Episode 1 – Treaty Promises: Treaty making
Summary
TLDRThe video script discusses the historical and ongoing significance of treaties between Indigenous peoples and the Crown, emphasizing their role in peaceful coexistence and resource sharing. It highlights the importance of understanding Indigenous perspectives and oral traditions in treaty interpretation. The script also explores the concept of unceded territories, where Indigenous peoples maintain rights due to non-negotiated land seizures. Modern treaties are presented as evolving agreements that redefine relationships, incorporating land management and self-governance, with the ultimate goal of reconciliation and self-determination for Indigenous communities.
Takeaways
- 📜 Treaties are agreements between the Crown and Indigenous peoples that affirm peaceful coexistence, land and resource sharing, and mutual recognition of authority.
- 🌿 Indigenous nations had a long-standing practice of developing treaties with each other, including with non-human beings, before the Crown's involvement.
- 🔍 There are often differing interpretations of treaties between the Crown and Indigenous peoples, highlighting the importance of understanding Indigenous perspectives and oral traditions.
- 🏞 Treaties with the Crown were historically seen as land purchases, but Indigenous peoples viewed them as agreements about the future and the environment they depend on.
- 🤝 Treaties are based on peace-building and the sharing of land, with oral agreements symbolized by wampum belts representing peaceful relations.
- 🏡 Treaties are foundational to the legitimacy of settler presence and define how relationships with Indigenous peoples, including land and water, should be conducted.
- 🔄 Treaties are built on reciprocity, renewal, and respect, which are essential to understanding and maintaining good relationships.
- 📍 The concept of 'unceded' land refers to territories not signed away by Indigenous peoples but taken by the Crown, emphasizing Indigenous rights to manage those lands.
- 📝 Modern treaties redefine relationships between Indigenous peoples and the state, including land management and partnerships with local governments.
- 🌐 Self-governance for Indigenous nations was pursued through treaty negotiations, aiming to establish governance models that respect Indigenous autonomy.
- 🛠 The first modern Inuit treaty, the James Bay Northern Quebec Agreement, was a result of large-scale development projects and the need for government cooperation.
- 💡 Compromise is a key aspect of treaty negotiations, both historic and modern, reflecting the balance between Indigenous self-determination and Crown interests.
Q & A
What is the primary purpose of treaties between the Crown and Indigenous peoples?
-The primary purpose of treaties is to confirm arrangements of peaceful coexistence, land and resource sharing, and to recognize each party's authority or jurisdiction.
How were Indigenous nations interacting with each other and other beings prior to contact with the Crown?
-Indigenous nations were developing treaties amongst themselves, with other nations, and even with non-human beings such as animal nations across Turtle Island.
