UP TALKS | Dynamics in Population | Dr. Aimee Dupo
Summary
TLDRThis script delves into the dynamics of population ecology, explaining the significance of studying population changes for conservation and pest control. It introduces demographic processes like births, deaths, immigration, and emigration, and illustrates the impact of intrinsic growth and carrying capacity on population size. The script also touches on the logistic growth model, describing the transition from exponential to stable population growth, and discusses the role of environmental resistance and human intervention in altering carrying capacity.
Takeaways
- 🌿 The study of population dynamics is crucial for the conservation of biodiversity and determining species extinction risks.
- 🐝 Population dynamics is applied to manage economically important species like bees, with their caste system playing a vital role in honey production.
- 📊 The model C describes the population lifecycle and is used to analyze birth, death, immigration, and emigration rates affecting population size.
- 🕷️ Dispersal mechanisms such as spiderlings' ballooning effect are essential for species to expand their geographic range and prevent competition.
- 📈 The intrinsic population growth formula \( n_{t+1} = B - D + I - E \) helps determine if a population is increasing or declining based on birth and death rates.
- 🌱 Biotic potential represents the maximum reproductive rate of a species, influenced by factors like sex ratio and age distribution.
- 📉 Ecologists use methods to measure population changes over time, represented by the formula \( \frac{n_t - n_{t-1}}{T} \), to understand population growth or decline.
- 📈 The Lotka-Volterra equations predict exponential population growth under ideal conditions, represented by a J-shaped curve.
- 🌳 Environmental limits to growth are represented by the carrying capacity (k), leading to logistic growth and an S-shaped curve in natural populations.
- 🔄 The logistic growth curve consists of a lag phase, exponential growth phase, stationary phase, and death phase, reflecting the population's response to environmental constraints.
- 🏭 Human activities, such as agriculture and construction, have increased the carrying capacity of the environment, impacting population dynamics.
Q & A
What is the definition of a population in the context of population ecology?
-A population refers to a group of individuals belonging to the same species that occupy the same place at the same time.
What are the four demographic processes that influence population dynamics?
-The four demographic processes are births, deaths, immigration, and emigration.
Why is the study of population dynamics important for conservation efforts?
-Studying population dynamics helps in the conservation of diverse plants and animals by determining whether a species is at risk of extinction.
How does the study of population dynamics assist in controlling noxious pests and pathogens?
-Understanding population dynamics can help in managing the population sizes of pests and pathogens, preventing their overgrowth and spread.
What is the significance of the caste system in the social insects like bees?
-The caste system in social insects like bees ensures the proper functioning of the colony with roles such as egg-laying queens, workers for care and food gathering, and drones for mating.
What is the formula used to compute the intrinsic population growth mechanisms?
-The formula is n(T+1) = B - D + I - E, where B is the per capita birth rate, D is the per capita death rate, I is immigration, and E is emigration.
What does the term 'biotech potential' refer to in the context of population dynamics?
-Biotech potential refers to the maximum reproductive rate for each organism, influenced by factors such as sex ratio and age distribution.
How can the population growth formula be represented graphically?
-In a graph, population growth can be represented by a J-shaped curve for exponential growth or an S-shaped curve for logistic growth.
What is the term for the phase in population growth when the environment's carrying capacity is reached and growth becomes zero?
-This phase is known as the stationary phase.
What is the term for the phase in population growth when the population has exceeded the carrying capacity and begins to decline?
-This phase is referred to as the death phase.
How have humans increased the carrying capacity of the environment?
-Humans have increased the carrying capacity through technologies such as agriculture and construction of buildings for habitation.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Population Ecology: The Texas Mosquito Mystery - Crash Course Ecology #2
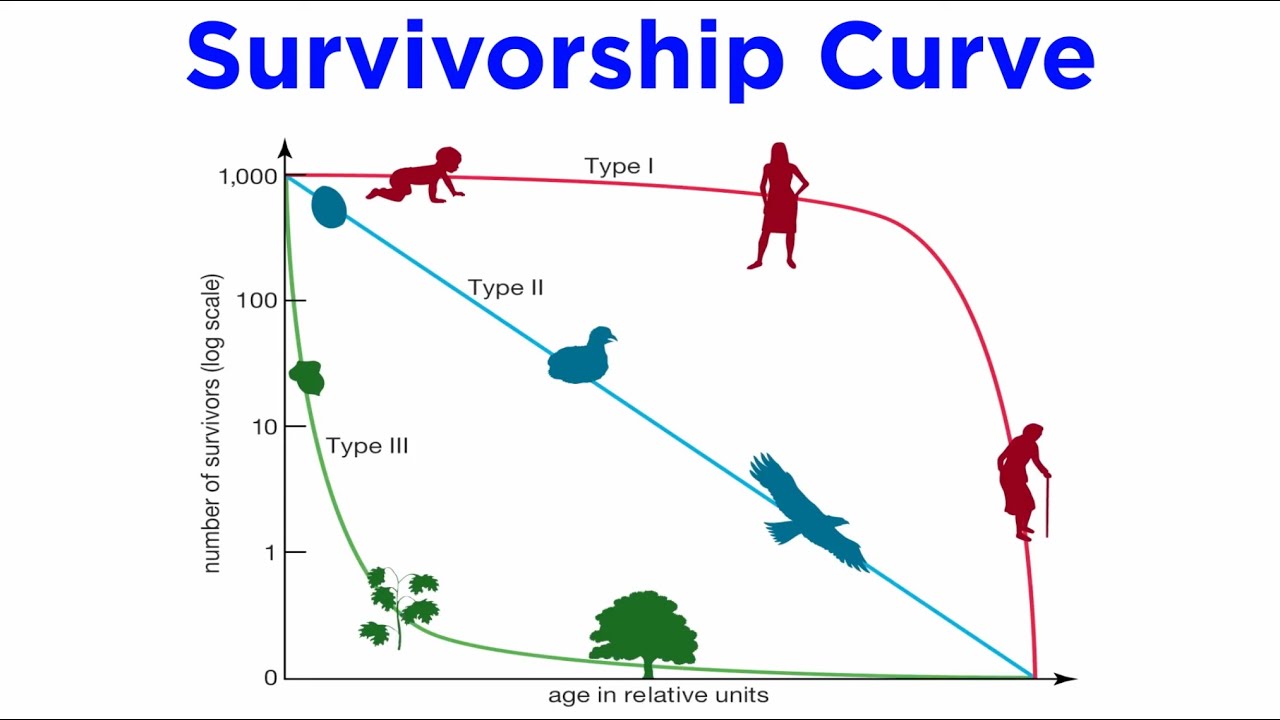
Population Ecology (Life Tables, Age Structure, Population Growth)

Densidade Populacional - Conceito e Fatores que Influenciam - Dinâmica das Populações - Ecologia

Chapter 53: Population Ecology

Population Ecology

Population Ecology ANIMATION VIDEO
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)