Lesson 5.1 - Ectomycorrhizal fungi
Summary
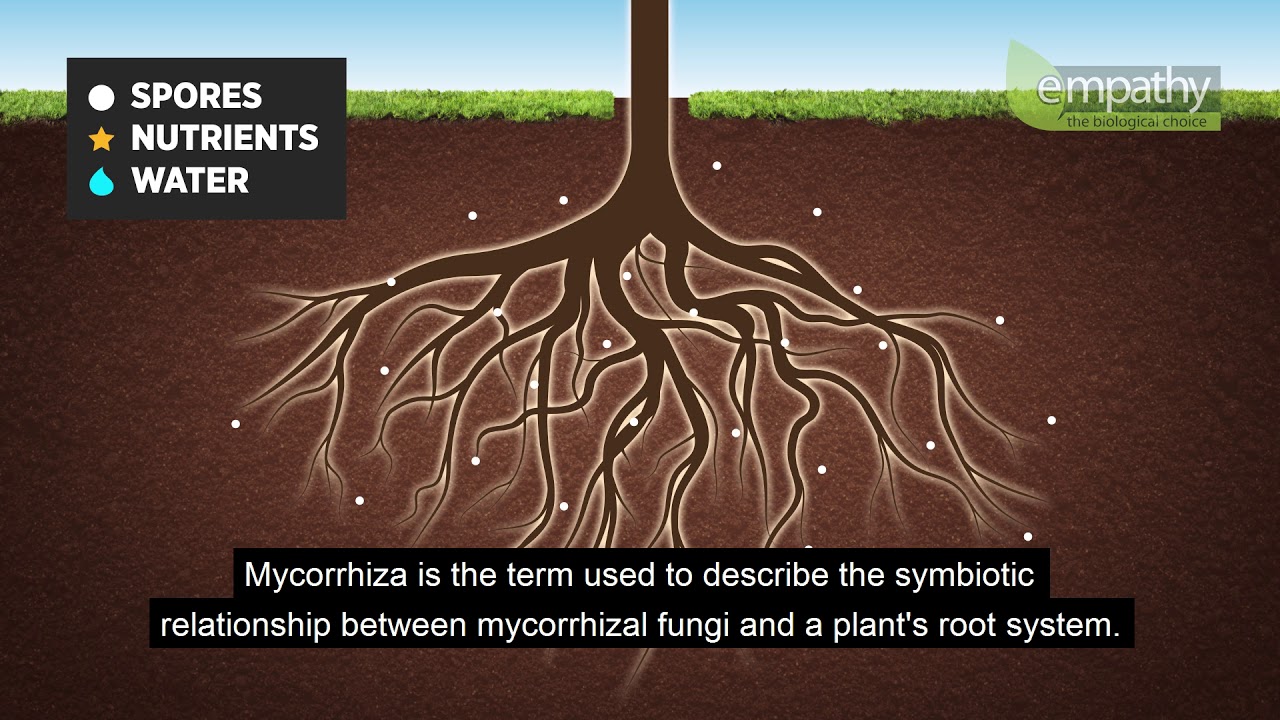
TLDRThe video explores the crucial role of mycorrhizal fungi in ecosystems, focusing on their symbiotic relationship with plants. These fungi help plants absorb essential nutrients like phosphorus and nitrogen in exchange for carbon. They contribute to carbon sequestration, enhance nutrient recycling, and prevent nutrient leaching. The process involves fungi breaking down organic matter, forming humus, and improving soil health. The concept of the 'Wood Wide Web' highlights the interconnectedness of ecosystems through fungal networks, facilitating interspecies nutrient exchange. Fungi’s role in mitigating the effects of climate change and supporting ecosystem stability is emphasized.
Takeaways
- 😀 Mycorrhizal fungi form a symbiotic relationship with plants, exchanging sugars for essential nutrients from the soil.
- 🌱 These fungi help plants absorb minerals like phosphorus and nitrogen, which are critical for plant growth.
