How does Water enter a cell?
Summary
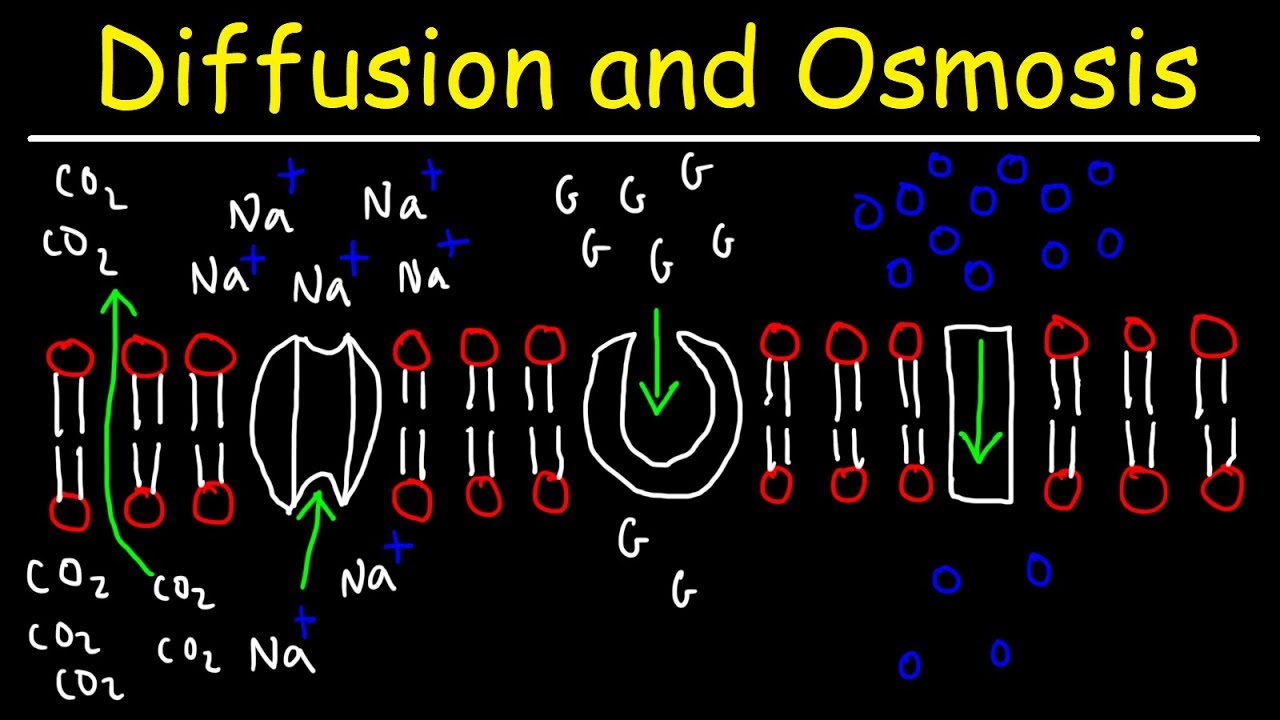
TLDRIn this video, the importance of facilitated diffusion in cellular function is explained. The cell must move molecules like water, glucose, and ions across the membrane, but these substances face difficulty due to their size and polarity. The process of facilitated diffusion, involving proteins such as aquaporins, helps molecules move more efficiently. While water can pass through the membrane via simple diffusion, it moves faster through aquaporins, which make the process quicker. The video also touches on passive transport and the role of channel and carrier proteins in assisting molecular movement, ultimately ensuring the cell stays alive.
Takeaways
- 😀 The cell must move water, glucose, and ions like sodium across the cell membrane to survive.
- 😀 Water, glucose, and ions cannot easily pass through the cell membrane on their own.
- 😀 Water can pass through the cell membrane slowly, but the process is difficult due to its polarity.
- 😀 Molecules move across the membrane down their concentration gradient, from high to low concentration.
- 😀 Facilitated diffusion helps molecules like glucose, ions, and water enter the cell through proteins in the membrane.
- 😀 Proteins that span the cell membrane create pathways for facilitated diffusion.
- 😀 Aquaporins are channel proteins that specifically allow water to move into and out of the cell.
- 😀 While water is small enough for simple diffusion, its polar nature makes this process slow.
- 😀 The majority of water enters the cell through aquaporins rather than simple diffusion.
- 😀 Facilitated diffusion is a type of passive transport that uses channel or carrier proteins to assist molecule movement.
- 😀 The cell uses facilitated diffusion to transport certain molecules or ions without expending energy (passive transport).
Q & A
What is the main problem the cell faces in the video?
-The cell needs to move water, glucose, and ions like sodium across its membrane to stay alive, but these molecules can't pass through the membrane easily on their own.
Why can't water, glucose, and ions easily pass through the cell membrane?
-These molecules are either too large or polar, which prevents them from passing through the cell membrane directly.
How does water move through the cell membrane?
-Water can move through the cell membrane, but the process is slow and difficult due to its polar nature. Most water enters or exits the cell through specialized proteins called aquaporins.
What is facilitated diffusion?
-Facilitated diffusion is a process where proteins in the cell membrane help move molecules like glucose, ions, and water across the membrane. It does not require energy and works by allowing molecules to move down their concentration gradient.
What are aquaporins?
-Aquaporins are specialized channel proteins in the cell membrane that help facilitate the movement of water into and out of the cell.
Why is simple diffusion of water slow?
-Simple diffusion of water is slow because water is a polar molecule, which makes it harder for it to pass through the non-polar lipid bilayer of the cell membrane.
What does 'moving down the concentration gradient' mean?
-It means that molecules move from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration, which is the natural direction for diffusion to occur.
What are the two types of proteins involved in facilitated diffusion?
-The two types of proteins involved in facilitated diffusion are channel proteins and carrier proteins. These proteins help molecules move across the cell membrane.
What type of transport is facilitated diffusion?
-Facilitated diffusion is a type of passive transport, meaning it does not require energy (ATP) to move molecules across the membrane.
How does facilitated diffusion assist molecules that cannot pass through the membrane easily?
-Facilitated diffusion assists molecules by providing an alternate route across the membrane via channel or carrier proteins, which makes it easier for molecules to move in or out of the cell.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Course: Membrane Transport in Cells Via "Diseases and Drugs"

Transpor membran lengkap- difusi sederhana, osmosis, difusi terfasilitasi, pompa NA+/K+, biologi sel

Facilitated Diffusion: Ion Channels, Carrier Proteins, and Aquaporins | AP Biology 2.7
Diffusion and Osmosis - Passive and Active Transport With Facilitated Diffusion

Diffusion, Osmosis, Active Transport for Anatomy and Physiology

Structure Of The Cell Membrane: Active and Passive Transport
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)