Eukaryotic Cell Structure - Organelles - Post 16 Biology (A Level, Pre-U, IB, AP Bio)
Summary
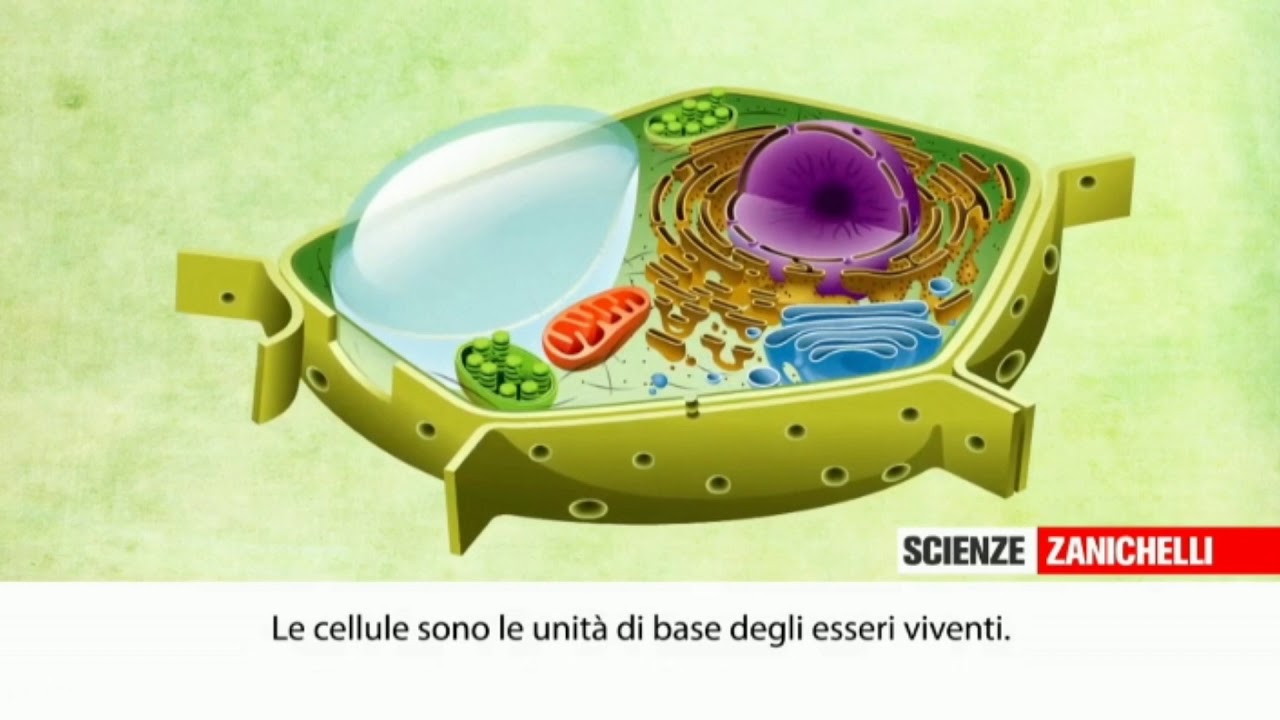
TLDRThis video explores the essential structures found in eukaryotic cells, known as organelles, including the nucleus, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, and mitochondria. It explains their functions, such as protein synthesis, energy production, and cell division. Key differences between animal and plant cells are highlighted, including the presence of chloroplasts and large vacuoles in plants. The video also covers specialized structures like ribosomes, lysosomes, and the cytoskeleton. By diving into the ultra-structure visible only through electron microscopy, it offers a detailed look at the building blocks that power life at the cellular level.
Takeaways
- 😀 The cell's internal structures, called organelles, are essential for its function, but they vary in specialized cells.
- 😀 The nucleus is the largest organelle, surrounded by the nuclear envelope, and contains DNA in the form of chromatin, which forms chromosomes during cell division.
- 😀 The nucleolus inside the nucleus is responsible for producing ribosomes and RNA, which are critical for protein synthesis.
- 😀 The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) has two types: rough ER (with ribosomes for protein synthesis) and smooth ER (for lipid and steroid production).
- 😀 Ribosomes, composed of ribosomal RNA and protein, are the site of protein synthesis and can be found on the rough ER or floating freely in the cytoplasm.
- 😀 Eukaryotic ribosomes are called 80S ribosomes, with 60S and 40S subunits, whereas prokaryotic cells have 70S ribosomes.
- 😀 Mitochondria are the powerhouses of the cell, generating ATP through aerobic respiration, and contain their own ribosomes and DNA.
- 😀 Chloroplasts, found only in plant cells, are responsible for photosynthesis and contain chlorophyll, stacked into thylakoids to increase surface area.
- 😀 Plant cells have a large central vacuole filled with cell sap, which helps maintain cell shape, stores substances, and contributes to cell turgidity.
- 😀 The cytoskeleton provides structural support, enables movement within the cell, and is made of microtubules and protein filaments.
- 😀 Animal cells have centrioles that play a role in cell division by forming the microtubule spindle, whereas plant cells use microtubule organizing centers for the same function.
Q & A
What is the primary function of the nucleus in a eukaryotic cell?
-The nucleus serves as the control center of the cell, containing all the DNA, which is essential for cell functions and reproduction. It also plays a key role in protein synthesis through its involvement in the production of ribosomes.
Why does the rough endoplasmic reticulum (ER) have ribosomes attached to its membrane?
-The rough ER has ribosomes on its membrane because these ribosomes are responsible for protein synthesis. Once proteins are produced, the rough ER helps transport them to other parts of the cell for processing or secretion.
What is the function of the smooth endoplasmic reticulum (ER)?
-The smooth ER is involved in the synthesis of lipids and steroids, including hormones. Unlike the rough ER, it lacks ribosomes on its surface.
Why do mitochondria contain their own DNA and ribosomes?
-Mitochondria contain their own DNA and ribosomes as part of the endosymbiotic theory. This suggests that mitochondria were once free-living bacteria that formed a symbiotic relationship with eukaryotic cells.
What is the role of the Golgi apparatus in the cell?
-The Golgi apparatus modifies, processes, and packages proteins received from the rough ER. It adds molecules like carbohydrates to proteins and then transports them to their final destinations within or outside the cell.
How are lysosomes involved in cellular digestion?
-Lysosomes contain hydrolytic enzymes that break down substances the cell ingests or recycles. They play a key role in processes like phagocytosis, where the cell takes in particles or microorganisms.
What is the function of vacuoles in plant cells?
-Vacuoles in plant cells store water, dissolved substances, and waste products. They help maintain cell shape and turgidity, supporting the plant cell structure.
What is the difference between the cell wall in plant cells and the plasma membrane?
-The cell wall in plant cells provides structural support, strength, and shape, while the plasma membrane controls the entry and exit of substances. The cell wall is freely permeable, while the plasma membrane is selectively permeable.
What are centrioles, and what role do they play in cell division?
-Centrioles are structures found in animal cells that organize microtubules during cell division. They help form the spindle apparatus that separates chromosomes during mitosis.
What is the structure and function of cilia and flagella?
-Cilia and flagella are microtubule-based structures involved in cell movement. Cilia are short and numerous, while flagella are long and usually singular. They are powered by ATP and are used for locomotion or moving substances along the surface of the cell.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)