What does the term 'Turtle Island' refer to in the context of the script?
-Turtle Island is a term used to refer to the territory of North America, highlighting the Indigenous perspective and history.
Why do treaties have different meanings for the Crown and Indigenous peoples?
-Treaties have different meanings because they often represent vastly different interpretations and understandings of the agreements, with Indigenous perspectives and oral versions of treaties providing a crucial context.
What is the significance of wampum belts in the context of treaties?
-Wampum belts are symbolic representations of oral agreements and communicate peaceful relations between nations, serving as a central element in the treaty-making process.
How do Indigenous elders view the concept of making a treaty?
-Elders view making a treaty as more than just a signature on paper; it's a deep and meaningful process that establishes a relationship and involves responsibilities towards the land and each other.
What is the basis for the legitimate settler presence within Indigenous territories?
-The basis for legitimate settler presence is the treaties that have been made, which establish the foundations for relationships including how to interact with lands and waters.
What are the core factors in understanding a good relationship as per the treaties?
-The core factors in understanding a good relationship are reciprocity, renewal, and respect, which are fundamental to the treaty agreements.
What is the definition of 'unceded' in the context of land rights?
-Unceded land refers to territories that were not signed away or given away by Indigenous peoples but were taken by the Crown, thus the Indigenous peoples maintain their rights and responsibilities to manage those lands and resources.
How do modern treaties redefine the relationship between Indigenous peoples and the state?
-Modern treaties define new relationships by establishing land management under Indigenous control and jurisdiction, creating partnerships with local governments, and solidifying roles and responsibilities.
What was the significance of the James Bay Northern Quebec Agreement in 1975?
-The James Bay Northern Quebec Agreement was the first Inuit modern treaty, spurred by the Quebec government’s interest in hydroelectric development, and it set a precedent for future agreements and negotiations.
Why is compromise often inherent in treaty negotiations?
-Compromise is inherent in treaty negotiations because it allows for the balancing of interests and the creation of agreements that, while not optimal, can provide necessary incremental changes and protections for Indigenous rights and self-determination.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
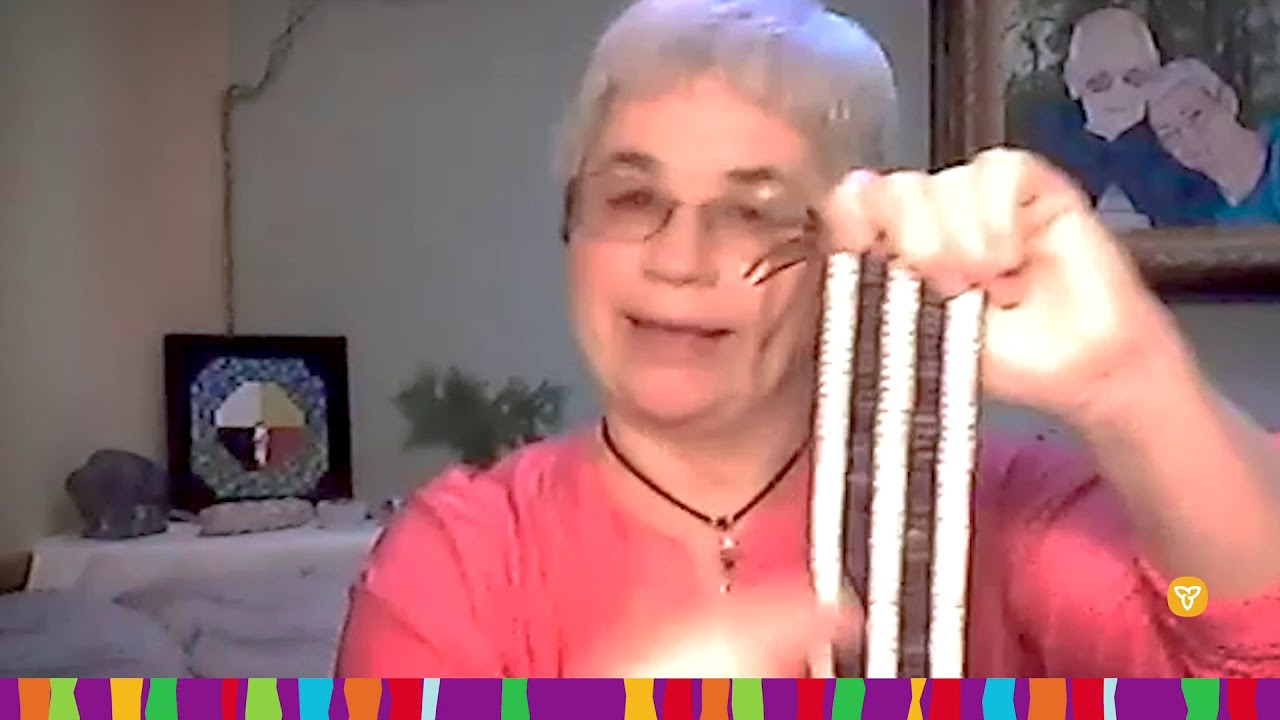

Brenda Collins, Knowledge Keeper and artist, Treaty 94, on "What is a Wampum belt?"

Episode 2 – Treaty Promises: Interpreting and understanding treaties

What the heck is the Royal Proclamation of 1763?

Justice for Aboriginal Peoples -- It's time
Land governance: Past

Richard Hill | Ep 4 | Oral History | Voices From Here
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)