2-Minute Neuroscience: Hypothalamus
Summary
TLDRThe hypothalamus, located deep in the brain beneath the thalamus, plays a crucial role in regulating various bodily functions essential for homeostasis. It connects to the pituitary gland and is involved in processes such as hunger, thirst, body temperature regulation, stress responses, and reproductive behaviors. The hypothalamus is divided into three regions: the preoptic area, which manages body temperature and circadian rhythms; the tuberal hypothalamus, involved in hunger and sexual behavior; and the posterior region, responsible for wakefulness and memory. Its complex structure helps maintain balance across physiological systems.
Takeaways
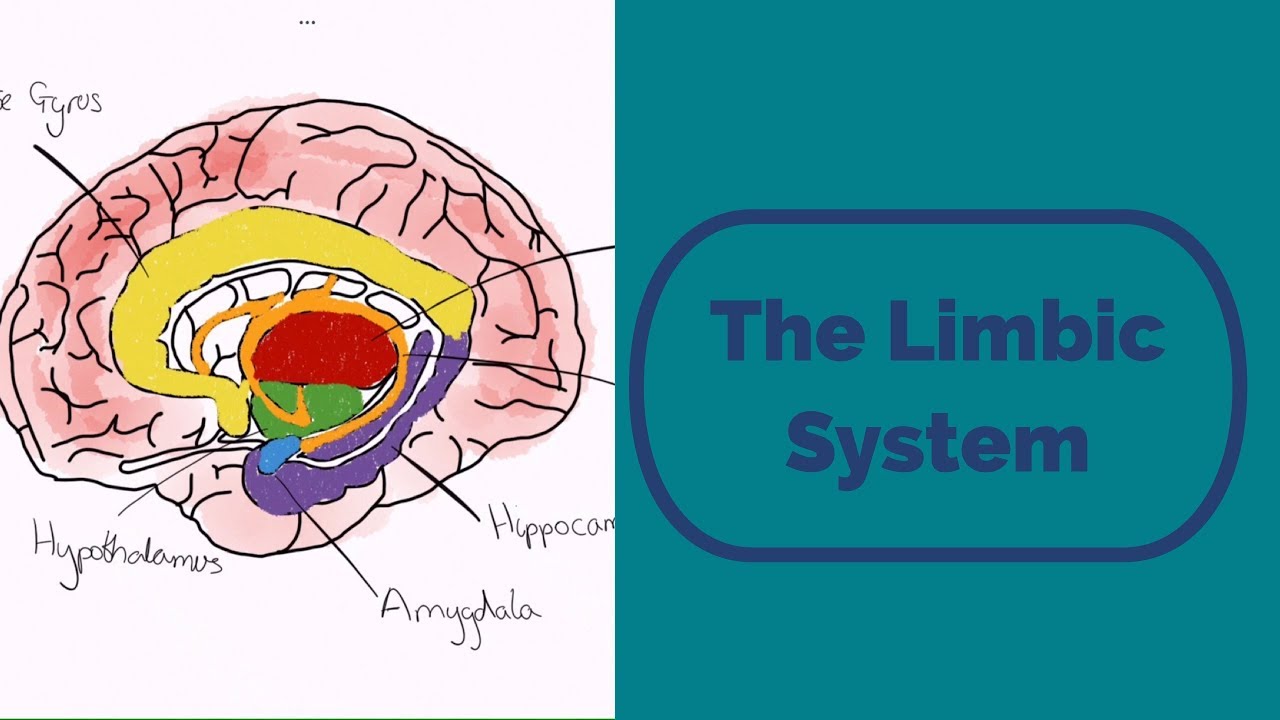
- 😀 The hypothalamus is a small, deep brain region located below the thalamus, above the pituitary gland.
- 😀 It is connected to the pituitary gland, which is a neuroendocrine gland regulated by the hypothalamus.
- 😀 The hypothalamus contains more than a dozen nuclei, each with different functional specializations.
- 😀 It is crucial in maintaining homeostasis across various bodily systems by regulating multiple processes.
- 😀 The hypothalamus receives physiological information from the body and the nervous system to restore homeostasis.
- 😀 Major functions of the hypothalamus include regulating thirst, hunger, body temperature, stress, and reproductive behaviors.
- 😀 The hypothalamus also controls circadian rhythms and the sleep-wake cycle.
- 😀 Anatomically, the hypothalamus is divided into three regions: the preoptic area, tuberal hypothalamus, and posterior region.
- 😀 The preoptic area plays a key role in body temperature regulation, fever, electrolyte balance, and sexual behavior.
- 😀 The tuberal hypothalamus contains the infundibulum, which connects the hypothalamus to the pituitary gland, and regulates hunger, aggression, and autonomic responses.
- 😀 The posterior region of the hypothalamus is involved in wakefulness, stress responses, memory, and other functions.
Q & A
What is the hypothalamus and where is it located?
-The hypothalamus is a small region located deep in the brain, just below the thalamus. It sits above and is connected to the pituitary gland.
How many nuclei are there in the hypothalamus, and what is their role?
-The hypothalamus contains more than a dozen nuclei, each with different functional specializations, playing roles in regulating various bodily processes.
What processes is the hypothalamus involved in?
-The hypothalamus is involved in maintaining homeostasis across various bodily systems, such as regulating thirst, hunger, body temperature, stress responses, reproductive behaviors, and circadian rhythms.
How does the hypothalamus maintain homeostasis?
-The hypothalamus receives information from the body and other parts of the nervous system and influences behavioral, autonomic, and neuroendocrine systems to restore homeostasis when needed.
What are some of the major functions attributed to the hypothalamus?
-Some major functions of the hypothalamus include the regulation of thirst and drinking behavior, fluid and electrolyte balance, hunger and feeding, body temperature, stress responses, aggressive behaviors, reproductive behaviors, circadian rhythms, and the sleep-wake cycle.
How is the hypothalamus anatomically subdivided?
-The hypothalamus is subdivided into thirds from front to back: the preoptic area, the tuberal hypothalamus, and the posterior region.
What is the function of the preoptic area of the hypothalamus?
-The preoptic area plays critical roles in the regulation of body temperature, fever, electrolyte balance, circadian rhythms, and sexual behavior.
What is the tuberal hypothalamus, and what functions does it perform?
-The tuberal hypothalamus is the middle region of the hypothalamus, and it contains nuclei involved in hunger, feeding, sexual behavior, aggressiveness, and autonomic and endocrine responses.
What is the infundibulum, and what is its role?
-The infundibulum, or pituitary stalk, emerges from the tuberal hypothalamus and connects the hypothalamus to the pituitary gland.
What functions are associated with the posterior region of the hypothalamus?
-The posterior region of the hypothalamus contains nuclei involved in wakefulness, stress responses, memory, and other functions.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)