Anuitas | Matematika kelas XI SMA/SMK Kurikulum Merdeka
Summary
TLDRThis video script delves into the concept of annuities in mathematics for high school students, particularly under the independent curriculum. It explains annuities as a series of payments, including principal and interest, using the formula for calculating annuity payments. The script provides a detailed example of how to determine monthly payments for a loan, including the initial principal and interest over time, and illustrates the changing proportion of principal and interest in each payment. It also includes a second example to demonstrate the application of the annuity formula in different scenarios, offering a comprehensive understanding of annuity calculations in finance.
Takeaways
- 📚 The video discusses the concept of annuities in mathematics for high school level, specifically for the independent curriculum.
- 💡 Annuities are compared to installment credit, which includes bank loans and leasing, like for motorcycles, and are paid in regular installments.
- 🔢 The formula for annuity includes principal payments (A) and interest payments (B), with the total payment varying each month due to changing interest and principal components.
- 📈 The initial payments have higher interest and lower principal, while the later payments have higher principal and lower interest.
- 🧮 The annuity formula is derived from borrowing a sum 'M' with an interest rate 'I' over 'n' periods, using the formula M * i * (1 + I)^n / (1 + I)^N - 1.
- 📝 To find the principal payment of the first period (A1), the formula A1 = M * i / (1 + I)^n is used, which requires knowing the total borrowed amount, interest rate, and number of periods.
- 📉 The interest payment for any period can be found by subtracting the principal payment from the total annuity payment for that period.
- 🏦 The script provides an example of Mr. Bagas taking a loan from Bank ABC for 40 million with a 12-month repayment period and a 6% annual interest rate, which is divided by 12 for a monthly rate.
- 📊 The script also explains how to calculate the total annuity payment, principal payment for the first and last periods, and the interest for the last payment using the provided formulas.
- 📋 The video concludes with a table summarizing the annuity payments, showing how the principal and interest payments change over the repayment period.
- 🤔 The video encourages viewers to understand these calculations as they are used by banks and other institutions when calculating credits and loans.
Q & A
What is the topic of the video?
-The video discusses the concept of annuities in the context of high school mathematics, specifically for the Indonesian curriculum.
What is an annuity and how is it related to installment payments?
-An annuity is a financial product similar to installment payments, which can be found in banking, leasing for motorcycles, and other services. It consists of regular payments that include both principal and interest.
What are the components of an annuity payment?
-An annuity payment is composed of the principal payment and the interest payment. The principal is the amount borrowed, and the interest is the cost of borrowing money over time.
What is the formula used to calculate the annuity payment?
-The formula to calculate the annuity payment is the borrowed amount (M) multiplied by the interest rate (i), then multiplied by (1 + I) to the power of n, and finally divided by (1 + I) to the power of N - 1.
How does the interest rate affect the annuity payment over time?
-The interest rate affects the annuity payment by making the interest component higher in the beginning and lower towards the end of the payment period, while the principal payment is smaller in the beginning and larger at the end.
What is the first step in calculating the annuity payment for the first period?
-The first step is to calculate A1, which is the principal payment for the first period. This is done using the formula for the annuity payment, but with adjustments specific to the first period.
What is the example given in the video about Mr. Bagas' loan from Bank ABC?
-Mr. Bagas takes a loan of 40 million with a repayment period of 12 months, with an annual interest rate of 6%, which is then divided by 12 to get a monthly interest rate of 0.5%.
How is the total annuity payment calculated for Mr. Bagas' loan?
-The total annuity payment is calculated by using the formula with the known values of the loan amount, the monthly interest rate, and the number of periods, and then using a calculator to find the result.
What is the difference between the principal payment and the interest payment in the first and last periods of the loan?
-In the first period, the principal payment is smaller, and the interest payment is larger. In the last period, the principal payment is larger, and the interest payment is smaller.
What is the second example provided in the video about Bu Desi's loan?
-Bu Desi takes a loan with a repayment period of 3 years, which is equivalent to 36 months. The annual interest rate is 12%, which is divided by 12 to get a monthly interest rate of 1%.
How is the loan amount determined in Bu Desi's example?
-The loan amount is determined by using the annuity formula with the known values of the annuity payment, the monthly interest rate, and the number of periods, and then solving for the unknown loan amount (M).
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
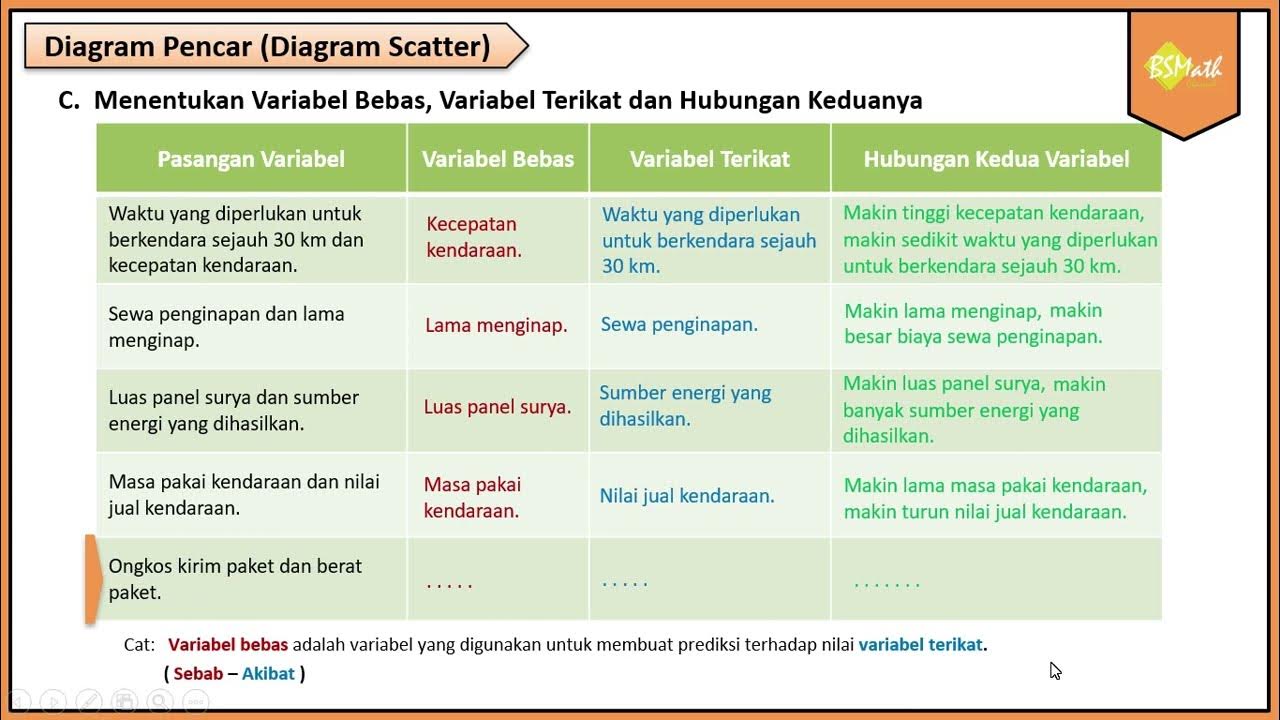
Menentukan Variabel Bebas dan Variabel Terikat - Matematika Wajib SMA Kelas XI Kurikulum Merdeka

