Materiais e Processos de Fabricação para Engenharia de Produção - Extrusão e Trefilação
Summary
TLDRThis video lecture explores two important manufacturing processes: extrusion and drawing, focusing on their principles and applications. Extrusion involves the deformation of materials under high pressure through a die, which can be performed hot or cold. Direct and indirect extrusion methods are discussed, highlighting their differences. The lecture also covers the drawing process, which reduces the cross-sectional area of material, typically to produce wires and small profiles. Key formulas for calculating forces and tensions in these processes are provided, emphasizing factors like friction and material deformation, crucial for optimizing production.
Takeaways
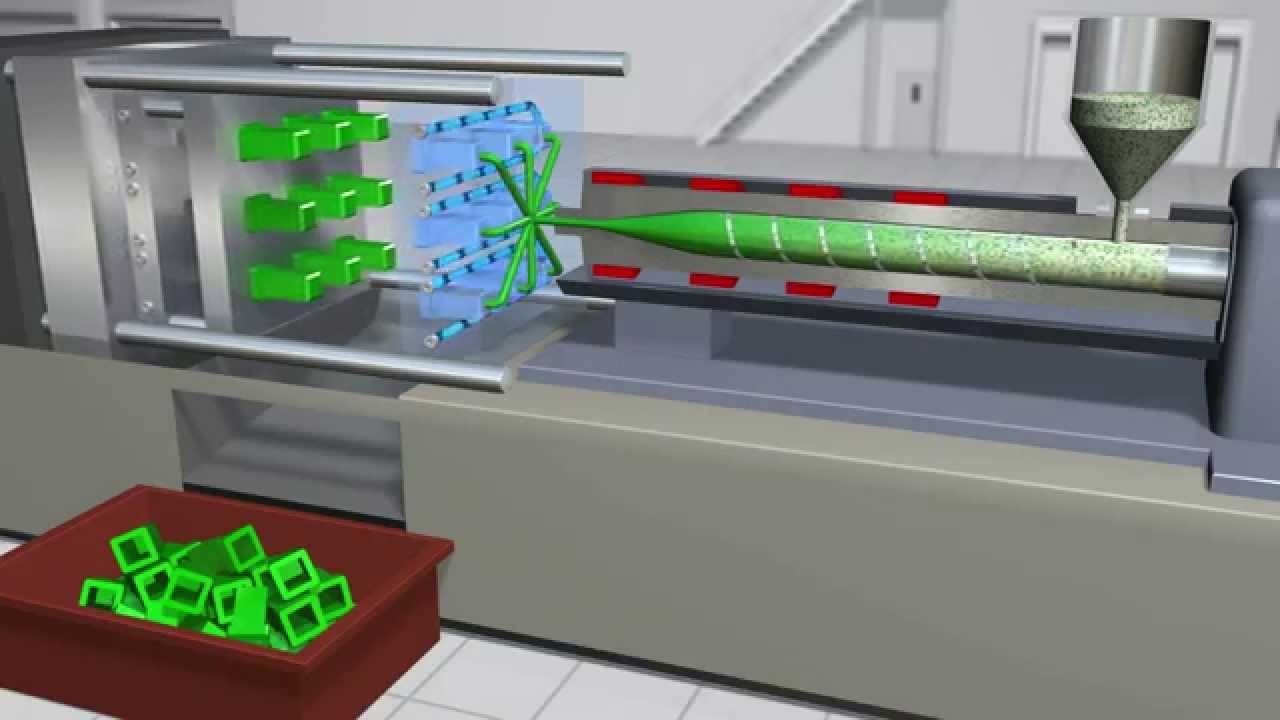
- 😀 The extrusion process is a type of plastic deformation where a material is compressed through a fixed die, creating products with a cross-sectional shape of the die.
- 😀 The material used in extrusion is typically a circular bar (billet), which can be deformed by compression using a piston or hydraulic system.
- 😀 Extrusion can be done hot or cold, with hot extrusion being more common. Hot extrusion allows for easier deformation due to the material being more malleable at high temperatures.
- 😀 In direct extrusion, the billet is pushed through the die by a piston, whereas in indirect extrusion, the die is fixed and the piston is hollow, pushing the material in the opposite direction.
- 😀 A major challenge in hot extrusion is preventing oxidation of the material’s surface due to the high temperature, which could affect the quality of the final product.
- 😀 Cold extrusion, as opposed to hot, offers advantages such as improved mechanical properties (due to strain hardening), higher precision, and better surface finish. It is often used for parts requiring high strength.
- 😀 The extrusion process is suitable for producing profiles and tubes, with reductions in cross-sectional area being possible, with some materials reducing by ratios as high as 1:100.
- 😀 The drawing process (trefilação) is used to create small cross-sectional areas such as wires and thin bars. It uses a die that reduces the material’s diameter through a pulling force.
- 😀 Trefilação, or drawing, is typically performed cold, leading to strain hardening of the material. This process is ideal for making wires, bars, and products that need precise dimensions.
- 😀 In both extrusion and drawing processes, friction between the material and the die plays a critical role in the required force, and specialized formulas are used to calculate the forces involved.
- 😀 Both extrusion and trefilação processes can utilize multiple dies in sequence, with each die progressively reducing the material’s size, facilitated by equipment like accumulator drums to maintain a continuous flow of material.
Q & A
What is the principle of extrusion?
-Extrusion is a plastic deformation process where a material, typically a metal billet, is forced through a die to create a continuous shape with a consistent cross-section. The material is usually compressed by a piston, either pneumatically or hydraulically, to pass through the matrix and form the desired shape.
What are the two main types of extrusion?
