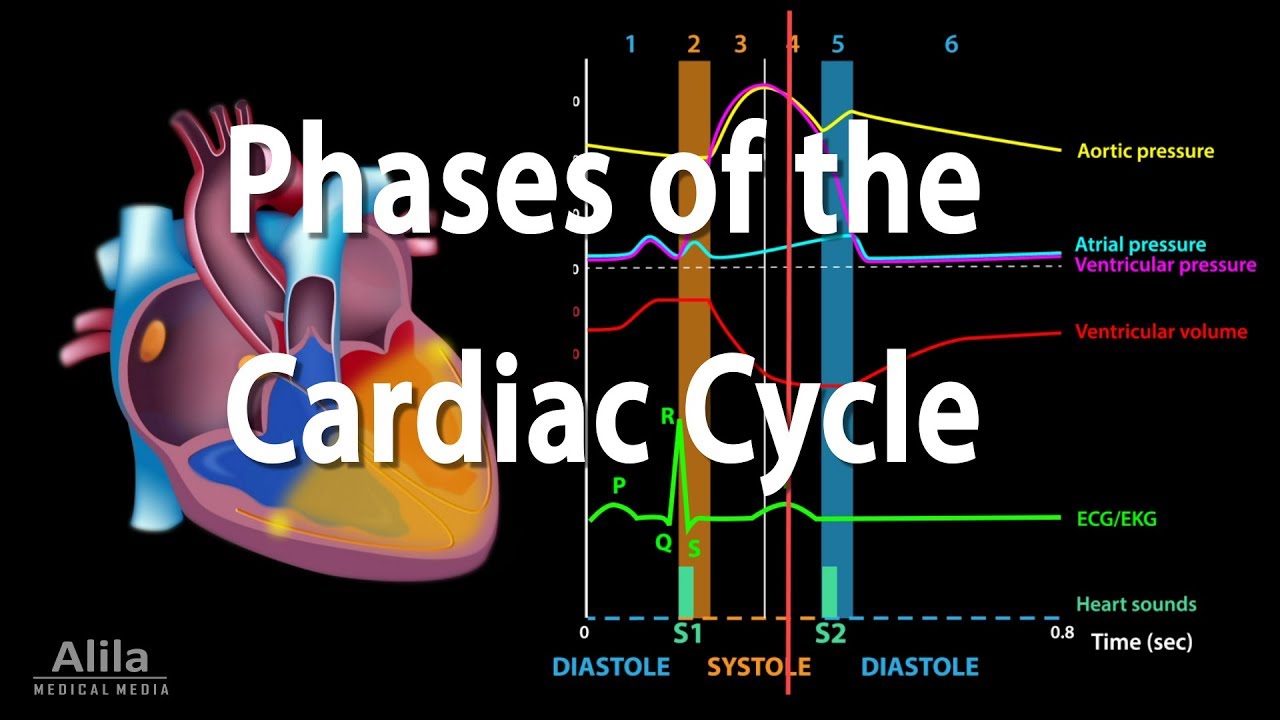
A level Biology Revision "The Cardiac Cycle"
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the events of the cardiac cycle, where blood flows through the heart. It covers key terms like systole (contraction) and diastole (relaxation), detailing the movement of blood through the heart's chambers. Blood enters the atria, causing them to contract and push blood into the ventricles. As the ventricles contract, blood is pumped out to the lungs and body. The video also highlights the role of the heart valves in preventing backflow. The process concludes with ventricular relaxation, ready to begin another cycle. Understanding these stages is key to grasping heart function.
Takeaways
- 😀 The cardiac cycle refers to the events that occur when blood moves through the heart.
- 😀 'Systole' means contraction, and 'diastole' means relaxation in the context of the heart.
- 😀 The heart begins the cycle in a state of diastole, with both atria and ventricles relaxed.
- 😀 Blood flows into the atria from the vena cava and pulmonary vein, increasing pressure in the atria.
- 😀 When atrial pressure exceeds ventricular pressure, the atrioventricular (AV) valves open, allowing blood to flow from the atria to the ventricles.
- 😀 Atrial systole occurs, pushing the remaining blood into the ventricles.
- 😀 Ventricular systole follows, causing rapid pressure rise in the ventricles.
- 😀 The AV valves close during ventricular systole, preventing blood from flowing back into the atria.
- 😀 The semilunar valves in the pulmonary artery and aorta open during ventricular systole, allowing blood to be pumped out of the heart.
- 😀 After ventricular contraction, the ventricles relax (ventricular diastole), and the pressure falls below that in the pulmonary artery and aorta, causing the semilunar valves to close.
Q & A
What is the cardiac cycle?
-The cardiac cycle refers to the events that take place when blood moves through the heart. It involves the contraction and relaxation of the heart chambers, ensuring blood is pumped effectively throughout the body.
What does the term 'systole' refer to?
-'Systole' refers to the phase of contraction in the heart. For example, 'atrial systole' means the contraction of the atria, while 'ventricular systole' means the contraction of the ventricles.
What is the meaning of 'diastole' in the context of the heart?
-'Diastole' refers to the phase of relaxation in the heart. For example, 'ventricular diastole' means the relaxation of the ventricles.
How does blood flow into the heart at the beginning of the cardiac cycle?
-At the start of the cardiac cycle, both the atria and ventricles are in diastole. Blood flows into the atria from the vena cava and pulmonary vein, causing the pressure in the atria to rise.
What causes the atrioventricular (AV) valves to open during the cardiac cycle?
-The AV valves open when the pressure in the atria exceeds the pressure in the ventricles, allowing blood to flow from the atria into the ventricles.
What happens during atrial systole?
-During atrial systole, the atria contract, pushing the remaining blood into the ventricles. This helps fill the ventricles more completely before they contract.
What triggers the closure of the atrioventricular valves?
-The atrioventricular valves close when the pressure in the ventricles becomes greater than the pressure in the atria, preventing blood from flowing backward into the atria.
Why do the semilunar valves open during ventricular systole?
-The semilunar valves open when the pressure in the ventricles exceeds the pressure in the pulmonary artery and aorta, allowing blood to be pumped from the ventricles into these vessels.
What is the significance of ventricular diastole in the cardiac cycle?
-Ventricular diastole marks the relaxation of the ventricles. During this phase, the pressure in the ventricles drops, causing the semilunar valves to close and preventing blood from flowing back into the ventricles.
What happens after the semilunar valves close during the cardiac cycle?
-Once the semilunar valves close, the heart is ready to enter the next cardiac cycle. The ventricles are relaxed, and blood will begin to flow back into the atria, starting the cycle over again.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)