What is Cryptography? | Introduction to Cryptography | Cryptography for Beginners | Edureka
Summary
TLDRThis video script by Aria from Eddie Rocca delves into the world of cryptography, a crucial tool for secure communication. It outlines the basics of cryptography, explains its importance in protecting data, and covers various cryptographic classifications including symmetric and asymmetric key cryptography. The script provides a practical demonstration of the RSA algorithm, showcasing how it secures data on platforms like YouTube. It also explores encryption techniques such as transposition and substitution ciphers, stream and block ciphers, and the significance of digital certificates in cybersecurity.
Takeaways
- 🔒 Cryptography is essential for securing data and protecting against unauthorized access, identity theft, and tampering.
- 📚 The video session will cover the basics of cryptography, classifications, and a demonstration of the RSA algorithm.
- 🗣 The example of Andy and Sam illustrates the need for secure communication over public channels like the internet.
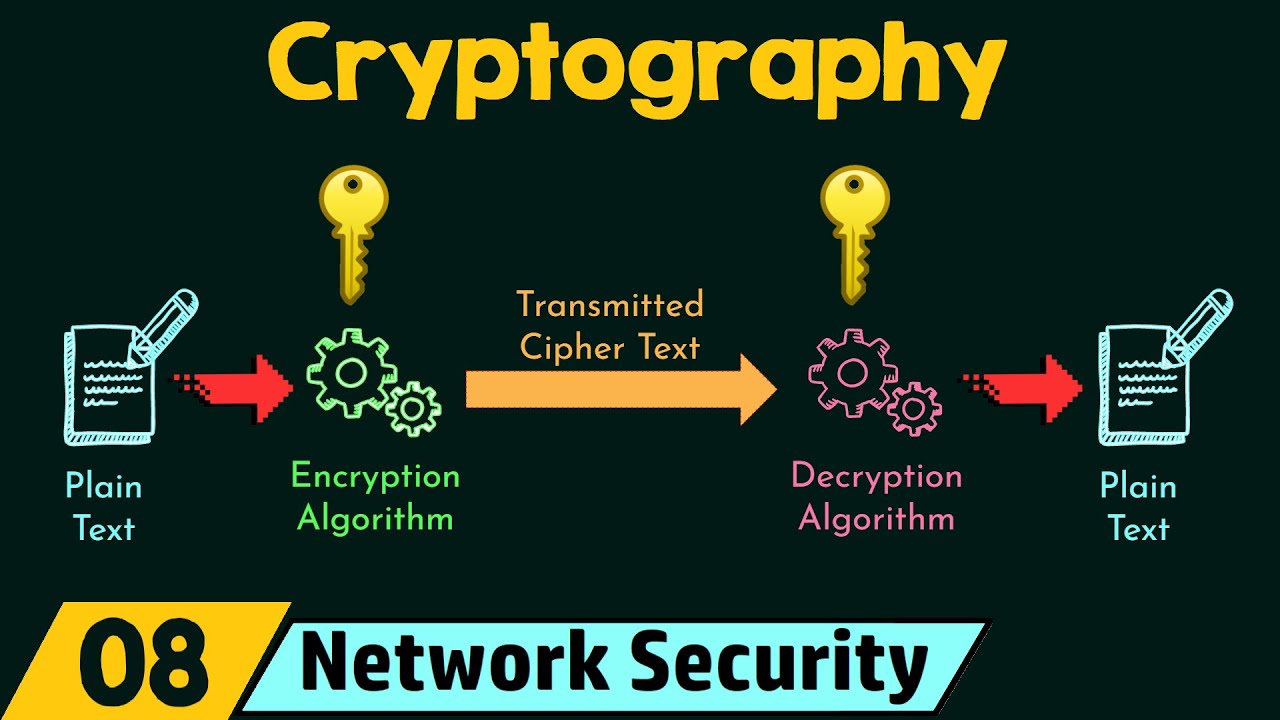
- 🔑 Cryptography involves converting messages into numeric forms, encrypting them with a key, and then decrypting them with a corresponding key.
- 🔄 The process of encryption and decryption is vital to ensure that messages remain private and intact during transmission.
- 🔒🔓 Cryptography is divided into symmetric key cryptography, which uses the same key for encryption and decryption, and asymmetric key cryptography, which uses a pair of keys.
- 🔄🔄 Symmetric key cryptography includes classical methods like transposition and substitution ciphers, and modern methods like stream and block ciphers.
- 🔑🔑 Asymmetric cryptography, or public key cryptography, uses a public key for encryption and a private key for decryption, enhancing security.
- 🔐 The RSA algorithm, used widely on the internet, is an example of asymmetric cryptography that relies on the difficulty of factoring large prime numbers.
- 🌐 The security of modern cryptography systems, like RSA, depends on keeping the private key secret while the public key can be openly distributed.
- 📈 The strength of public key cryptography systems is based on the computational difficulty of deriving the private key from the public key, ensuring robust security.
Q & A
What is the primary purpose of cryptography?
-The primary purpose of cryptography is to securely protect data and communication from unauthorized access, ensuring the privacy and integrity of information such as corporate secrets, classified information, and personal data.
What is the scenario presented in the video to explain cryptography?
-The scenario involves a person named Andy who wants to send a private message to his friend Sam over the internet. The goal is to secure the message against eavesdroppers and potential tampering by a third party named Eve.
How is the message converted into a numeric form in cryptography?
-The message is first converted into a numeric form, which is then combined with an encryption key using an encryption algorithm to produce a ciphertext that can be securely transmitted.
What is a ciphertext?
-A ciphertext is the result of encrypting a message using an encryption key and an encryption algorithm, transforming the original message into a form that is unreadable without the decryption key.
How does cryptography help secure the connection between Andy and Sam?
-Cryptography helps secure the connection by allowing Andy to convert his readable message into an unreadable form (ciphertext) using a key. This ensures that even if someone intercepts the message, they cannot decipher it without the proper decryption key.
What are the two broad classifications of cryptography mentioned in the script?
-The two broad classifications of cryptography are symmetric key cryptography and asymmetric key cryptography, also known as public key cryptography.
What is symmetric key cryptography?
-Symmetric key cryptography is a type of cryptography where the same cryptographic key is used for both encryption and decryption of the message. This requires the key to be shared between the communicating parties.
What is the difference between a transposition cipher and a substitution cipher?
-A transposition cipher rearranges the positions of the plaintext characters according to a system, while a substitution cipher replaces each plaintext character with another character based on a fixed system or rule.
What is a block cipher and how does it differ from a stream cipher?
-A block cipher is an encryption method that applies a symmetric key to encrypt a fixed-size block of text at once, rather than encrypting one bit at a time as in stream ciphers.
What is asymmetric cryptography and how does it differ from symmetric cryptography?
-Asymmetric cryptography, also known as public key cryptography, uses a pair of keys consisting of a public key (which can be widely distributed) and a private key (which is known only to the owner). This allows for both encryption and authentication, where only the paired private key can decrypt messages encrypted with the public key.
What is the significance of the RSA algorithm mentioned in the script?
-The RSA algorithm is a widely used public key encryption system that is based on the computational difficulty of factoring large prime numbers. It is commonly used for secure data transmission over the internet and is an example of asymmetric cryptography.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)