector to transfer the gene into a host cell.
- ✂️ **Restriction Enzyme**: This enzyme cuts the DNA fragment and the plasmid at specific points, acting like molecular scissors.
- 🧷 **DNA Ligase**: This enzyme acts like molecular glue, joining the DNA fragment to the plasmid.
- 🔄 **Recombinant Plasmid Formation**: The final product is a recombinant plasmid that combines the foreign gene with the plasmid.
- 🏭 **Host Cell Introduction**: The recombinant plasmid is introduced into a host cell for various applications.
- 💊 **Applications**: It's used to produce proteins from other species, like human insulin, or to create genetically modified organisms with new traits.
Q & A
What is recombinant DNA technology?
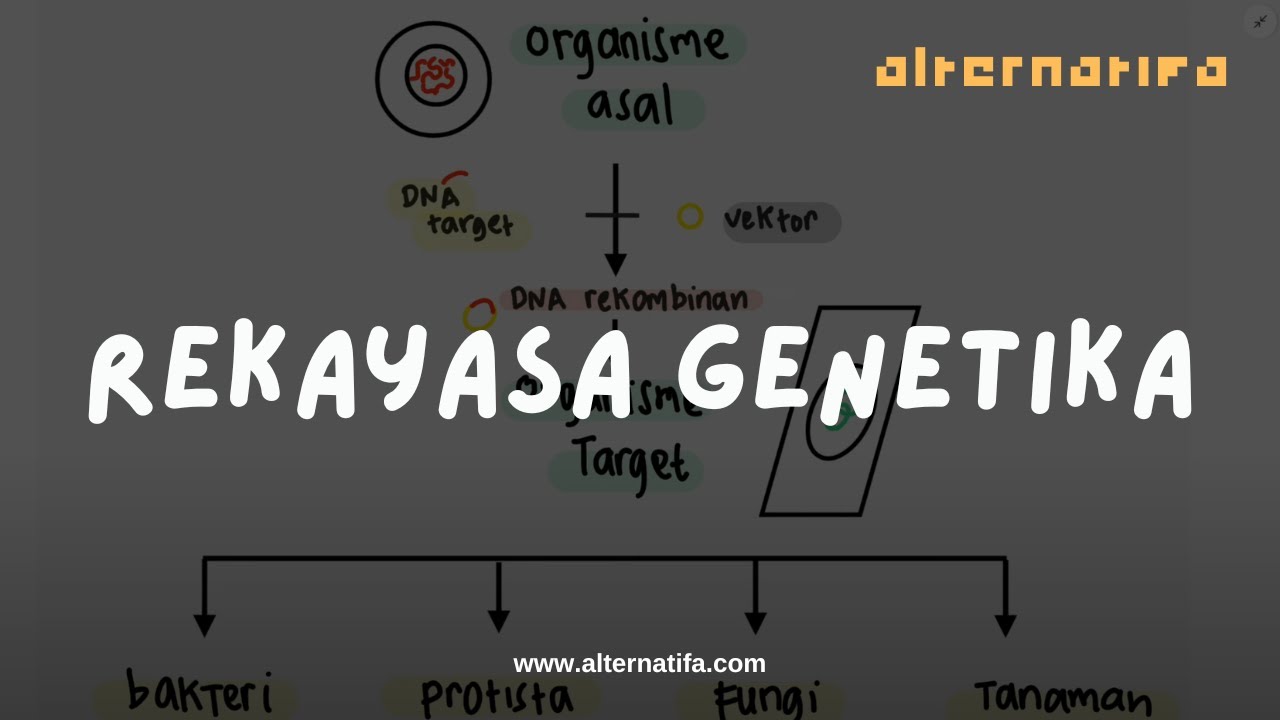
-Recombinant DNA technology is a technique in which a fragment of DNA from a donor cell or organism is isolated and inserted into the DNA of another cell or organism. This allows scientists to introduce a new characteristic into an organism by inserting a new gene.
What are the four major steps in recombinant DNA technology?
-The four major steps are: 1) Obtaining a DNA fragment containing the gene of interest from a donor cell, 2) Obtaining a suitable plasmid from a bacterium, 3) Cutting the DNA fragment and plasmid using a restriction enzyme, and 4) Inserting the gene of interest into the plasmid using DNA ligase to form a recombinant plasmid.
What role do plasmids play in recombinant DNA technology?
-Plasmids are commonly used as vectors to transfer the gene of interest into a host cell for expression. They carry the foreign DNA and facilitate its incorporation into the host.
What is a restriction enzyme and how does it function in this process?
-A restriction enzyme is an enzyme that acts like scissors. It recognizes specific base sequences in DNA and cuts the DNA at those points. This allows for the precise extraction of the gene of interest and the opening of the plasmid.
What is the function of DNA ligase in recombinant DNA technology?
-DNA ligase is an enzyme that acts like glue. It catalyzes the joining of the DNA fragment containing the gene of interest with the plasmid, forming a recombinant plasmid.
What is a recombinant plasmid?
-A recombinant plasmid is a plasmid that has had a foreign DNA fragment (the gene of interest) inserted into it. This plasmid can then be introduced into a host cell for expression.
How can recombinant DNA technology be used in protein production?
-Recombinant DNA technology can be used to produce proteins of other species, such as human insulin, by introducing the necessary genes into host cells, which then express the protein.
What is the importance of using the same restriction enzyme on both the plasmid and the DNA fragment?
-Using the same restriction enzyme ensures that the cut ends of the plasmid and the DNA fragment are compatible, allowing them to be joined together by DNA ligase to form a stable recombinant plasmid.
What are genetically modified organisms (GMOs), and how does recombinant DNA technology create them?
-Genetically modified organisms (GMOs) are organisms that possess new characteristics due to the introduction of foreign genes. Recombinant DNA technology creates GMOs by inserting specific genes into the organism's DNA, resulting in desired traits such as resistance to pests or improved nutritional value.
What are some practical applications of recombinant DNA technology?
-Practical applications of recombinant DNA technology include the production of therapeutic proteins like insulin, the creation of genetically modified crops with improved traits, and the development of new medical treatments through gene therapy.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)