A física dos transformadores elétricos e suas aplicações indispensáveis
Summary
TLDRThis video delves into the fascinating history and working principles of transformers, key devices in electrical power transmission. It traces the 'War of Currents' between Thomas Edison and Nikola Tesla, highlighting Tesla's victory thanks to the invention of the transformer. The video explains how transformers efficiently convert voltage levels for long-distance power transmission, reducing energy loss. It covers the core concepts of induction, the transformer equation, and energy conservation, while also comparing the alternating current (AC) system to Edison's direct current (DC) system, showing the advantages of AC in modern electrical grids.
Takeaways
- 😀 The War of Currents was a historical dispute between Thomas Edison, who advocated for direct current, and Nikola Tesla, who supported alternating current.
- 😀 Tesla's success in the War of Currents was largely due to the invention of the electrical transformer, which allowed for efficient voltage conversion.
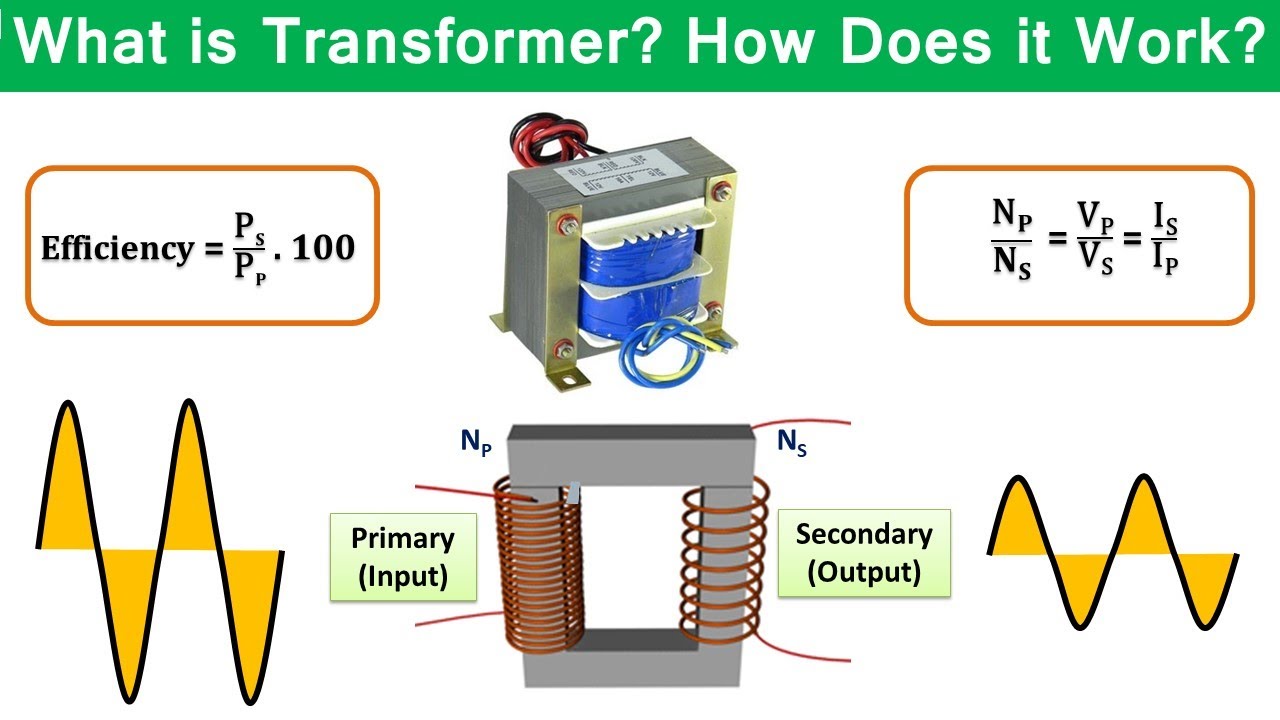
- 😀 A transformer is a device that changes alternating voltage levels, either stepping it up or stepping it down for various electrical applications.
- 😀 Transformers are used to adjust voltages for different purposes, such as reducing high voltage for household use or increasing voltage for long-distance power transmission.
- 😀 The transformer consists of two coils: a primary coil and a secondary coil, which are wound around the same core to induce electromotive force based on the changing magnetic field.
- 😀 The ratio of turns between the primary and secondary coils determines whether the transformer steps up or steps down the voltage.
- 😀 In a step-down transformer, the secondary coil has fewer turns than the primary, reducing voltage; in a step-up transformer, the secondary coil has more turns, increasing voltage.
- 😀 Transformers adhere to the principle of energy conservation: as voltage increases, current decreases, ensuring that power remains constant across the primary and secondary circuits.
- 😀 High voltage transmission, such as in Tesla's alternating current system, allows for efficient long-distance power delivery with reduced power loss.
- 😀 Direct current systems, like those proposed by Edison, cannot use transformers because transformers rely on varying magnetic fields, which direct current does not produce.
- 😀 Transformers are crucial for modern power transmission and are used in various settings, from industrial power stations to household devices like phone chargers.
Q & A
What was the War of Currents about?
-The War of Currents was a dispute in the late 1880s between Thomas Edison, who advocated for direct current (DC), and Nikola Tesla, who supported alternating current (AC) for large-scale electrical power transmission.
How did Nikola Tesla's triumph in the War of Currents relate to transformers?
