A DESCOLONIZAÇÃO DA ÁFRICA || VOGALIZANDO A HISTÓRIA
Summary
TLDRThe video delves into Africa's decolonization process, starting from the Berlin Conference of 1884-1885 where European powers divided the continent. It highlights the struggles and resilience of African nations as they fought for independence, particularly after WWII. The narrative showcases the differing paths to independence, with peaceful negotiations in some regions and violent revolts in others. The lasting impact of colonialism, the role of pan-Africanism, and the legacy of independence struggles are explored, emphasizing how Africa’s liberation shaped its modern identity and political landscape.
Takeaways
- 😀 The African continent, where our species originated, has relatively recent countries, most of which gained independence less than 100 years ago.
- 😀 The Berlin Conference (1884-1885), organized by German Chancellor Otto von Bismarck, divided Africa among European powers, with the goal of peaceful exploitation of its resources.
- 😀 The African resistance to European colonization existed but lacked strength to challenge colonial powers, which dominated the continent into the 20th century.
- 😀 Over one million African soldiers fought in World War II, often against their will, contributing to the decline of European racial superiority narratives and sparking independence movements.
- 😀 The end of World War II marked the beginning of stronger decolonization efforts, as colonial powers were weakened and Africans began to demand independence.
- 😀 Pan-Africanism, led by intellectuals like Kwame Nkrumah, grew in popularity, advocating for unity and independence from colonial powers across the continent.
- 😀 Ghana was the first African country to achieve independence in 1957, followed by many others, including Sudan (1956) and Morocco and Tunisia (1956).
- 😀 Some African countries, like Guinea (1958), achieved independence through peaceful means, while others, like Algeria (1962), fought violent wars against French colonial rule.
- 😀 Portugal held on to its colonies for longer, with Guinea-Bissau, Angola, and Mozambique gaining independence in the 1970s after prolonged struggles.
- 😀 Despite the formal end of colonization, post-independence African nations often faced authoritarian regimes and internal conflicts, influenced by Cold War tensions between the US and the USSR.
- 😀 The legacy of the Berlin Conference's arbitrary borders remains, with ethnic groups divided and rival groups forced to share territories, leading to ongoing political instability and conflicts.
Q & A
What was the purpose of the Berlin Conference of 1884-1885?
-The Berlin Conference, proposed by German Chancellor Otto von Bismarck, aimed to divide Africa among European powers. While the official goal was to combat slavery and ensure free trade in certain regions, the true intent was to peacefully divide Africa for European exploitation.
How did the European colonization of Africa impact the local populations?
-European colonization in Africa exploited local populations, forcing them to work under poor conditions with little to no financial reward. The territories were rich in natural resources, such as rubber, cotton, gold, and diamonds, which were extracted for the benefit of the colonial powers.
What role did African soldiers play during World War I and World War II?
-During both world wars, many African soldiers fought alongside European powers, often without military experience. They were frequently placed on the front lines and suffered high casualties. Those who returned home were poorly compensated and faced continued subjugation in their own countries.
How did World War II contribute to the decolonization of Africa?
-World War II weakened European powers, and many African soldiers returned home with a new perspective on racial equality. The war also highlighted the contradictions of colonialism, as European countries that preached self-determination were themselves subjugating African peoples. This led to a stronger push for independence across the continent.
Which African country was the first to gain independence, and when?
-Ghana, then known as the Gold Coast, was the first African country to gain independence from a European power, achieving independence from the United Kingdom in 1957.
What were the key factors behind the violent independence struggles in some African countries?
-Some African countries, like Algeria and the Portuguese colonies, faced violent independence struggles due to the reluctance of European powers to relinquish control. These conflicts were fueled by pride, economic interests, and the unwillingness of colonial powers to accept the changing geopolitical landscape.
How did the independence of African countries affect their political structures?
-While many African countries gained independence, the political systems often remained unchanged. Authoritarian leadership, similar to colonial rule, persisted in many cases, leading to power struggles and political instability.
What was the role of Pan-Africanism in the decolonization movement?
-Pan-Africanism was a movement that advocated for African unity and resistance against European exploitation. It gained popularity as a way to unite African nations in the fight for independence, with key leaders like Kwame Nkrumah championing the cause.
How did the Cold War influence African decolonization?
-During the Cold War, both the United States and the Soviet Union sought to gain allies in Africa. This geopolitical competition fueled internal conflicts and power struggles within newly independent African countries, often exacerbated by foreign intervention.
Why did some African countries, like Liberia and Ethiopia, avoid colonization?
-Liberia was founded by freed American slaves, and Ethiopia successfully resisted colonization, notably defeating an Italian invasion in the late 19th century. These two countries maintained their independence during the height of European colonialism.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

