Government Intervention- Micro Topic 2.8
Summary
TLDRIn this educational video, Jacob Clifford uses a chicken murder mystery to explain the economic concept of price controls, including price ceilings and floors, subsidies, and taxes. Set in 1971 during inflation, the video illustrates how government interventions like Nixon's price freeze led to unintended consequences. It explores how these controls affect consumer and producer surplus, leading to inefficiencies like surpluses or shortages, and introduces deadweight loss. The video concludes with a pop quiz to test viewers' understanding.
Takeaways
- 🐔 The video discusses a chicken murder mystery using economic principles to explain why it happened.
- 📈 The script explains how inflation in 1971 led President Nixon to implement a price freeze, affecting the chicken market.
- 📉 The price freeze caused unintended consequences for chicken farmers who couldn't profit from selling chickens at the controlled price.
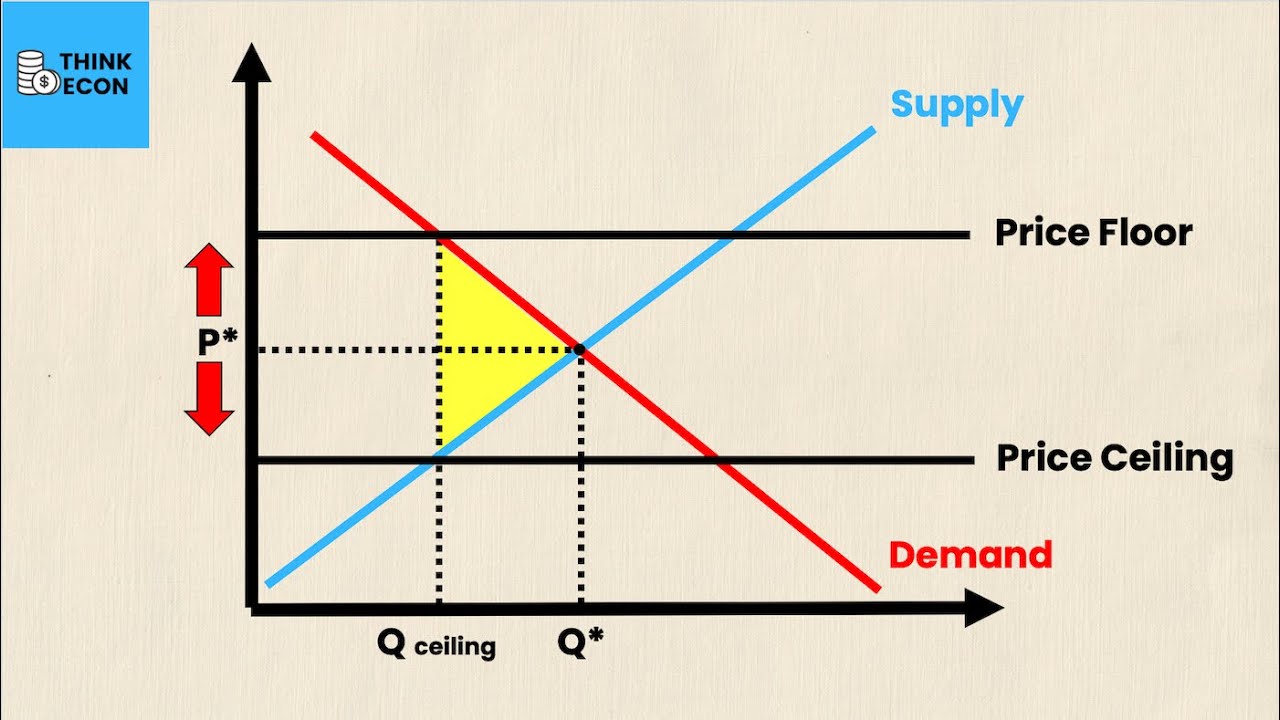
- 📊 The video uses diagrams to illustrate the effects of government interventions like price ceilings and floors on consumer and producer surplus.
- 💰 It discusses how price ceilings can lead to shortages and price floors can lead to surpluses, both resulting in deadweight loss.
- 🚫 The script points out that price controls need to be binding (below or above equilibrium) to affect the market.
- 💵 The video explains subsidies, showing how they can lead to overproduction and hidden costs for taxpayers.
- 💼 It also covers taxes, demonstrating how they can reduce production and result in government revenue but still cause deadweight loss.
- 📚 The script emphasizes the importance of understanding these concepts for microeconomics classes and provides resources for further study.
- 🎓 The video concludes with a pop quiz to test the viewer's understanding of the discussed economic concepts.
Q & A
What is the main topic discussed in the video script?
-The main topic discussed in the video script is the impact of government intervention in the market, specifically using the example of a chicken farmer and price controls to explain economic concepts such as consumer surplus, producer surplus, and deadweight loss.
What is the 'chicken murder mystery' mentioned in the script?
-The 'chicken murder mystery' refers to a real incident where a farmer was filmed drowning live baby chickens in a barrel. The video uses this incident as a starting point to discuss the economic reasons behind such actions, which are linked to government price controls and inflation.
Why did President Nixon implement a price freeze in 1971?
-President Nixon implemented a price freeze in 1971 to combat serious inflation in the U.S. economy, aiming to prevent prices from rising further by freezing all prices and wages for a period of 90 days.
What unintended consequences did economists predict from Nixon's price freeze?
-Economists predicted that Nixon's price freeze would lead to unintended consequences such as shortages, surpluses, and deadweight loss due to market imbalances caused by the price controls.
