Sistema respiratório dos Osteíctes - Vertebrados - Biologia
Summary
TLDRIn this educational script, the respiratory system of osteichthyes (bony fish) is explored, focusing on the role of gills in gas exchange. The process involves water passing through the gills, where oxygen is absorbed and carbon dioxide is released via a countercurrent mechanism. The heart pumps venous blood to the gills, where oxygen is diffused into the bloodstream. Additionally, lungfish are introduced, highlighting their unique adaptation of having rudimentary lungs to supplement their gills, allowing them to breathe air. This fascinating biological system showcases the intricate ways fish have evolved to survive underwater.
Takeaways
- 😀 The respiratory system of osteichthyes (bony fish) is primarily based on gills, which are specialized structures for gas exchange in aquatic environments.
- 😀 Gills are organized into gill arches and are covered by a structure called the operculum, which protects the gills in bony fish.
- 😀 The respiratory system is closely linked to the circulatory system, with blood being pumped by the heart through arteries that supply the gills for gas exchange.
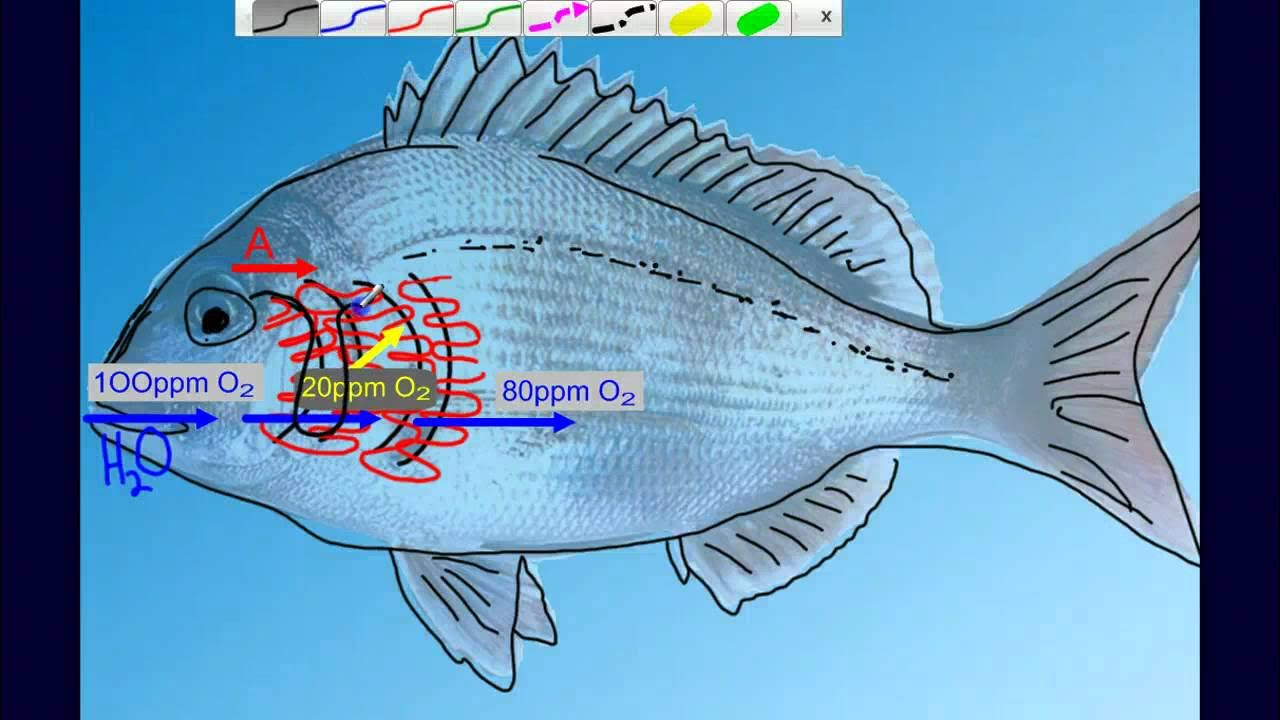
- 😀 Oxygen from the water is absorbed through the gills by diffusion, while carbon dioxide is released from the fish's bloodstream into the water.
- 😀 The direction of water flow over the gills is opposite to the direction of blood flow in the fish's circulatory system, creating a countercurrent mechanism for more efficient oxygen exchange.
- 😀 Blood entering the gills is rich in carbon dioxide and low in oxygen (venous blood), and as it passes through the gill capillaries, it becomes oxygenated.
- 😀 Oxygenated blood (arterial blood) is then pumped to the rest of the fish's body for cellular respiration, while carbon dioxide is transported back to the gills for removal.
- 😀 Fish have specialized capillaries in the gills where gas exchange occurs, and these capillaries are key to the efficient movement of gases.
- 😀 Lungfish (class Dipnoi) have both gills and rudimentary lungs, which allows them to breathe air in addition to extracting oxygen from the water.
- 😀 Lungfish can inhale atmospheric air, storing it in their rudimentary lung, where oxygen diffuses into the blood, and carbon dioxide diffuses out, a process that differs from gill respiration.
- 😀 The evolution of the primitive lung in lungfish is considered an important step towards the development of the swim bladder in other fish species.
Q & A
What is the main topic of this lesson?
-The main topic of the lesson is the respiratory system of osteichthyes, specifically focusing on the gills and their function in respiration, as well as a comparison with lungfish.
How do osteichthyes breathe?
-Osteichthyes, or bony fish, breathe through their gills. The gills are specialized structures that allow for gas exchange with the water, facilitating the absorption of oxygen and the release of carbon dioxide.
What is the role of the operculum in fish respiration?
-The operculum is a structure that covers the gills of bony fish. It helps control the flow of water over the gills during respiration. When the operculum closes, water enters the fish's mouth and flows over the gills before exiting through the operculum.
What is the connection between the circulatory and respiratory systems in fish?
-The circulatory system is closely associated with the respiratory system in fish. Blood from the heart is pumped through arteries to the gills, where gas exchange occurs. Venous blood, rich in carbon dioxide, enters the gills, while oxygen from the water diffuses into the blood.
What is the countercurrent mechanism in fish respiration?
-The countercurrent mechanism occurs when water flows in the opposite direction to the blood flow in the gills. This increases the efficiency of oxygen absorption because the concentration gradient between the water and blood is maintained throughout the entire gill region.
What happens during gas exchange in the gills of bony fish?
-In the gills, carbon dioxide from the blood diffuses into the surrounding water, while oxygen from the water diffuses into the blood. This process occurs in the gill capillaries, the thin blood vessels where the gas exchange takes place.
What are the afferent and efferent gill arteries?
-Afferent gill arteries carry venous blood (rich in CO2) to the gills, while efferent gill arteries carry oxygen-rich blood away from the gills to the rest of the body. These arteries are crucial for transporting blood during respiration.
What is the difference between venous and arterial blood in fish?
-Venous blood in fish is low in oxygen and high in carbon dioxide, while arterial blood is oxygen-rich after gas exchange in the gills. Venous blood is pumped from the heart to the gills, and after oxygenation, it becomes arterial blood and circulates to the body.
How do lungfish differ from bony fish in terms of respiration?
-Lungfish have both gills and rudimentary lungs, allowing them to breathe atmospheric air in addition to underwater respiration. They can surface to inhale air, which is stored in their primitive lung, and oxygen is absorbed into the blood via diffusion.
What is the function of the rudimentary lung in lungfish?
-The rudimentary lung in lungfish allows them to inhale atmospheric air when needed. The air is stored in the lung, and oxygen diffuses into the blood, while carbon dioxide diffuses out, similar to the process in the gills.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)