The Scramble for Africa - The Berlin Conference: Grade 8 Term 3 History

Imperialismo na África

O IMPERIALISMO EUROPEU E O NEOCOLONIALISMO | Resumo de História Enem. Professor Dudu Volpato

The Berlin Conference (1884 - 1885)

Resumo de História: IMPERIALISMO (Débora Aladim)
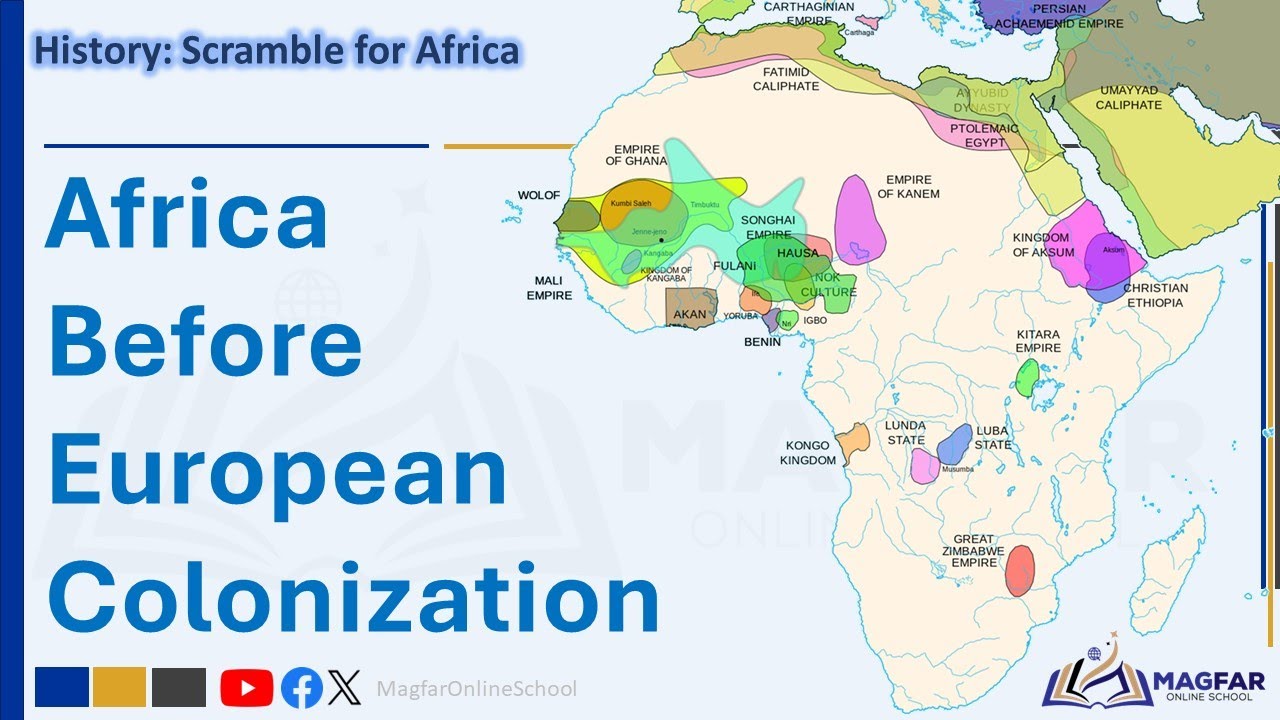
Scramble for Africa: Africa before European Colonization. Grade 8 Term 3 History.
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)