Sistema Muscular 2ª parte
Summary
TLDRThe transcript explains the three main types of muscles in the human body: smooth muscle, cardiac striated muscle, and skeletal striated muscle. It highlights their morphological and functional differences, such as smooth and cardiac muscles being involuntary, while skeletal muscles are voluntary. The script also details the anatomy of skeletal muscle, including its components like tendons and aponeuroses. Additionally, it touches on the function of structures such as synovial bursae and fibrous sheaths, which protect tendons and help with muscle movement. The lecture provides an in-depth look at muscle structure, function, and their roles in body movement.
Takeaways
- 😀 There are three types of muscles in the human body: smooth muscle, cardiac striated muscle, and skeletal striated muscle.
- 😀 Smooth muscle differs in both morphology and function from cardiac striated muscle and skeletal striated muscle.
- 😀 Smooth muscle is found in the walls of internal organs, while cardiac striated muscle is found in the heart and skeletal striated muscle is associated with the skeleton.
- 😀 Smooth and cardiac striated muscles are involuntary, meaning they function without conscious control.
- 😀 Skeletal striated muscle is voluntary, allowing control over body movements like walking or lifting.
- 😀 Smooth muscle and cardiac striated muscle share similar functional characteristics, as both are involuntary.
- 😀 Skeletal muscle fibers have a visible striated appearance, while smooth muscle appears smooth and uniform.
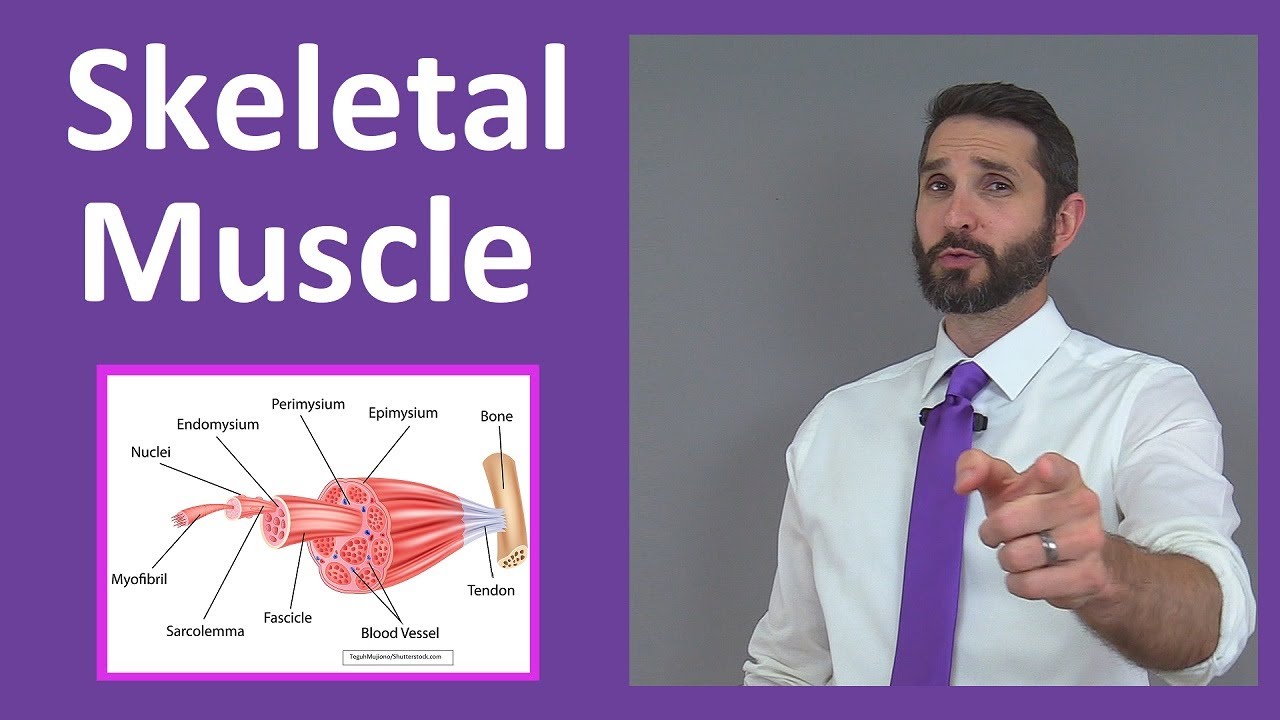
- 😀 Muscles are composed of three key components: the muscle belly (ventre muscular), tendons, and aponeuroses.
- 😀 Tendons are narrow and white, attaching muscles to bones, while aponeuroses are broader and connect muscle groups.
- 😀 Fascial structures such as muscle fascia, synovial bursae, and fibrous sheaths protect and assist with the movement of tendons and muscles during action.
Q & A
What are the three types of muscles in the human body?
-The three types of muscles in the human body are smooth muscles, cardiac striated muscles, and skeletal striated muscles.
What is the main difference in the structure of smooth muscles compared to cardiac and skeletal muscles?
-Smooth muscles do not have visible striations, while both cardiac and skeletal muscles have striations. Cardiac muscles are found in the heart, while skeletal muscles are attached to bones.
How do the functions of smooth muscles differ from those of skeletal muscles?
-Smooth muscles are involuntary and control functions like digestion and blood vessel constriction, while skeletal muscles are voluntary and control movements like walking and lifting.
Where are smooth muscles located in the body?
-Smooth muscles are located in the walls of internal organs, such as the stomach, blood vessels, and intestines.
Why are skeletal muscles considered voluntary?
-Skeletal muscles are considered voluntary because they are controlled consciously by the brain, allowing us to move parts of the body deliberately.
What is the role of tendons in the muscular system?
-Tendons are fibrous tissues that connect muscles to bones, allowing for the transfer of muscle contractions to produce movement at the joints.
What is the difference between tendons and aponeuroses?
-Tendons are thin, ribbon-like structures that connect muscles to bones, while aponeuroses are broad, flat structures that connect muscles to other muscles or bones.
How do synovial bursae help in muscle function?
-Synovial bursae are fluid-filled sacs that reduce friction between tendons and other structures, allowing for smooth and efficient movement, especially in high-movement areas like the wrist and ankle.
What is the function of the fibrous sheath in muscle anatomy?
-The fibrous sheath, or fascial covering, surrounds muscles, providing structural support and minimizing friction between muscle layers during movement.
How does the peristalsis in the digestive system relate to smooth muscle?
-Peristalsis is the involuntary, wave-like contraction of smooth muscles in the digestive system that moves food through the esophagus and intestines.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)