云计算概览
Summary
TLDRCloud computing, as defined by the US National Institute of Standards and Technology, is an IT model characterized by on-demand self-service, broad network access, resource pooling, elasticity, and pay-per-use. It evolved from colocation to virtualized data centers and now to container-based architectures, exemplified by Google Cloud's automated, scalable services. This model is compelling as it enables businesses to leverage technology and data, becoming essential for differentiation in a competitive landscape.
Takeaways
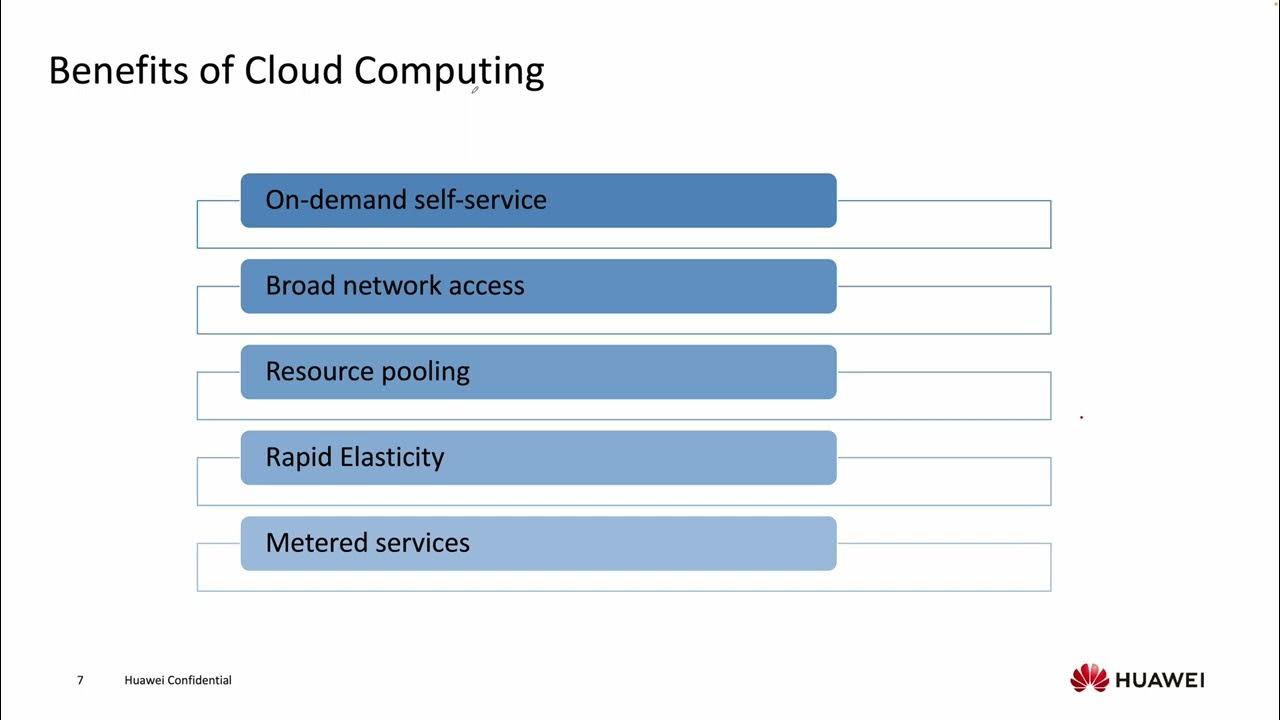
- 🌐 **Cloud Computing Defined**: Cloud computing is a model that allows on-demand access to computing resources over the internet, with self-service and minimal human intervention.
- 🔑 **Self-Service Access**: Users can access computing power, storage, and network resources through a web interface without requiring human involvement.
- 🌍 **Global Accessibility**: Resources are accessible from anywhere with an internet connection, providing global reach.
- 💧 **Resource Pooling**: Cloud providers maintain a large pool of resources, which are dynamically allocated to users, allowing for cost efficiencies.
- 🔄 **Elasticity**: Cloud resources are scalable, meaning users can adjust their resource usage up or down based on their needs.
- 💸 **Pay-as-you-go**: Users are billed based on the resources they use, making cloud computing a cost-effective option.
- 🏭 **Colocation Beginnings**: The shift to cloud computing started with colocation, offering financial efficiency by renting space instead of investing in data centers.
- 🛠️ **Virtualized Data Centers**: The second wave of cloud computing involved virtualized data centers, which are similar to colocation but with virtual devices.
- 🚀 **Container-based Architecture**: Google pioneered a third wave with container-based architecture, offering fully automated and elastic cloud services.
- 🌟 **Future of Companies**: Google envisions a future where every company, regardless of size or industry, will use technology, particularly software, to differentiate themselves, with data at the core.
Q & A
What is cloud computing according to the US National Institute of Standards and Technology?