- 🌍 Fungi play a significant role in carbon sequestration by converting organic matter into humus, trapping carbon in the soil.
- 🔬 Ectomycorrhizal fungi can absorb up to 50% of a plant's carbon and return 80% of the nutrients like phosphorus and nitrogen.
- 🍂 Decomposing fungi break down organic matter, like fallen tree limbs, enriching the soil and contributing to nutrient cycling.
- 💧 Mycorrhizal fungi help prevent nutrient leaching, retaining nitrogen and phosphate and preventing soil erosion and pollution.
- 🌳 Micro heterotrophic plants rely entirely on fungi for their nutrients, as they cannot perform photosynthesis themselves.
- 🌍 Fungi are crucial for maintaining the balance of ecosystems by holding nutrients in place and preventing pollution runoff.
- 🌿 Fungi interact with soil bacteria and other organisms to decompose organic matter, enhancing soil fertility.
- ⚒️ Mycorrhizal fungi play a role in disturbed environments, such as mining sites, by aiding in soil restoration and nutrient cycling.
- 🌐 The 'Wood Wide Web' refers to the interconnected mycorrhizal networks that link plants and ecosystems, facilitating nutrient exchange and communication.
Q & A
What is the role of mycorrhizal fungi in plant root systems?
-Mycorrhizal fungi form a symbiotic relationship with plant roots, where the plant provides sugars (carbohydrates) to the fungi. In return, the fungi help the plant acquire essential nutrients, such as phosphorus and nitrogen, from the soil.
How do mycorrhizal fungi contribute to carbon sequestration in the soil?
-Mycorrhizal fungi play a significant role in carbon sequestration by breaking down organic matter. The sugars excreted by plants and the fungi's decomposition process contribute to the formation of organic carbon in the soil, which can be stored as humus, especially when conditions are favorable.
What happens to the organic matter in soil after it is decomposed by fungi?
-When fungi decompose organic matter, such as fallen plant material, it breaks down through various stages. Ultimately, the organic carbon becomes humic acids and forms humus, a stable form of organic material in the soil.
What are micro heterotrophs, and how do they interact with mycorrhizal fungi?
-Micro heterotrophs are plants that lack photosynthetic capability and depend entirely on mycorrhizal fungi for nutrients. These plants receive carbon from the fungi, which is connected to trees or other plants through fungal networks.
How do mycorrhizal fungi reduce nutrient leaching in soil?
-Mycorrhizal fungi reduce nutrient leaching by binding essential nutrients like nitrogen and phosphate within their structures, preventing these nutrients from washing away with water runoff. This helps maintain soil fertility and reduces pollution in nearby rivers.
What is the role of saprotrophic fungi in ecosystems?
-Saprotrophic fungi decompose dead organic matter, breaking it down into simpler forms that can be used by other organisms in the ecosystem. This decomposition process is crucial for nutrient cycling and the formation of stable organic carbon in the soil.
How much of the plant's nutrients are supplied by ectomycorrhizal fungi?
-Ectomycorrhizal fungi can supply up to 80% of a plant's required nutrients, including essential elements like phosphorus and nitrogen, in exchange for carbon provided by the plant.
What is the 'Wood Wide Web,' and how does it function in ecosystems?
-The 'Wood Wide Web' refers to the interconnected network of mycorrhizal fungi that links plants in ecosystems. This network facilitates nutrient exchange between plants and different species, allowing for efficient communication and resource sharing.
What are the potential benefits of mycorrhizal fungi in disturbed environments like mining sites?
-Mycorrhizal fungi can play a critical role in ecosystem restoration, especially in disturbed environments such as mining sites. They help improve soil fertility, enhance nutrient cycling, and support plant growth in degraded soils, aiding in ecological recovery.
Why are fungi considered essential for soil health and nutrient cycling?
-Fungi are essential for soil health because they break down organic matter, recycle nutrients, and help maintain soil structure. Their ability to hold onto nutrients, prevent leaching, and form beneficial relationships with plants makes them indispensable in sustaining healthy ecosystems.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)