What is a price ceiling and how does it affect the market?
-A price ceiling is a government-imposed maximum price limit on goods or services. It can lead to shortages if set below the equilibrium price because consumers will demand more than producers are willing to supply at that price, resulting in a decrease in producer surplus and potential deadweight loss.
What is a price floor and how does it affect the market?
-A price floor is a government-imposed minimum price limit on goods or services. It can lead to surpluses if set above the equilibrium price because producers will supply more than consumers are willing to buy at that price, resulting in an increase in producer surplus but also potential deadweight loss.
How does a government subsidy affect the market for chickens in the script?
-A government subsidy in the form of $10 per chicken leads to an increase in production as the supply curve shifts right, reducing the price consumers pay. However, it results in overproduction and a hidden cost to taxpayers, who fund the subsidy, potentially leading to deadweight loss.
What is the effect of a tax on chicken production as described in the script?
-A tax on chicken production increases the cost for consumers and reduces the income for producers. It shifts the supply curve left, leading to a higher price for consumers and a lower quantity produced, which can also result in deadweight loss.
What is deadweight loss and how does it relate to government intervention in the market?
-Deadweight loss is a decrease in economic efficiency that occurs when the quantity of a good or service demanded and supplied in a market does not equal the socially optimal quantity due to market distortions like taxes, subsidies, or price controls. It represents the loss of total surplus that could have been achieved at the equilibrium.
Why might government intervention sometimes be necessary despite the potential for deadweight loss?
-Government intervention might be necessary to address market failures, promote social welfare, correct externalities, or reduce income inequality. While it can lead to deadweight loss, the intervention aims to achieve broader economic or social goals that may outweigh the loss.
What is the significance of the 'pop quiz' at the end of the script?
-The 'pop quiz' is a teaching tool used to engage viewers and test their understanding of the economic concepts discussed in the video. It encourages active learning and reinforces the key points of the lesson.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频

Price Controls, Subsidies, and the Risks of Good Intentions: Crash Course Economics #20

Consumer and Producer Surplus- Micro Topic 2.6 (Holiday Edition)

Old Version- Micro Unit 2 Summary- Supply and Demand

Price Ceilings and Floors- Micro Topic 2.8

Micro: Unit 1.4 -- Government Intervention: Price Controls, Quotas, and Subsidies
Price Ceiling and Price Floor | Think Econ
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
