A Verdade Sobre O Hidrogênio
Summary
TLDRThis video explores hydrogen as a promising clean energy source, capable of powering everything from vehicles to industries like steel production. It explains hydrogen’s basic properties, its production through electrolysis, and its potential to reduce emissions in sectors like aviation and shipping. However, the video also addresses challenges, such as the high costs and environmental impact of hydrogen production, primarily from fossil fuels. It contrasts gray, blue, and green hydrogen, highlighting green hydrogen’s future potential as it becomes more affordable. The video concludes by acknowledging hydrogen's promise while emphasizing the need for ongoing research and development.
Takeaways
- 😀 Hydrogen is considered a revolutionary fuel that could power cars, trucks, trains, boats, and airplanes, with water and energy as its only byproducts.
- 😀 Hydrogen is the most abundant element in the universe and can be separated from compounds like water using electrolysis.
- 😀 Hydrogen can be used in fuel cells to generate electricity, where the byproducts are only heat and water.
- 😀 Hydrogen as a fuel source has been explored for centuries, with applications dating back to the 18th century.
- 😀 Today, most hydrogen is used in industries like fertilizer production, but it hasn’t yet become a mainstream fuel source due to cost and infrastructure limitations.
- 😀 The use of hydrogen as a fuel is gaining momentum as the world addresses climate change, with countries and companies working towards carbon neutrality.
- 😀 The steel industry, which is responsible for a significant portion of global CO2 emissions, could benefit from using hydrogen as a cleaner alternative to fossil fuels.
- 😀 Hydrogen-powered ships and airplanes are being developed, with promising pilot projects, though challenges remain, especially for long-distance travel.
- 😀 The majority of hydrogen produced today is 'gray hydrogen,' made from fossil fuels, which is not environmentally friendly.
- 😀 'Blue hydrogen' involves capturing CO2 emissions during production, but it still has a significant environmental impact. 'Green hydrogen,' produced using renewable energy sources, is cleaner but currently more expensive.
Q & A
What makes hydrogen considered a revolutionary fuel?
-Hydrogen is considered a revolutionary fuel because its combustion produces only water and energy as byproducts, making it a clean energy source with the potential to power vehicles, ships, planes, and even be used in steel production.
What is the process to obtain pure hydrogen?
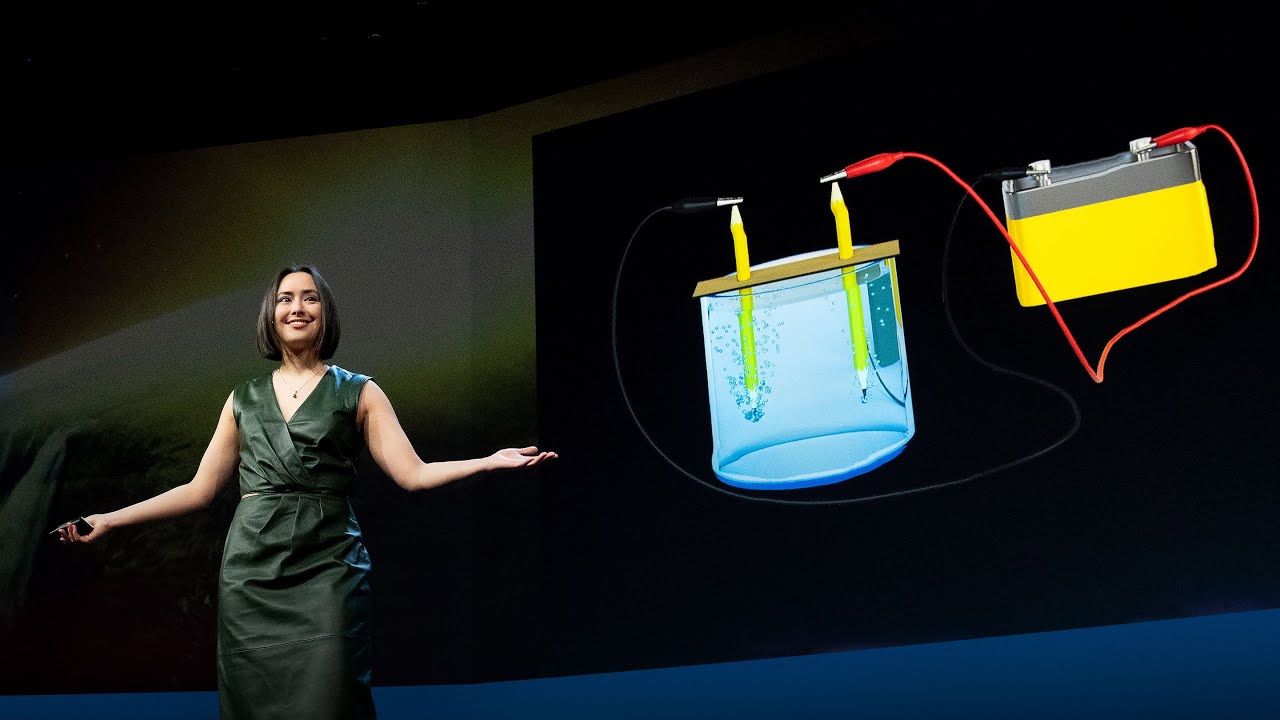
-Pure hydrogen can be obtained through electrolysis, a process where an electric current is passed through water (with added sodium bicarbonate) to break the bonds between hydrogen and oxygen, producing hydrogen gas.
How does a hydrogen fuel cell work?
-A hydrogen fuel cell generates electricity by combining hydrogen and oxygen. The only byproducts of this process are water and heat, making it an environmentally friendly method of energy generation.
When was the concept of hydrogen fuel cells first invented?
-Hydrogen fuel cells were invented in the 18th century, and by the 1960s, General Motors developed a hydrogen-powered pickup truck, showcasing its practical applications.
What are the main types of hydrogen, and how do they differ?
-There are three main types of hydrogen: gray, blue, and green. Gray hydrogen is produced from natural gas with significant CO2 emissions. Blue hydrogen uses carbon capture to reduce emissions. Green hydrogen is produced using renewable energy sources, such as wind or solar power, and has minimal environmental impact.
What is the challenge with producing hydrogen using natural gas?
-Producing hydrogen from natural gas (gray hydrogen) results in high CO2 emissions, making it an environmentally harmful process despite being a widely used method.
Why is green hydrogen considered the ideal solution for the future?
-Green hydrogen is produced using renewable energy sources, like wind and solar, which means it has no carbon emissions. It is seen as the most sustainable and environmentally friendly option for hydrogen production.
What are the current challenges with large-scale hydrogen production?
-The main challenges include high production costs, particularly for green hydrogen, and issues with storage and transportation due to hydrogen's low energy density, requiring specialized infrastructure.
What role could hydrogen play in reducing emissions in the steel industry?
-Hydrogen can replace fossil fuels in the steelmaking process, which is responsible for a significant portion of global CO2 emissions. By using hydrogen, steel production could become much cleaner, reducing its environmental impact.
What are the predictions for hydrogen's future in the energy sector?
-Hydrogen is expected to play a significant role in the global energy transition, potentially covering up to 20% of our energy needs by 2050. As renewable energy costs decrease and technology improves, hydrogen's production and use are anticipated to become more cost-effective.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)