ISÓTOPOS, ISÓBAROS, ISÓTONOS e ISOELETRÔNICOS - QUÍMICA - Prof. Marcus
Summary
TLDRThis educational video script explores the concept of isotopes and their importance in various scientific applications. It covers the use of carbon-14 for dating ancient artifacts, explains different types of atomic relationships such as isotopes, isoelectronic species, and isobars, and delves into the mechanics of carbon-14's decay process. The script highlights how isotopic abundance influences atomic mass calculations, emphasizing the significance of average atomic mass and half-life in practical scientific scenarios. Engaging and informative, it breaks down complex concepts for students, providing interactive learning moments and real-life applications of atomic science.
Takeaways
- 😀 Carbon-14 dating is used to determine the age of organic matter by measuring the decay of Carbon-14 isotopes over time.
- 😀 The half-life of Carbon-14 is approximately 5,730 years, meaning it takes that long for half of the Carbon-14 in an object to decay.
- 😀 The Carbon-14 decay process is used in archaeological dating, such as determining the age of fossils and ancient remains.
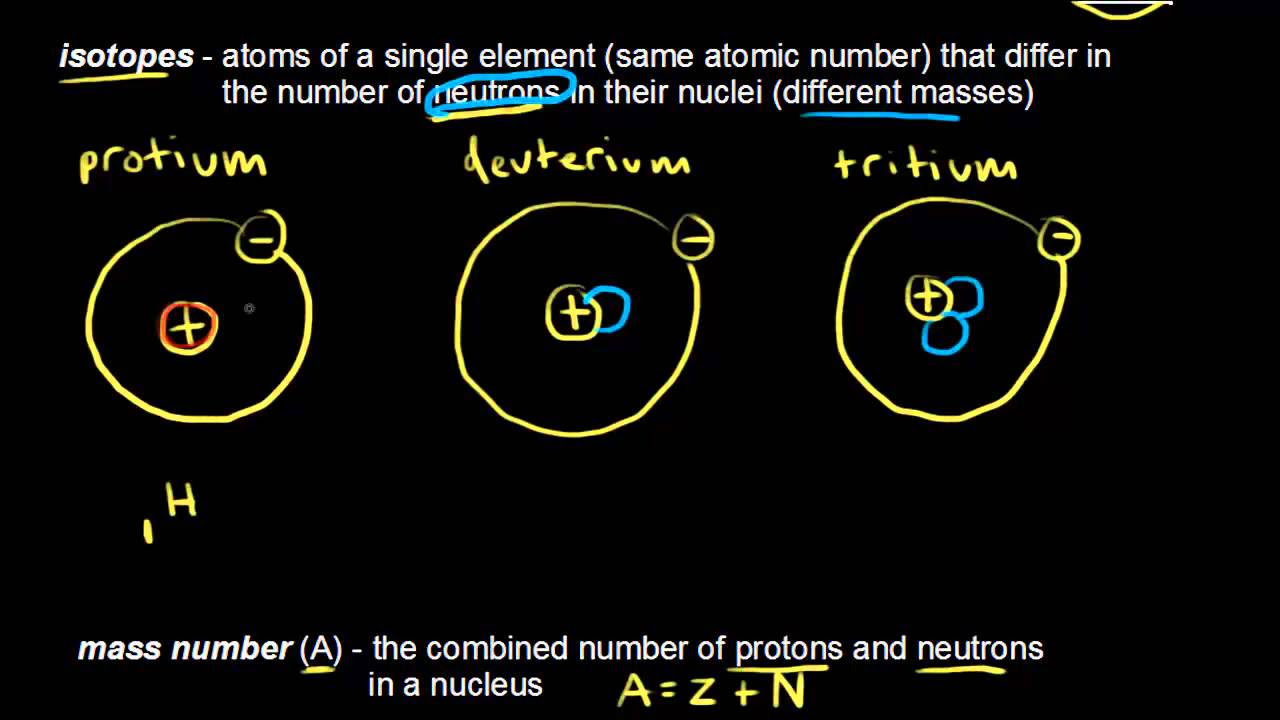
- 😀 Isotopes are elements with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons, leading to variations in their atomic mass.
- 😀 Carbon-12 and Carbon-14 are isotopes of the same element, carbon, with the difference in neutron count determining their mass and properties.
- 😀 Isotopes, isoelectronic species, and isotonic species are defined by shared properties such as the number of protons, electrons, or neutrons.
- 😀 An example of isotopes is the comparison between Fluorine-19 and Fluorine-18, where Fluorine-19 has 10 neutrons and Fluorine-18 has 9 neutrons.
- 😀 Isobars are species with the same atomic mass but different numbers of protons, like Carbon-14 and Nitrogen-14.
- 😀 Isoelectronic species have the same number of electrons, such as Oxygen-2 and Sodium+ which both have 10 electrons.
- 😀 The concept of average atomic mass takes into account the relative abundance of different isotopes of an element, such as chlorine, which has isotopes Cl-35 and Cl-37 with different abundances.
Q & A
What is the significance of carbon-14 in determining the age of fossils?
-Carbon-14 is used in radiometric dating to determine the age of fossils. Since its half-life is approximately 5,730 years, it decays over time, and the remaining amount of carbon-14 in an organism can help estimate how long it has been since the organism's death.
What is the definition of isotopes?
-Isotopes are chemical species of the same element that have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons, resulting in different atomic masses.
How does the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons relate to isotopes?
-Isotopes of the same element have the same number of protons, which defines the element, but differ in the number of neutrons, leading to different atomic masses. Electrons are typically equal to protons in neutral atoms.
What does the term 'half-life' mean in the context of carbon-14?
-Half-life refers to the time it takes for half of the original amount of carbon-14 in a sample to decay. For carbon-14, the half-life is 5,730 years.
Why is the concept of half-life important in dating ancient organisms?
-The concept of half-life allows scientists to estimate the time that has passed since an organism died by measuring the remaining carbon-14 in its remains. This method is crucial for dating fossils and archaeological finds.
What is the relationship between isotopes and their stability?
-The stability of isotopes depends on the balance between protons and neutrons in the nucleus. Isotopes with a higher mass are often less stable and may undergo radioactive decay to achieve a more stable configuration.
Can isotopes of different elements have similar properties?
-Isotopes of the same element have similar chemical properties because they have the same number of protons and electrons. However, isotopes of different elements will have different chemical properties due to differing numbers of protons and electrons.
What are 'isotopic abundances,' and how are they used to calculate atomic mass?
-Isotopic abundances refer to the relative amounts of each isotope of an element present in nature. These are used to calculate the average atomic mass of an element, where the mass of each isotope is weighted by its abundance.
What does the term 'isoelectronic' mean in atomic chemistry?
-Isoelectronic species are atoms or ions that have the same number of electrons. These species may be different elements but share similar chemical properties due to their identical electron configuration.
Why does the atomic mass of chlorine appear as 35.5 on the periodic table?
-The atomic mass of chlorine is 35.5 because it is a weighted average of the masses of its two stable isotopes, chlorine-35 and chlorine-37, which have different abundances in nature.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Isotopes Explained in Simple Words with Real-life Examples

SOAL DAN PEMBAHASAN STRUKTUR ATOM DAN NANOTEKNOLOGI - PART 1
Atomic number, mass number, and isotopes | Chemistry | Khan Academy

GEO 1 4 FIN

Biosensors (principle, components and mechanisms, features, and applications)

"الوحدة الثانية: مهارة استخدام المكتبات ـ الدرس الأول: تعريف المكتبات وأهميتها.
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)