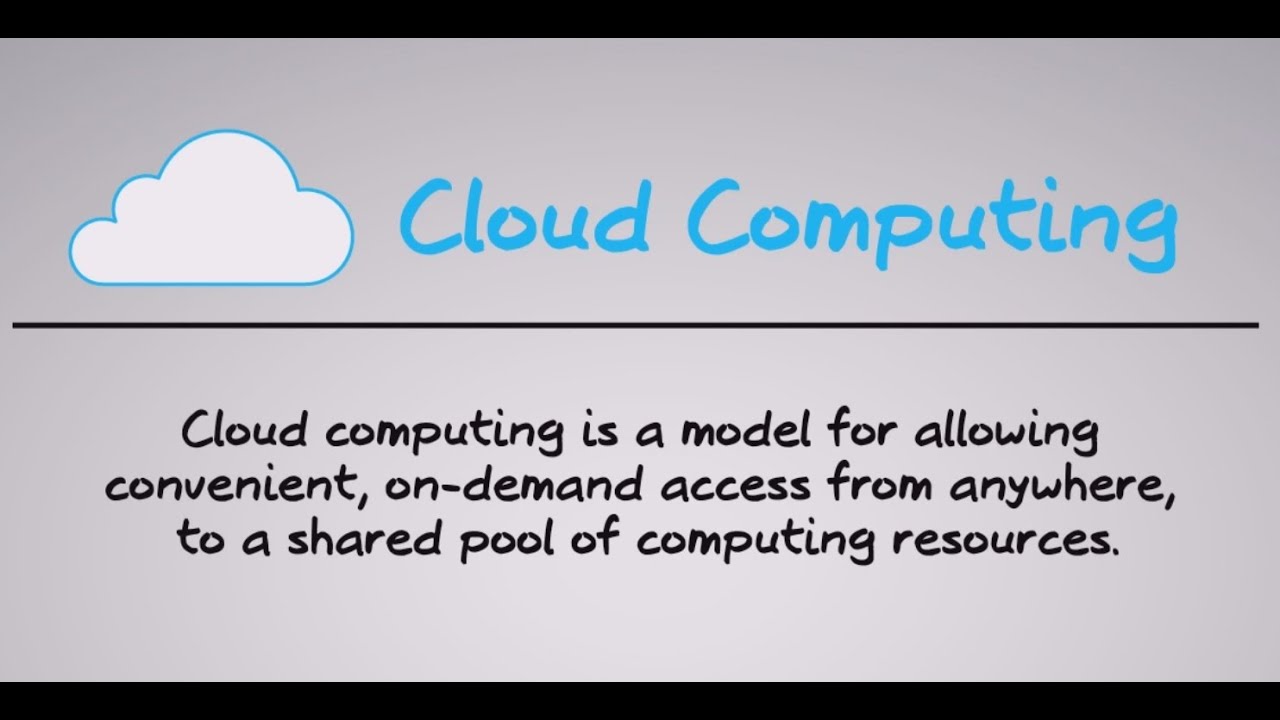
-Cloud computing is a way of using information technology that has five equally important traits: on-demand self-service, broad network access, resource pooling, elasticity, and measured service.
How does the on-demand self-service trait of cloud computing work?
-Customers can get computing resources such as processing power, storage, and network through a web interface without the need for human intervention.
What is the significance of the cloud provider's resource pool?
-The cloud provider has a large pool of resources from which they allocate to users, allowing them to buy in bulk and pass the savings on to customers while maintaining flexibility in resource allocation.
Why is the cloud model considered compelling in the current technological landscape?
-The cloud model is compelling because it offers financial efficiency, scalability, and flexibility, allowing businesses to adapt quickly to changing demands and reduce the need for large upfront investments in infrastructure.
What is the difference between colocation and virtualized data centers in the context of cloud computing?
-Colocation involves renting physical space in a data center for servers, while virtualized data centers use virtual devices such as servers, CPUs, disks, and load balancers, providing a user-controlled and user-configured environment.
Why did Google transition from a virtualization model to a container-based architecture?
-Google transitioned to a container-based architecture to achieve a fully automated, elastic cloud that allows for faster business operations and scalability.
What is the third wave of cloud computing as described in the script?
-The third wave of cloud computing is characterized by a container-based architecture that combines automated services and scalable data, enabling services to automatically provision and configure infrastructure for running applications.
How does Google Cloud's third-wave cloud benefit its customers?
-Google Cloud's third-wave cloud benefits customers by providing access to an automated, elastic infrastructure that can quickly adapt to changing resource needs and support the running of applications.
What role does technology play in differentiating companies in the future according to Google's belief?
-According to Google, technology, particularly software, will be a key differentiator for companies in the future, with high-quality data being the foundation of great software.
Why will every company eventually become a data company?
-Every company will eventually become a data company because the creation and use of high-quality data are essential for developing great software, which is increasingly important for business differentiation and growth.
How does the elasticity of cloud resources benefit customers?
-The elasticity of cloud resources allows customers to scale up or down quickly according to their needs, ensuring they only pay for what they use and can adapt to changing business demands without over-provisioning.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级5.0 / 5 (0 votes)