-Tesla's success in the War of Currents was largely due to his development of the electrical transformer, a device that efficiently converts voltage levels, making high-voltage AC transmission viable.
What is the primary function of a transformer?
-A transformer is a device that either raises or lowers the voltage of alternating current (AC), enabling efficient energy transmission and use in various applications.
Why is it necessary to change voltage levels in electrical systems?
-Voltage changes are necessary to efficiently transmit electricity over long distances and to power various devices at appropriate voltage levels, such as reducing high voltage from transmission lines or stepping up voltage for specific equipment.
How does a transformer work?
-A transformer operates through mutual induction between two coils (primary and secondary), where an alternating current in the primary coil creates a varying magnetic field that induces a voltage in the secondary coil, depending on the ratio of turns between the coils.
What is the transformer equation?
-The transformer equation relates the voltage and number of turns in the primary and secondary coils, stating that the ratio of voltages is equal to the ratio of the number of turns in each coil.
What is the difference between a step-up and a step-down transformer?
-A step-up transformer increases the voltage by having more turns in the secondary coil than the primary coil, while a step-down transformer reduces the voltage by having fewer turns in the secondary coil compared to the primary coil.
How does energy conservation work in transformers?
-In transformers, the power (product of voltage and current) remains conserved. When the voltage is increased, the current decreases, and vice versa, ensuring no energy is lost in the process, in line with the conservation of energy principle.
Why is alternating current (AC) more efficient than direct current (DC) for long-distance transmission?
-AC is more efficient than DC for long-distance transmission because it allows the use of transformers to step up voltage, reducing current and minimizing energy losses due to resistance in the transmission lines.
Why couldn't Thomas Edison use transformers with direct current (DC) in the same way Tesla did with alternating current (AC)?
-Transformers rely on a varying magnetic field to induce voltage in the secondary coil, but direct current (DC) provides a constant current, preventing the magnetic field from varying. This makes transformers ineffective with DC, unlike AC, which enables efficient voltage conversion.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Transformadores Eléctricos Explicados

How Power Transformers work ? | Epic 3D Animation #transformers
What is a Transformer? Transformers Explained - Working Principle (Transformer Tutorial)

IGCSE Physics (2023-2025) + PYQ - C21/25: Electromagnetic Induction

How does a Transformer work - Working Principle electrical engineering

FISIKA Kelas 12 - Induksi Elektromagnetik: Generator & Transformator | GIA Academy
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)