I FINALLY understand the Maillard reaction
Summary
TLDRThis video explores the fascinating science behind the Maillard reaction, the chemical process responsible for the golden, brown, and delicious flavors in many cooked foods. It explains how reducing sugars and amino acids react under heat, creating complex flavors and aromas. Viewers learn how factors like temperature, moisture, and pH influence the speed and results of this reaction. The video also touches on other related processes, such as caramelization, and provides tips on how to optimize the Maillard reaction for tastier food. Finally, it invites viewers to join a community for exclusive content and guides.
Takeaways
- 😀 The Maillard reaction is the key to achieving golden brown and delicious (GBD) food, often seen in grilled, roasted, or baked items.
- 😀 The Maillard reaction is not a single reaction but a series of complex chemical processes that result in browning and flavor creation.
- 😀 Reducing sugars and amino acids are the primary reactants in the Maillard reaction, forming hundreds of different compounds as the process unfolds.
- 😀 Some of the compounds produced in the Maillard reaction reflect light in a way that creates the characteristic brown color in food.
- 😀 The Maillard reaction also produces volatile molecules responsible for the complex flavors and aromas that make food taste delicious.
- 😀 Other reactions like caramelization and dextrinization can also contribute to food browning, but the Maillard reaction is the primary cause of the deep, complex flavors.
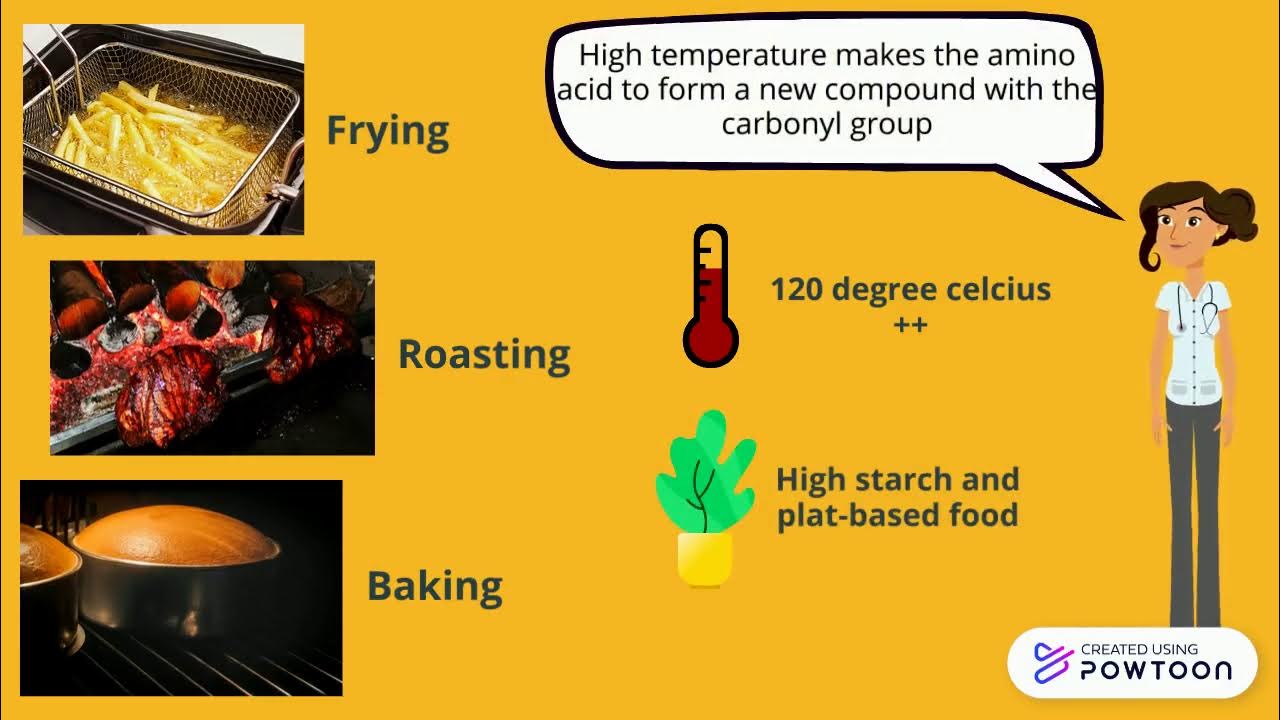
- 😀 To maximize the Maillard reaction, heat is crucial; higher temperatures speed up the process, resulting in more flavorful and browned food.