-The two main types of extrusion are direct extrusion and indirect extrusion. In direct extrusion, the material is pushed through the die by a piston, whereas in indirect extrusion, the material is moved by a hollow piston with the die remaining fixed.
What is the difference between hot and cold extrusion?
-Hot extrusion is performed at elevated temperatures, which makes the material more plastic and easier to deform. However, it requires careful temperature control to avoid material fusion or oxidation. Cold extrusion is done at room temperature, which increases the material's strength due to work hardening, and is often used for precise dimensions and better surface finishes.
What challenges can occur during hot extrusion?
-During hot extrusion, one of the challenges is oxidation on the material's surface due to high temperatures. Additionally, the material can experience localized fusion if the temperature is too high, which can impair the process.
How is the extrusion pressure calculated?
-The extrusion pressure is calculated by multiplying the average yield stress by the natural logarithm of the extrusion ratio (the ratio of the initial area to the final area). The friction between the material and the die also affects the pressure, requiring higher force to overcome this resistance.
What is the role of the mandrel in the extrusion process?
-In extrusion, the mandrel is used to create hollow sections within the extruded piece. It is fixed inside the die, and as the material is pushed through the die, the mandrel forms a hole in the middle of the material, allowing for the creation of tubes or hollow shapes.
What are the key advantages of cold extrusion?
-Cold extrusion offers several advantages, including better dimensional control, improved surface finish, higher material strength due to work hardening, and higher production rates. Additionally, it avoids oxidation on the material's surface and eliminates the need for pre-heating the material.
What is the principle of drawing (trefilação)?
-Drawing is a process where a material is pulled through a die to reduce its cross-sectional area and elongate it. This process is typically used to produce thin wires or rods. The material is subjected to tensile forces, which pull it through the die, causing a reduction in diameter.
How is the tension during drawing calculated?
-The tension during drawing is calculated by multiplying the average yield stress by a factor that includes the coefficient of friction and the tangent of the die angle. The natural logarithm of the ratio of the initial and final cross-sectional areas is also factored into the equation, accounting for the material's deformation.
Why are accumulator drums used in drawing machines?
-Accumulator drums are used in drawing machines to manage the elongating wire. As the wire passes through the die, its length increases, and the drums store the wire, rotating at different speeds to maintain the continuous reduction process. This ensures that the drawing process can proceed without interruption.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

EXTRUSÃO E TREFILAÇÃO

Materiais e Processos de Fabricação para Engenharia de Produção - Usinagem convencional: conceitos

Aprenda os processos de CONFORMAÇÃO / FABRICAÇÃO - Laminação, trefilação, extrusão e forjamento
Plastic Processing Overview

Proses Pembentukan Logam: Teknik, Metode, dan Aplikasi Terbaru!

Aturan Gambar Teknik Mesin (Gambar Kerja) - Gambar Teknik Manufaktur
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)