Learn Queue data structures in 10 minutes 🎟️
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the concept of queues in computer science, a FIFO (First In, First Out) linear data structure used to manage elements in order. Using a fun analogy of people waiting in line at a cashier, it illustrates enqueuing (adding to the tail) and dequeuing (removing from the head). The tutorial demonstrates how to implement queues in Java using the LinkedList class, highlighting key methods like offer(), poll(), and peek(), as well as additional useful methods inherited from the Collection class. Practical applications such as keyboard buffers, printer queues, and BFS algorithms are also discussed, making the concept clear and relatable.
Takeaways
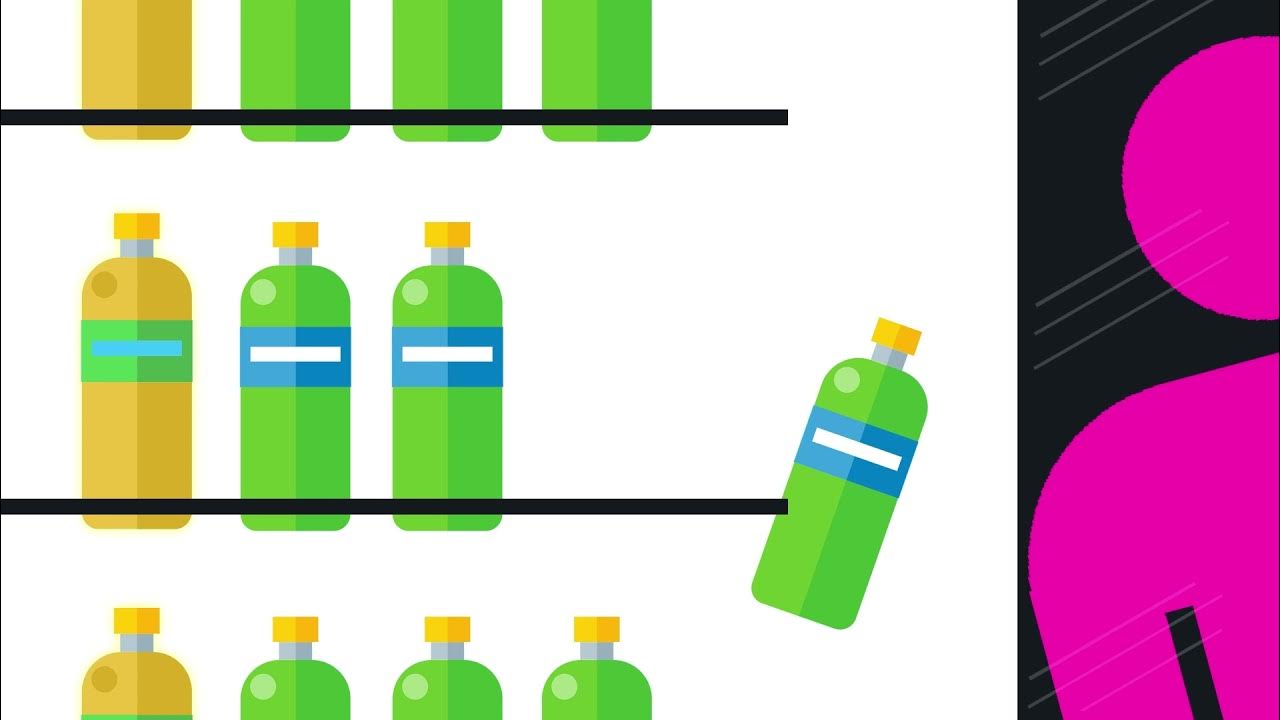
- 😀 A queue is a FIFO (First In, First Out) data structure, meaning the first element added is the first to be removed.
- 😀 Queues are linear data structures used to hold elements prior to processing.
- 😀 The front of the queue is called the head, and the back is called the tail.
- 😀 Enqueuing is the process of adding an element to the tail of the queue.
- 😀 Dequeuing is the process of removing an element from the head of the queue.
- 😀 The peek operation allows you to view the element at the head without removing it.
- 😀 In Java, `Queue` is an interface and cannot be instantiated directly; a class like `LinkedList` is used instead.
- 😀 Key Java queue methods include `offer()` to enqueue, `poll()` to dequeue, and `peek()` to examine the head element.
- 😀 Additional useful methods inherited from the Collection class include `isEmpty()`, `size()`, and `contains()`.
- 😀 Queues have practical applications in keyboard buffers, printer queues, linked lists, priority queues, and BFS algorithms.
- 😀 Using `offer()`, `poll()`, and `peek()` is preferred over `add()`, `remove()`, and `element()` because they handle exceptions more gracefully.
Q & A
What is a queue in computer science?
-A queue is a linear data structure that follows the FIFO (First In, First Out) principle, where elements are added at the tail and removed from the head.
What does FIFO mean in the context of queues?
-FIFO stands for First In, First Out, meaning the first element added to the queue will be the first one to be removed.
What are the head and tail of a queue?
-The head is the front of the queue where elements are removed, and the tail is the end of the queue where elements are added.
What is the difference between enqueuing and dequeuing?
-Enqueuing is the process of adding an element to the tail of the queue, while dequeuing is the process of removing an element from the head of the queue.
Why can't you instantiate a Queue interface directly in Java?
-Because Queue is an interface, not a class, and interfaces cannot be instantiated directly. A class that implements the Queue interface, such as LinkedList or PriorityQueue, must be used.
Which Java classes implement the Queue interface?
-The main classes are LinkedList and PriorityQueue. LinkedList maintains FIFO order, while PriorityQueue orders elements based on priority.
What are the core methods of the Queue interface in Java?
-The core methods are: offer() to enqueue, poll() to dequeue, and peek() to examine the head element without removing it.
What additional useful methods are inherited from the Collection class for queues?
-Queues inherit methods like isEmpty() to check if the queue is empty, size() to get the number of elements, and contains() to check if a specific element exists in the queue.
Can you give a real-world example of where queues are used?
-Queues are used in keyboard buffers to process characters in order typed, in printer job queues to print documents sequentially, and in breadth-first search algorithms in graphs.
Why is it recommended to use offer(), poll(), and peek() instead of add(), remove(), and element()?
-Because offer(), poll(), and peek() return special values instead of throwing exceptions, making them safer and more predictable to use in Java.
How does the queue change when multiple elements are dequeued?
-Each dequeue operation removes the head element, and the next element in line moves to the head. The tail remains the last element until new elements are added.
What is a practical analogy used in the video to explain queues?
-The video uses a line of people waiting at a cashier or concert tickets, including a humorous example of a 'wild Karen' to demonstrate how elements are processed sequentially.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)