- 😀 Moisture can hinder the Maillard reaction, so drying the surface of foods like meat or vegetables before cooking can lead to better results.
- 😀 The pH level also plays a significant role; higher pH (more basic conditions) accelerates the Maillard reaction, creating more browning and flavor.
- 😀 Small changes in the cooking process, like adding an egg wash, butter, or baking soda, can raise the pH and help achieve a better Maillard reaction.
- 😀 Although some Maillard reaction byproducts can be harmful in large quantities, moderate amounts during regular cooking are safe and contribute to delicious flavors.
- 😀 The MinuteFood community on Patreon offers exclusive content, including guides and behind-the-scenes videos, to help people dive deeper into food science and cooking tips.
Q & A
What is the Maillard reaction, and why is it important in cooking?
-The Maillard reaction is a complex series of chemical reactions between reducing sugars and amino acids that occur when food is heated. It is responsible for the browning and the development of complex flavors and aromas in food, making it key to the golden-brown, deliciousness of cooked food.
How does the Maillard reaction differ from caramelization and dextrinization?
-The Maillard reaction involves both sugars and amino acids and produces complex flavors and browning. Caramelization, on the other hand, involves only sugars and heat, leading to a different type of sweetness and color. Dextrinization occurs when heat breaks down starches into smaller, browner molecules.
What are the main ingredients involved in the Maillard reaction?
-The main ingredients in the Maillard reaction are reducing sugars and amino acids. Reducing sugars are simpler sugars found in all living things, and amino acids are the building blocks of proteins.
Why is heat important in the Maillard reaction?
-Heat accelerates the Maillard reaction. While it can occur at room temperature, it happens much faster at higher temperatures, which is why we commonly see it in foods cooked at high heat, like grilled meats, roasted vegetables, and baked goods.
How does moisture affect the Maillard reaction?
-Moisture can prevent the Maillard reaction from happening effectively because it lowers the surface temperature of the food. To enhance the reaction, it's important to dry the surface of food before cooking, like patting meat dry or dehydrating veggies before roasting.
What role does pH play in the Maillard reaction?
-The pH of the cooking environment affects the speed of the Maillard reaction. A higher pH, which is more basic, accelerates the reaction because it makes the amino acids more reactive. This is why some breads, like sourdough, don’t brown as well due to their lower pH.
How can I tweak the Maillard reaction to get more flavor and browning?
-To enhance the Maillard reaction, you can increase the heat during cooking, reduce moisture by drying food before cooking, and raise the pH by using ingredients like baking soda, milk, egg wash, butter, or mayonnaise.
What happens when the Maillard reaction goes too far?
-While the Maillard reaction creates desirable flavors and colors, overdoing it can lead to harmful molecules in large amounts. However, as long as you don't excessively brown your food, this shouldn't be a major concern.
How does the Maillard reaction relate to non-food items?
-The Maillard reaction isn't limited to the kitchen. It's also involved in processes outside the kitchen, such as the browning of self-tanners, certain types of cataracts, and even the color of preserved ancient remains like bog bodies.
What practical tips can I use to improve my Maillard reaction skills in cooking?
-To improve your Maillard reaction skills, try drying your food's surface before cooking, adjusting your cooking temperatures to high heat, and manipulating pH with ingredients like baking soda or dairy-based washes. Additionally, managing moisture is key to achieving that perfect golden-brown finish.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)