Cyclotron and Cyclotron Frequency
Summary
TLDRThe script explores the cyclotron, an early high-energy particle accelerator developed by Ernest O. Lawrence in 1930. It describes how the cyclotron uses electric and magnetic fields to accelerate protons to high velocities and energies. The device's structure, consisting of two vacuum chambers and an alternating electric field, is explained. The protons move in a circular path due to the magnetic field and gain velocity through the electric field, eventually exiting to collide with a target, such as a tumor in medical applications. The script also delves into the cyclotron frequency equation, relating it to the particle's motion and the magnetic field's influence.
Takeaways
- 🔬 The cyclotron is an early high-energy particle accelerator developed by Ernest O. Lawrence in 1930.
- 🧲 It uses electric and magnetic fields to accelerate particles, typically protons, to high velocities and energies.
- 🏥 Modern cyclotrons are still used in medicine, particularly for treating tumors with accelerated particles.
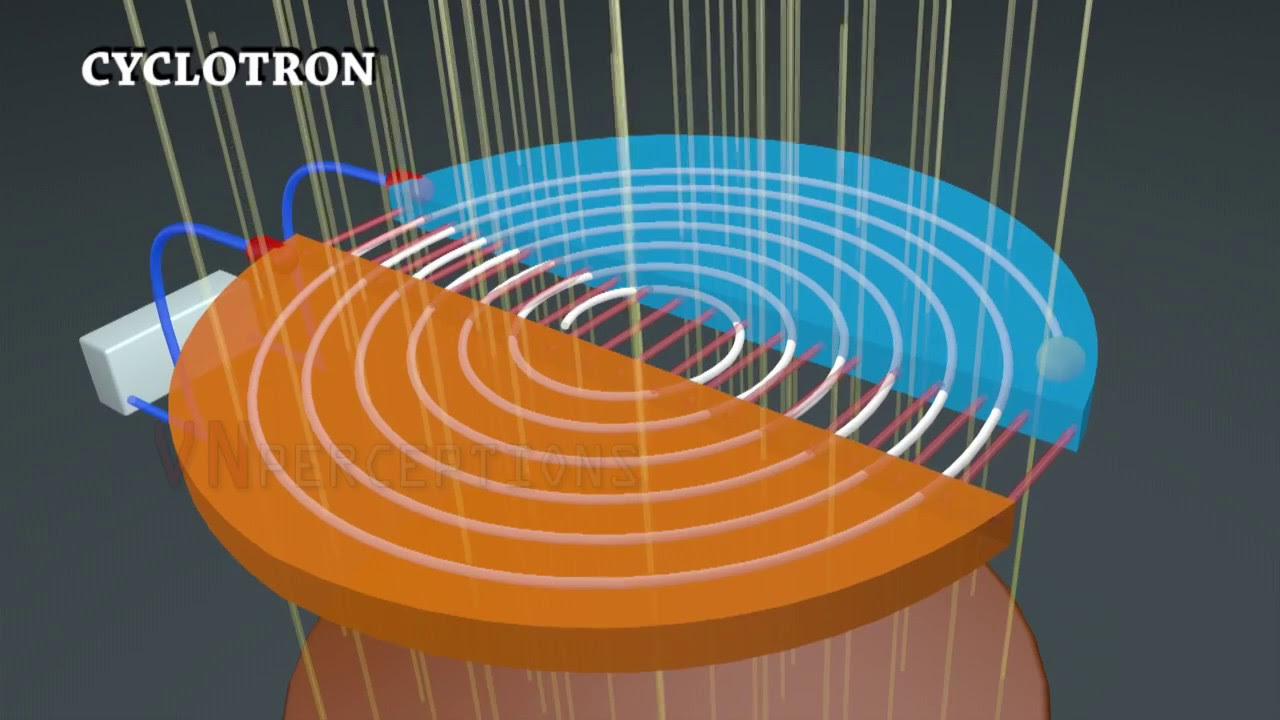
- 🛠️ The cyclotron consists of two vacuum chambers and a magnetic field that directs particles in a circular path.
- 🔋 An electric potential difference is created between the chambers to accelerate the particles as they move between them.
- ⚛️ The magnetic field creates a force that causes the charged particles to undergo centripetal acceleration, maintaining a circular motion.
- 🔄 As the particle's velocity increases, so does the radius of its circular path, allowing it to eventually exit the cyclotron.
- 🎯 The exiting particle can be directed towards a target, such as a tumor, for medical treatment.
- 🔀 An alternating electric current is used to create an alternating electric field, which is necessary for continuous particle acceleration.
- 🔁 The frequency of the alternating voltage source must match the cyclotron frequency, which is the frequency of the particle's circular motion.
- ⚖️ The cyclotron frequency can be calculated using the equation derived from the relationship between charge, magnetic field, and mass of the particle.
- 📚 Newton's second law and the right-hand rule are applied to understand the forces acting on the particles within the cyclotron.
Q & A
What is a cyclotron and who developed it?
-A cyclotron is an early high-energy particle accelerator developed by Ernest O. Lawrence in 1930. It uses electric and magnetic fields to accelerate particles, typically protons, to very high velocities and energies.
What is the primary use of cyclotrons in modern times?
-In modern times, cyclotrons are primarily used in medicine for treating tumors by accelerating particles to high energies to target and destroy cancer cells.
What are the two main components of a cyclotron's structure?
-The two main components of a cyclotron's structure are the vacuum chambers and the semicircular vacuum chambers, which create a magnetic field for the particles to move in a circular path.
How does the magnetic field in a cyclotron affect the charged particles?
-The magnetic field in a cyclotron creates a magnetic force that acts as centripetal acceleration, causing the charged particles to move in a circular pathway within the vacuum chambers.
What role does the electric field play in the acceleration of particles in a cyclotron?
-The electric field, created by a voltage difference between the two semicircular vacuum chambers, accelerates the particles linearly when they travel between the chambers, increasing their velocity.
How does the radius of curvature of a particle's path change as it accelerates in a cyclotron?
-As the velocity of the particle increases, the radius of curvature of its circular path also increases, allowing the particle to eventually exit the cyclotron when it reaches a sufficient energy level.
What is the purpose of using an alternating electric current in a cyclotron?
-An alternating electric current is used to create an alternating electric field that changes direction with each half-cycle, ensuring that the electric field always accelerates the particle in the direction of its motion.
What is the significance of the cyclotron frequency in the operation of a cyclotron?
-The cyclotron frequency is the frequency at which the voltage source oscillates, and it must match the frequency of the particle's circular motion to maintain continuous acceleration.
How is the cyclotron frequency related to the particle's motion and magnetic field?
-The cyclotron frequency is determined by the particle's charge, mass, and the strength of the magnetic field. It is the frequency at which the particle completes one full cycle of its circular motion.
What is the equation that describes the magnetic force acting on a charged particle moving in a magnetic field?
-The magnetic force (F) acting on a charged particle with charge (q) moving with velocity (v) in a magnetic field (B) is given by the equation F = q * v * B, where the force is perpendicular to both the velocity and the magnetic field.
How can the period of a particle's circular motion in a cyclotron be calculated?
-The period (t) of a particle's circular motion can be calculated by dividing the circumference of the circle (2 * π * r) by the velocity of the particle (v), which is given by the equation v = q * B * r / m.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)