Pertumbuhan,Peluruhan,Bunga,dan Anuitas Kelas X SMK
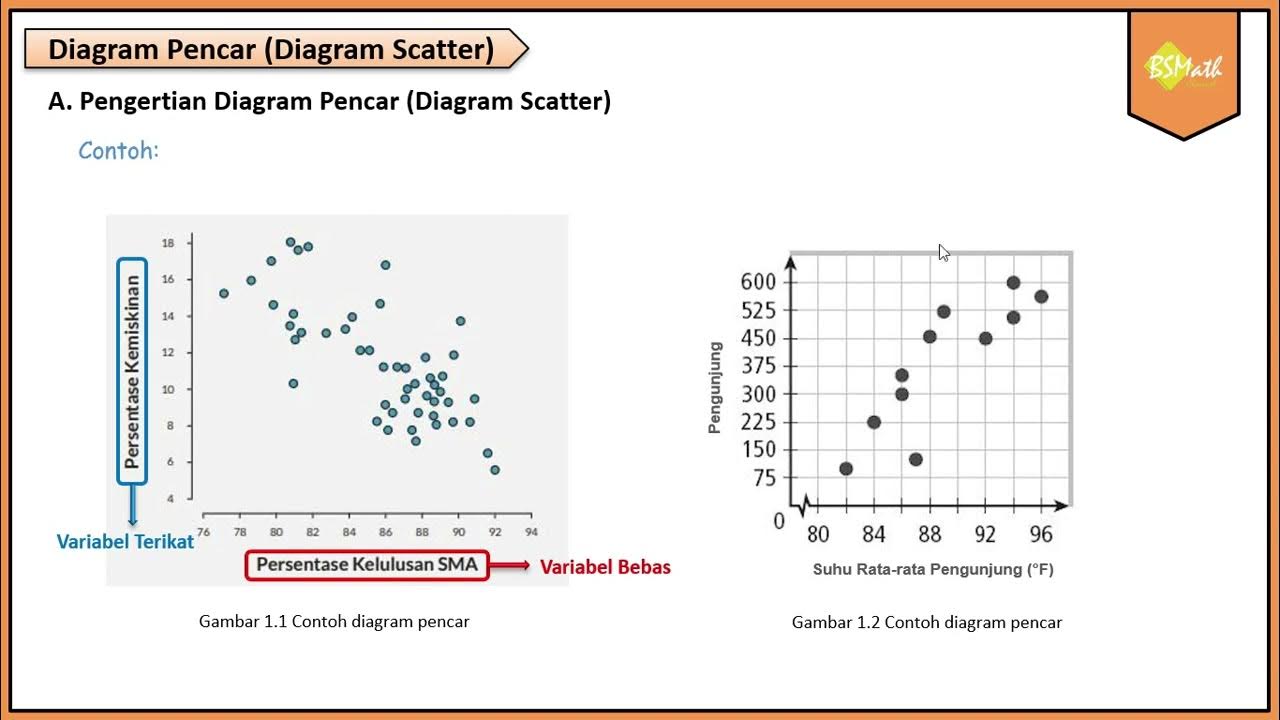
Pengertian Diagram Pencar - Matematika Wajib SMA Kelas XI Kurikulum Merdeka

Konsep Fotosintesis : Reaksi Terang dan Reaksi Gelap

Sosialisasi Pemilihan Mata Pelajaran | Kelas X Menuju Kelas XI Kurikulum Merdeka

Pensamiento Matemático II PROGRESION 10
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)