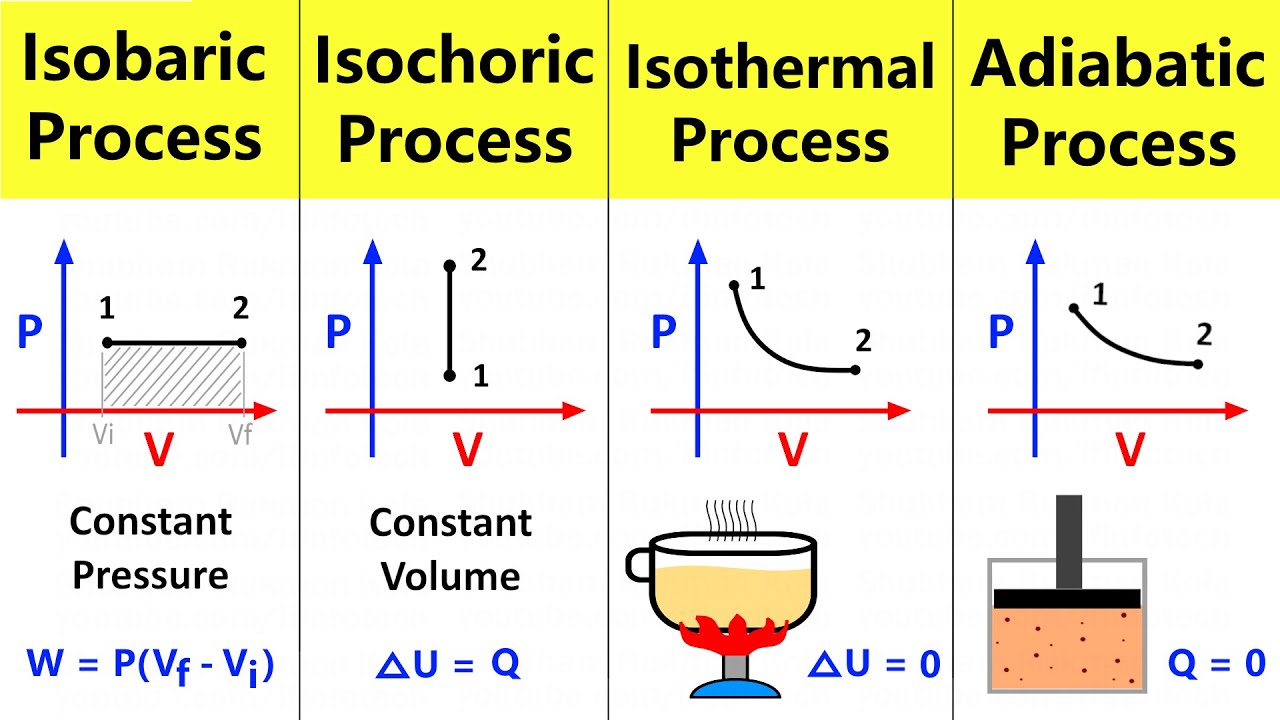
Transformação isobárica (utilizando o PHET)
Summary
TLDRThis video script explains the behavior of an ideal gas during an isobaric transformation, where pressure remains constant while temperature and volume change. The speaker demonstrates that temperature and volume are directly proportional in this process, meaning that as temperature increases, volume increases in a consistent manner. The video emphasizes the experimental aspect of observing these changes, illustrating how manipulating the temperature leads to predictable changes in volume, according to the ideal gas laws.
Takeaways
- 😀 The script discusses the isobaric transformation, where pressure remains constant while temperature and volume of a gas change.
- 😀 An ideal gas is confined in a container, and the temperature is increased to observe the effect on the gas volume.
- 😀 As the temperature increases, the volume of the gas increases proportionally, demonstrating Charles's Law.
- 😀 In the experiment, doubling the temperature leads to a nearly double increase in volume.
- 😀 Similarly, tripling the temperature causes the volume to triple, showing a directly proportional relationship.
- 😀 The relationship between temperature and volume is observed under constant pressure, which is the core of isobaric transformation.
- 😀 The script emphasizes that the process and outcomes are consistent, meaning that the same behavior can be expected each time the temperature is changed.
- 😀 The experiment takes place in a laboratory setting, and the temperature changes are controlled to maintain constant pressure.
- 😀 The behavior of the gas follows the ideal gas laws, particularly Charles's Law, where volume and temperature are directly proportional.
- 😀 There is no need to focus on units during the experiment, as the main focus is on the conceptual demonstration of the relationship between volume and temperature.
- 😀 The speaker assures that the experiment is simple and should work as expected, with volume changing predictably as temperature increases.
Q & A
What is an isobaric transformation?
-An isobaric transformation is a thermodynamic process in which the pressure of a gas remains constant while its temperature and volume change.
How does the temperature affect the volume of an ideal gas in an isobaric process?
-In an isobaric process, the volume of the gas is directly proportional to its temperature. As the temperature increases, the volume of the gas increases as well, provided the pressure remains constant.
What is the relationship between volume and temperature in an isobaric process?
-The relationship between volume and temperature in an isobaric process follows a direct proportionality. If the temperature doubles, the volume also doubles, and similarly for other proportional increases in temperature.
What law does the behavior of the gas in this experiment demonstrate?
-The experiment demonstrates **Gay-Lussac’s Law**, which states that for a fixed amount of gas at constant pressure, the volume is directly proportional to the absolute temperature.
Why does the volume of the gas increase when its temperature increases in this experiment?
-As the temperature increases, the kinetic energy of the gas molecules increases, causing them to collide with the walls of the container more forcefully. This results in an increase in the volume of the gas under constant pressure.
What does it mean for the pressure to remain constant in an isobaric transformation?
-For the pressure to remain constant during an isobaric transformation, the system must be set up in such a way that any change in temperature results in a corresponding change in volume, but without any fluctuation in the pressure exerted by the gas.
In the experiment described, how does the volume of the gas change when the temperature is doubled?
-When the temperature is doubled, the volume of the gas also doubles, illustrating the direct proportionality between temperature and volume in an isobaric transformation.
What does the experiment suggest about the predictability of the behavior of the gas?
-The experiment suggests that the behavior of the gas is highly predictable, following the direct proportionality between temperature and volume. This makes it easy to estimate changes in volume based on changes in temperature during an isobaric process.
Why is the concept of an ideal gas used in this experiment?
-The concept of an ideal gas is used because it simplifies the behavior of gases, assuming they follow the ideal gas law perfectly. This helps to make clear predictions about how the gas will behave when its temperature changes at constant pressure.
What does the transcript suggest about the precision of the experiment?
-The transcript suggests that the experiment may not be highly precise, as it mentions some imprecision in measurements and the fact that it is more about demonstrating the concept than achieving exact values. However, the fundamental relationships still hold true.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)