Qué hace un administrador de base de datos
Summary
TLDRA database administrator (DBA) is responsible for ensuring the availability and security of organizational data. Initially used for basic storage, databases now help predict behaviors by analyzing structured data. The DBA uses methodologies for data extraction, transformation, and normalization to create efficient databases tailored for analysis. The role requires strict adherence to ethical practices, including safeguarding sensitive data and notifying supervisors of any anomalies. By utilizing Database Management Systems (DBMS), DBAs support organizational goals while maintaining transparency in data handling and decision-making processes.
Takeaways
- 😀 A database administrator plays a crucial role in ensuring the availability and security of information within organizations.
- 😀 Databases were originally used to store data in computers or specialized servers to track business sales, customers, and purchases.
- 😀 Databases not only help organizations track data but also predict behavior patterns through structured information analysis.
- 😀 To make data suitable for analysis, a database administrator transforms raw data into structured information, facilitating predictions.
- 😀 Data must be ready before analysis, and this requires using extraction methodologies to transform data into more efficient information repositories.
- 😀 Efficient searches rely on normalized databases, ensuring that data modifications follow the organization's rules and objectives.
- 😀 The database management system (DBMS) is a crucial tool for a database administrator, as it enables the creation and manipulation of databases.
- 😀 As a database administrator, you handle information that doesn’t belong to you, so ethical practices are critical in data handling.
- 😀 Never share or modify database information without the proper authorization from your supervisors or clients.
- 😀 It is essential to report any unauthorized anomalies or modifications in the database to your supervisor immediately.
- 😀 The handling of information—storage, access, usage, communication, manipulation, and disposal—must always be communicated and authorized by your client or supervisor.
Q & A
What is the primary responsibility of a database administrator (DBA)?
-The primary responsibility of a database administrator (DBA) is to ensure the availability, security, and efficiency of data within an organization. This includes managing databases, maintaining data integrity, and ensuring data is properly structured for analysis and decision-making.
How did the use of databases evolve over time?
-Originally, databases were used simply to store data, such as sales information or customer records. However, over time, databases have evolved to not only store data but also to generate predictions about organizational behavior, which helps in decision-making.
What role does data transformation play in database management?
-Data transformation is critical because it converts raw data into structured information that can be easily analyzed. This helps the organization predict various trends and behaviors by making data more accessible and useful for decision-making.
What does it mean for a database to be 'normalized'?
-Normalization in database management refers to organizing the data in a way that minimizes redundancy and dependency, ensuring that any data modification adheres to specific organizational rules. This process makes data more efficient and easier to analyze.
Why is a database management system (DBMS) important for a DBA?
-A Database Management System (DBMS) is crucial for a DBA because it provides the tools necessary for creating, managing, and manipulating databases. The DBMS ensures that data is stored, accessed, and retrieved in an organized and efficient manner.
What ethical practices should a database administrator follow?
-A DBA should always adhere to ethical practices such as not sharing or modifying data without authorization, refraining from using data for personal gain, and immediately reporting any unauthorized changes or anomalies in the database.
What should a DBA do if they notice an unauthorized change in the database?
-If a DBA notices an unauthorized change in the database, they should report it to their supervisor immediately to address the issue and prevent potential damage or data breaches.
How does data extraction contribute to database management?
-Data extraction is the first step in making data ready for analysis. It involves pulling relevant data from various sources, which is then structured and transformed into a format that is easy to analyze and use for decision-making.
What is the significance of the DBA's relationship with supervisors and clients regarding data management?
-A DBA must ensure that all actions involving data storage, access, and manipulation are known and authorized by supervisors and clients. Clear communication about data handling is essential to maintain trust and avoid ethical or legal issues.
How does a database administrator support an organization's goals?
-A DBA supports an organization’s goals by ensuring that data is organized, secure, and available for analysis. By maintaining efficient databases, the DBA helps the organization make informed decisions and predict future trends based on accurate data.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

How To Become A Database Administrator and Earn 6 Figures | Management Information Systems
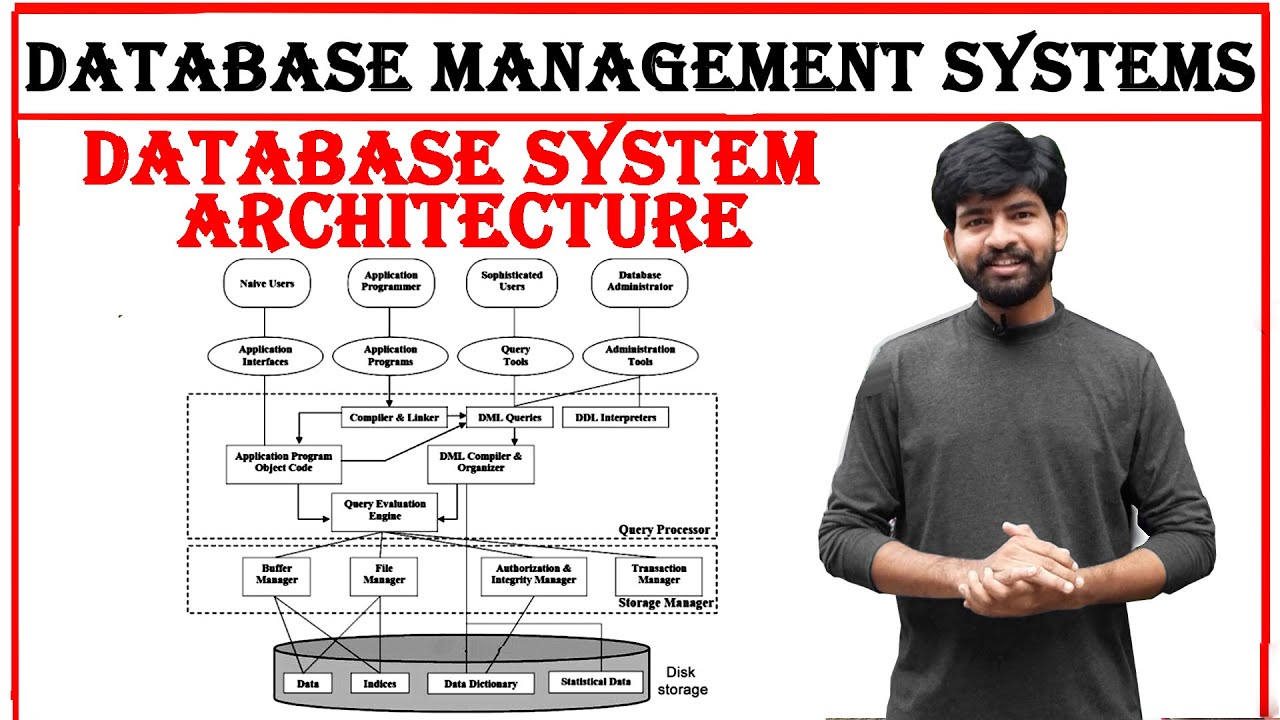
database system architecture in dbms | database management system | Architecture | DBMS | btech

DBMS - Definition

Contoh Kasus Basis Data di Software Manajemen Arsip : Part 1

The Core Data Roles

Siapa itu Database Administrator ?
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)